Explore comprehensive insights into migraines and headaches including causes, triggers, treatments, and natural remedies. Empower yourself with knowledge to manage pain effectively and improve your daily well-being
Making Informed ChoicesChoosing the right OTC medication requires evaluating individual health profiles and headache types. Weigh the pros and cons of each option and consult with healthcare professionals if needed. Ultimately, informed decisions about headache management can enhance your quality of life.Explore our resources to learn more about managing headaches effectively and safely. ---By understanding different OTC options and their proper usage, you'll be better equipped to tackle headaches and improve your overall wellbeing.
Jan 06, 2026
Debunking Common Myths and Recognizing Their ImpactMigraines are often underestimated, seen merely as intense headaches, yet they represent a complex neurological condition affecting millions worldwide. Approximately 12% of the population suffers from migraines, which can include debilitating pain, nausea, and sensitivity to light. While women are more likely to be affected, children and men also experience this condition. This article seeks to dispel common myths surrounding migraines and highlights the need for accurate diagnosis and effective management strategies. Myth 1: Migraines Are Just Bad HeadachesMigraines are more than severe headaches; they involve a range of neurological symptoms and require nuanced understanding for effective treatment. Mislabeling migraines can lead to inadequate management, making it essential for sufferers to advocate for themselves and seek thorough evaluations. Myth 2: Only Adults Get MigrainesChildren and teenagers are also affected by migraines, with about 10% experiencing symptoms that mirror those in adults. Recognizing early signs is crucial for effective intervention and treatment, preventing chronic issues later in life. Myth 3: Migraines Are Triggered Only by FoodWhile certain foods can trigger migraines, environmental factors and hormonal fluctuations play a significant role. Stress, weather changes, and hormonal shifts are often more influential than diet alone, necessitating a holistic approach to identifying triggers. Myth 4: You Can Suffer Through a Migraine without TreatmentMany believe they can endure migraines without seeking treatment, but this can exacerbate pain and lead to chronic issues. Effective treatments range from over-the-counter medications to lifestyle changes, emphasizing the importance of timely intervention. Myth 5: Migraines Are Only a Women's ProblemAlthough more women report migraines, men experience these debilitating headaches as well. Understanding this demographic spread is crucial for personalized care, as symptoms and treatment strategies often vary between genders. Myth 6: Migraines Go Away with AgeThough some experience a decrease in migraine frequency as they age, many continue to suffer into later years. Migraines can evolve and should not be dismissed as a phase, highlighting the need for continual monitoring and tailored management strategies. Myth 7: Migraines Don’t Affect Your LifeMigraines can severely disrupt daily activities, affecting work and social engagements. The condition often correlates with mental health issues, making comprehensive care crucial for overall well-being. Recognizing and educating those around migraine sufferers can foster a supportive environment.In summary, understanding the true nature of migraines and dispelling prevalent myths are vital to improving management strategies and enhancing the quality of life for those affected. If you or someone you know suffers from migraines, consider keeping a detailed diary and consulting healthcare professionals for tailored treatment options. Embracing a multidisciplinary approach that includes lifestyle changes, medication, and psychological support can lead to more effective management and personal empowerment.
Jan 06, 2026
Symptoms, Triggers, and Management Vestibular migraines are a specialized form of migraine that affects balance and spatial orientation, commonly causing dizziness and vertigo without the presence of a headache. According to the American Migraine Foundation, around 40% of migraine sufferers experience these vestibular symptoms, underscoring the need for awareness and effective management strategies. Mechanism and SymptomsVestibular migraines arise from disruptions in the vestibular system, crucial for maintaining balance. Triggers can vary widely, including stress, lack of sleep, hormonal changes, and certain types of food, such as aged cheeses and alcohol. Symptoms may manifest differently than typical migraines, including:- Dizziness or vertigo lasting from a few minutes to several days- Imbalance and nausea- Motion sensitivity and visual disturbances (aura)Recognizing these symptoms and their specific triggers is essential for forming an effective management plan. Effective Management StrategiesManaging vestibular migraines demands a multi-faceted approach:1. Lifestyle Modifications: Engage in regular physical activity, maintain a balanced diet, and adopt stress-reduction techniques like yoga or mindfulness meditation. Keeping a headache diary may help identify patterns and triggers.2. Dietary Adjustments: Avoid common food triggers, such as processed meats and caffeine. Staying hydrated and consuming magnesium-rich foods can help manage symptoms.3. Medical Interventions: Consult with healthcare professionals for personalized medication plans, often including beta-blockers or anticonvulsants. Cognitive-behavioral therapy can also assist in handling the psychological impacts of chronic dizziness.4. Alternative Therapies: Methods such as vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT), acupuncture, and nutritional changes can offer additional relief. Studies indicate VRT can enhance balance and reduce dizziness, while acupuncture has shown promise in decreasing migraine frequency and severity. When to Seek HelpRecognizing severe symptoms, such as prolonged dizziness hindering daily activities or changes in vision and hearing, is critical. If symptoms worsen or alter in nature, immediate medical consultation is necessary. Keeping a detailed symptom diary can aid both patients and healthcare providers in crafting an informed treatment approach. ConclusionVestibular migraines can severely impact daily life, but understanding the symptoms, triggers, and management strategies can lead to improved outcomes. Consultation with healthcare professionals, combined with lifestyle modifications, can pave the way for effective control over this condition, allowing individuals to lead a more balanced and active life. For personalized advice and treatment options, reach out to a specialist today.
Jan 06, 2026
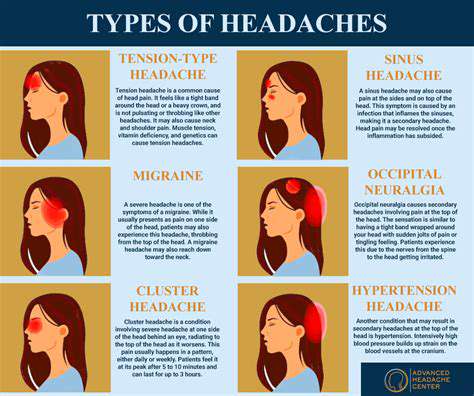
Types, Causes, and ManagementHeadaches are a common concern, impacting millions of people worldwide. Understanding their nature is essential for effective management and relief. Headaches are broadly categorized into primary and secondary types. Primary headaches, such as tension-type headaches and migraines, arise from overactivity within pain-sensitive structures in the head and neck. In contrast, secondary headaches signify an underlying medical condition, like sinus infections or high blood pressure, making it crucial to identify their origin for appropriate treatment. Types of Headaches Primary Headaches:- Tension-type Headaches: These present as a dull ache and are often associated with stress and poor posture.- Migraines: Characterized by severe, throbbing pain, migraines can cause sensitivity to light and nausea, affecting about 12% of the population. Secondary Headaches:- Related to conditions like sinus infections or injuries, these headaches can vary widely in presentation and severity. Symptoms to RecognizeTension headaches typically feel like a tight band around the head, whereas migraines involve intense, pulsating pain that can last for hours or days. Recognizing these symptoms aids in determining intervention strategies. Diagnosing and Treating HeadachesDiagnosis often necessitates a thorough medical history and physical examination. For tension headaches, over-the-counter pain relievers may suffice, while migraines might require prescription medications like triptans or preventive therapies. Keeping a headache diary helps identify triggers, facilitating better management. Lifestyle Modifications for PreventionAdopting preventive measures can significantly mitigate headache occurrence. Regular exercise, staying hydrated, and maintaining a balanced diet can help. Additionally, practicing stress management techniques like meditation or yoga can lessen tension headaches. Adequate sleep is also crucial, as disruptions can exacerbate headache frequency. When to Seek Medical AttentionConsult a healthcare professional if headaches become frequent or severe, particularly if they are accompanied by neurological symptoms. Sudden, intense headaches could indicate serious conditions such as an aneurysm or stroke. Migraines: Deeper InsightMigraines, affecting mostly women, can manifest in various forms. While most cases are migraines without aura—typified by unilateral, throbbing pain—migraines with aura include visual disturbances. Factors like hormonal changes, diet, and environmental triggers significantly contribute to migraine episodes. Treatment Strategies for MigrainesEffective migraine management involves both acute treatments and preventive strategies. Common acute treatments include over-the-counter medications, while preventive strategies may involve beta-blockers or antidepressants. Keeping a migraine diary can also support effective management. The Importance of Patient Education and SupportEducating patients about their condition and triggers fosters proactive management and facilitates informed discussions with healthcare providers. Support from family and friends is invaluable, as it helps create a more understanding environment for those battling frequent migraines. ConclusionUnderstanding the various types of headaches, their causes, and appropriate management strategies is key to improving quality of life. Consult healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans and always seek medical advice if headaches become increasingly problematic.
Jan 05, 2026
Understanding the Genetic Links to MigrainesMigraines are debilitating neurological conditions that heritably affect millions worldwide. Recent research has delved into the complex interplay of genetics and environmental influences that contribute to migraine susceptibility. This burgeoning field of genetic studies aims to uncover the specific genetic variants linked to migraines, offering potential avenues for personalized treatment strategies. Genetic Studies on Migraine SusceptibilitySignificant advancements have been made in identifying specific genes associated with a higher risk of migraines. A large-scale genome-wide association study (GWAS) published in *Nature Genetics* revealed crucial variations near the TRPM8 and LRP1 genes that correlate strongly with migraine susceptibility. Additional candidate genes like CACNA1A and ATP1A2 also play critical roles in neuronal excitability and ion channel regulation, providing insights into the biological mechanisms of migraines. Familial Patterns and HeritabilityStudies indicate that genetics accounts for approximately 40-60% of the risk for developing migraines, with familial clustering demonstrating a strong genetic component. Individuals with a parent or sibling who suffers from migraines have significantly elevated odds of experiencing headaches themselves. The correlation is especially pronounced for migraines with aura, highlighting the need for more in-depth familial studies. Environmental Influences on Genetic PredispositionWhile genetics plays a substantial role, environmental factors are equally significant triggers. Stress, dietary habits, and hormonal changes can provoke migraine episodes in those with a genetic predisposition. Integrating behavioral therapies and lifestyle adjustments could enhance treatment outcomes, showcasing the importance of a holistic approach in managing migraines. The Future of Genetic Research in TreatmentAs research evolves, the potential for incorporating genetic testing into migraine management is becoming increasingly plausible. Personalized medicine can tailor treatment plans based on an individual's genetic makeup, ultimately leading to more effective management of migraine symptoms. Identifying genetic markers associated with migraines could pave the way for innovative preventive therapies. Implications for Treatment and PreventionIdentifying specific genetic markers can aid healthcare professionals in creating tailored treatment plans. Future advances may allow for the development of preventative measures customized to individual genetic profiles. For example, healthcare providers can suggest lifestyle modifications or targeted medications for those identified as high-risk through genetic testing. ConclusionThe exploration of genetic links to migraines is not merely academic; it holds significant implications for personalized treatment strategies and preventative measures. By understanding both genetic and environmental factors, patients and providers can work together to formulate comprehensive management plans that address individual needs. As research progresses, it's clear that a dual focus on genetics and lifestyle will lead to improved outcomes for those facing the challenges of migraine disorders.
Jan 05, 2026
Key Factors in Migraine ManagementMigraine sufferers often seek answers in their lifestyle habits, and several overlooked factors can significantly impact migraine frequency and severity. This article provides insights into dehydration, sleep quality, screen time, environmental factors, and dietary triggers that can play a critical role in managing migraines. Dehydration: The Overlooked CulpritDehydration can lead to an imbalance that adversely affects both physical and cognitive functions. Research shows that even mild dehydration can impair cognitive performance and trigger headaches, which are common precursors to migraines. With approximately 75% of Americans being (chronically dehydrated)[], proper hydration can play a vital role in reducing headache frequency and enhancing overall physical performance.It's essential to recognize the signs of dehydration such as dry mouth, fatigue, and darker urine color. To prevent dehydration, consider drinking at least eight glasses of water per day and incorporating water-rich foods into your diet. Sleep Patterns: The Double-Edged SwordA good night's sleep is essential for those seeking relief from migraines. Disruptions in sleep cycles can significantly impact overall health and increase vulnerability to migraines. Research indicates that poor sleep quality serves as both a trigger and consequence of migraines. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and practicing good sleep hygiene can help mitigate these issues.Stress also plays a crucial role in sleep quality. Chronic stress can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to a higher likelihood of migraines. Incorporating mindfulness and relaxation techniques can enhance sleep quality and reduce migraine occurrences. Screen Time: The Digital DrainExcessive screen time, particularly before bed, can dramatically impact sleep quality due to blue light emission, which inhibits melatonin production. Reducing screen usage before sleep and taking regular breaks during prolonged screen exposure can alleviate eye strain and decrease migraine frequency.To counteract excessive screen time, consider engaging in alternative activities such as reading or exercising, thus benefiting both your mental and physical health. Environmental Factors: The Sneaky SourcesIndoor air quality can affect migraine frequency due to common allergens like dust and mold. Improper lighting conditions and fluctuations in weather also contribute to migraine episodes. Maintaining proper air quality and ensuring suitable lighting in your environment can help reduce migraine triggers. Keep a diary to track weather patterns alongside migraine occurrences, as many individuals report correlations between weather changes and attack frequency. Diet: The Hidden IngredientsMany people consume foods that can inadvertently trigger migraines. Common offenders include aged cheeses, processed meats, and artificial sweeteners. Keeping a detailed food diary can help identify personal dietary triggers, allowing better management of migraine symptoms.Moreover, staying hydrated and eating a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and vitamins is vital for overall health and can contribute to migraine management. In conclusion, understanding these interconnected factors—dehydration, sleep patterns, screen time, environmental conditions, and diet—can empower individuals to consciously manage their migraine triggers and enhance their quality of life.
Jan 05, 2026
Effective Strategies for ReliefMigraines can significantly impact daily life, but several strategies can help manage their frequency and severity. This guide provides valuable insights into maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including sleep patterns, hydration, diet, stress management, and the importance of a supportive environment. 1. Maintain Regular Sleep PatternsUnderstanding your sleep needs is crucial for migraine management. Adults typically require 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep per night. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing sleep environment can enhance sleep quality, helping to reduce migraine triggers. Techniques like keeping a sleep diary, limiting naps, and removing electronics from the bedroom can further improve sleep hygiene. 2. Stay HydratedProper hydration is essential for overall health and migraine prevention. Aim to drink 8–10 glasses of water daily and recognize the signs of dehydration, such as dry mouth and fatigue. Incorporating water-rich foods into your diet and maintaining a balance of electrolytes can support better hydration, potentially reducing the onset of migraines. 3. Adopt a Balanced DietIdentifying and avoiding nutritional triggers is key to managing migraines. Common offenders include aged cheeses and processed meats. A balanced diet should consist of vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, which support stable blood sugar levels. Mindful eating practices can also enhance your dietary experience and prevent overeating, a potential migraine trigger. 4. Manage Stress EffectivelyStress is a well-known migraine trigger. Recognizing what causes your stress and employing stress management techniques is crucial. Methods such as mindfulness meditation, regular exercise, and deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels, ultimately mitigating migraine occurrences. Building a supportive social network to discuss experiences can also provide emotional relief. 5. Limit Caffeine and Alcohol IntakeBoth caffeine and alcohol have been linked to migraine episodes. While moderate caffeine consumption can provide some benefits, excessive intake or withdrawal may lead to headaches. Alcohol, particularly red wine and beer, can trigger migraines in susceptible individuals. Keeping track of your intake can help manage these potential triggers effectively. 6. Create a Supportive EnvironmentA calming and supportive environment can greatly impact migraine management. Identifying personal triggers such as loud noises or strong odors is essential. Design your space to promote relaxation, communicate openly with loved ones about your needs, and incorporate stress-relief tools like yoga or meditation. 7. Keep a Migraine DiaryMaintaining a migraine diary is a powerful tool for identifying triggers and patterns. Document your migraines, including symptoms, duration, and potential triggers such as diet and stress levels. This information becomes invaluable for discussions with healthcare providers, facilitating more personalized migraine management strategies.---These strategies collectively contribute to an effective migraine management plan. By prioritizing healthy habits and being proactive about your health, you can significantly reduce migraine frequency and improve your overall quality of life. Always consult with healthcare professionals for tailored advice and management options.
Jan 05, 2026
- Complex carbohydrates (whole grains, oats)- Omega-3-rich foods (salmon, flaxseeds)- Tryptophan-rich fruits (bananas)- Leafy greens (high in folate)- Dairy products (rich in calcium and vitamin D)Incorporating these foods creates a balanced nutrient intake vital for optimal serotonin production. The Connection Between Exercise and SerotoninEngaging in regular physical exercise not only helps manage weight but significantly boosts serotonin levels. Aerobic exercises like jogging and cycling enhance serotonin production, improving mood and overall mental health. Additionally, exposure to sunlight while exercising can promote vitamin D synthesis, further contributing to serotonin enhancement. Importance of Sleep, Stress Management, and SupplementsQuality sleep and effective stress management are vital for maintaining optimal serotonin levels. Chronic stress can hinder sleep quality, creating a cycle detrimental to both mental health and migraine management. Implementing relaxing practices like mindfulness meditation and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can improve sleep hygiene.Incorporating natural supplements such as 5-HTP and Omega-3 fatty acids can additionally support serotonin production, offering potential migraine relief. Herbal remedies like St. John's Wort and Rhodiola Rosea may also enhance serotonin levels while assisting in stress management. Your Path to Migraine PreventionIntegrating these natural approaches into your daily routine can empower you to take control of your migraine management. Following a balanced diet, establishing an exercise regimen, and utilizing relaxation techniques are essential steps toward enhancing serotonin levels and potentially preventing migraines. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting new supplements or making significant lifestyle changes.By understanding and applying the strategies outlined in this article, you can effectively manage your migraines and improve your overall well-being.
Jan 05, 2026
- Stressful Situations: Ongoing anxiety or pressure can lead to muscle tension, which is a significant contributor to headache onset.- Poor Posture: Slouching or improper seating can lead to increased strain on neck muscles.- Eye Strain: Prolonged screen time can cause uncomfortable tension in the eye muscles, worsening headaches.- Sleep Deprivation: Lack of rest can intensify susceptibility to tension headaches.- Dehydration: Insufficient hydration can trigger and exacerbate headache symptoms. The Role of Stress in Tension HeadachesStress is arguably the most critical factor in the development of tension headaches. It engages the body's fight-or-flight response, leading to muscle tension and triggering headache episodes. Chronic stress contributes to a cycle of increasing headaches, often requiring strategic stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and regular physical activity, to mitigate. Diagnosing and Treating Tension HeadachesHealthcare professionals typically diagnose tension headaches through patient history and physical examinations, treating them with over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. For chronic patients, alternative therapies, including acupuncture and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), may offer effective relief. Preventive Strategies for Tension HeadachesPreventing tension headaches is crucial for those prone to frequent episodes. Simple lifestyle changes, such as maintaining proper posture, staying hydrated, and ensuring adequate sleep, can significantly reduce headache occurrences. Engaging in regular physical activity and taking consistent breaks from screens can help manage and prevent muscle tension linked to headaches. Signs and SymptomsSymptoms of tension headaches usually include a dull, persistent ache around the head, often described as a tight band, along with neck and shoulder discomfort. Emotional symptoms, including irritability and anxiety, may accompany physical discomfort, emphasizing the need for comprehensive management strategies. Effective Stress Management TechniquesPracticing mindfulness and meditation can notably reduce stress levels and headache frequency. Regular exercise serves dual purposes of alleviating stress and enhancing overall well-being. Keeping a headache diary to identify triggers and implementing ergonomic workspace adjustments can further support headache management. When to Seek Professional HelpIf tension headaches persist or escalate in severity, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable. They can help tailor treatment options to individual needs and address any underlying issues contributing to headache symptoms.In conclusion, managing tension headaches requires a multi-faceted approach that integrates lifestyle changes, stress management techniques, and when necessary, professional guidance. By addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of tension headaches, individuals can enhance their quality of life and experience fewer headache episodes.
Jan 05, 2026
//www.example.com/Early-Recognition-of-Health-Symptoms-A-Guide-to-Proactive-Care), can pave the way for reducing their impact. These may include flashing lights or zigzag patterns that interfere with your ability to work. Keeping a [Symptom Diary](https://www.example.com/Sharp-Neck-Pain-When-Turning-Head-Causes-and-Remedies) helps identify triggers and maintains clear communication with healthcare providers about effective treatment options. Flexible Work ApproachesAdopting a flexible work schedule can significantly enhance productivity for employees suffering from migraines. Studies indicate that workplaces accommodating flexible hours see higher employee satisfaction. By allowing adjustments to workspaces, organizations can optimize conditions that minimize triggers, like harsh lighting or noise. Creating a Migraine-Friendly WorkspaceImplementing a supportive environment involves adjusting lighting and reducing noise levels, which can exacerbate migraine symptoms. Ergonomic adjustments, such as standing desks, aid not just comfort but also productivity. Effective Coping MechanismsIdentifying personal triggers—whether they are related to diet, stress, or environmental factors—is a vital step towards managing migraines. Resources such as mindfulness techniques and proper routine maintenance can diminish stress, further lowering the chances of flare-ups.- Mindfulness Techniques: Simple breathing exercises or short meditation sessions can help maintain calmness.- Maintain a Balanced Routine: Regular eating and hydration habits are essential for migraine management. Open Communication and Support SystemsEncouraging an open dialogue about health issues within the workplace fosters an inclusive environment. Training sessions can enhance understanding among colleagues about migraine symptoms and how to communicate effectively during episodes. Collective awareness not only provides essential support for affected employees but can also promote a collaborative work culture. Harnessing TechnologyModern technology, including scheduling apps and pattern tracking tools, can empower employees managing migraines. Utilizing applications that offer reminders for breaks and hydration can bolster overall wellness, creating a productive work atmosphere tailored to individual needs. Consultation with Healthcare ProfessionalsLastly, consulting healthcare providers for comprehensive management strategies is crucial. This includes exploring medication options or alternative therapies, which can lead to personalized treatment plans, enhancing quality of life while maintaining workplace efficiency.Migraines can undoubtedly pose challenges, but through early recognition, flexible work arrangements, and effective coping strategies, both employees and employers can create a supportive environment that champions productivity and well-being.
Jan 04, 2026
- Ibuprofen is effective for headaches, muscle aches, and menstrual cramps.- Naproxen is favored for chronic pain management because of its longer-lasting effects.- Aspirin provides additional cardiovascular benefits but can pose gastrointestinal risks, particularly in children. 3. Topical Pain RelieversTopical options, including gels, creams, and patches, offer targeted relief with reduced systemic side effects. They are ideal for localized pain, such as arthritis or muscle strains, and often contain active ingredients like menthol or salicylate. Patients sensitive to oral medications can particularly benefit from these formulations. Choosing the Right Pain RelieverSelecting the appropriate OTC pain reliever depends on various factors, including personal health conditions, the type and intensity of pain, and potential drug interactions. For instance, those with liver conditions should steer clear of acetaminophen, while NSAIDs might not be suitable for individuals on blood-thinning medications. Key Considerations:- Dosage: Always adhere to recommended doses to prevent serious side effects.- Medical Consultation: Consulting with a healthcare provider ensures safe use, especially for individuals with chronic conditions or those taking multiple medications.- Holistic Approach: Integrating lifestyle changes, such as exercise and mindfulness, can enhance the effectiveness of pain management strategies. Final ThoughtsOver-the-counter pain relievers can be effective allies in managing discomfort, but an informed choice is paramount. Understanding the benefits and risks associated with each type empowers consumers to make better health decisions. For optimal results, consider personalized treatment plans and regular check-ins with healthcare professionals.Stay proactive about your health, and consult this guide whenever you need to choose the right OTC pain reliever for your needs!
Dec 28, 2025
A Soothing ElixirDerived from the peppermint plant, peppermint oil contains menthol, which provides a cooling sensation that can reduce headache intensity. When applied topically to the temples, it enhances blood circulation and blocks pain signals. Studies indicate that peppermint oil may serve as an alternative to conventional pain relievers for some individuals. 2. Lavender Essential Oil: The Calming AromaLavender is renowned for its relaxing properties and can effectively alleviate migraine symptoms. Research suggests that inhaling lavender oil can significantly reduce headache intensity and promote a sense of calm, making it particularly beneficial for those whose migraines are triggered by stress. 3. Ginger Tea: Nature’s Anti-InflammatoryGinger is rich in bioactive compounds that possess anti-inflammatory properties. Drinking ginger tea may not only reduce pain intensity but also combat nausea often associated with migraines. Its soothing qualities make it a clever addition to any migraine relief toolkit. 4. Cold Compress: Instant Relief in SecondsApplying a cold compress to the forehead or neck can constrict blood vessels and numb pain, often providing rapid relief from migraines. This technique is simple yet effective, and studies support its efficacy in alleviating headache pain. 5. Acupressure: Holistic HealingThis traditional Chinese therapy involves applying pressure to specific points on the body, potentially relieving migraine symptoms. Research highlights the effectiveness of acupressure techniques, fostering relaxation and reducing headache frequency when practiced regularly. 6. Stay Hydrated: The Power of WaterHydration is vital in managing migraines, as even mild dehydration can trigger headaches. Drinking adequate water daily can reduce headache frequency, making hydration a key aspect of migraine prevention. 7. Caffeine: A Double-Edged SwordCaffeine can relieve migraines for some but may increase headache frequency for others. Finding the right dosage is crucial, and it's advisable to monitor your intake to determine how your body reacts. 8. Chamomile Tea: Relaxation in a CupChamomile’s calming properties contribute to muscle relaxation and reduced headache intensity. Regular consumption of chamomile tea not only promotes relaxation but may also improve overall sleep quality, aiding in migraine prevention. 9. Rest in a Dark, Quiet RoomCreating a restful environment during a migraine is essential. Darkness and reduced noise can significantly alleviate symptoms, promoting a more effective recovery. 10. Magnesium: The Mineral MiracleMagnesium plays a crucial role in preventing migraines. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet can be beneficial, and studies suggest that supplementation may reduce migraine frequency for those who are deficient. ConclusionThese natural remedies offer a multifaceted approach to migraine management. Implementing these strategies may not only provide immediate relief but could also assist in reducing the frequency of future headaches. For persistent symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is always recommended.
Dec 28, 2025
Navigating Disability Claims for Chronic Migraine
Aug 02, 2025
Adapting Hobbies to Accommodate Migraine Needs
Aug 02, 2025
Managing Migraines in the Workplace: Tips for Success
Aug 02, 2025
The Role of Occupational Therapy in Adapting Daily Life with Migraines
Aug 02, 2025
The Role of Histamine Intolerance in Some Headaches
Aug 01, 2025
Understanding the Placebo Effect in Migraine Treatment
Aug 01, 2025
Celebrating Your Resilience: Living a Fulfilling Life with Migraines
Aug 01, 2025
Making Your Home Environment More Migraine Friendly
Aug 01, 2025
Artificial Sweeteners and Migraines: What's the Evidence?
Jul 31, 2025
Building a Support Network: Friends, Family, and Professionals
Jul 31, 2025
Q&A: Natural Remedies for Headaches Explained
Jul 31, 2025
How to Prepare for a Telemedicine Appointment for Migraines
Jul 30, 2025
How to Explain Your Migraines to Friends, Family, and Employers
Jul 30, 2025
Altitude Sickness Headaches: Prevention and Relief
Jul 30, 2025
What is Allodynia in Migraine? When Touch Becomes Painful
Jul 29, 2025
Using Progressive Muscle Relaxation for Tension Relief
Jul 29, 2025
Finding Joy and Maintaining Hobbies Despite Migraines
Jul 28, 2025
How Journaling Can Improve Migraine Management and Well being
Jul 28, 2025