Bump on the Back of the Head: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Common Causes of a Bump on the Back of the Head
Trauma or Injury
One of the most common reasons for a bump on the back of the head is trauma or injury. Even a minor bump can lead to swelling, resulting in a noticeable lump. This can occur from activities such as sports, falls, or accidental impacts.
In more severe cases, a concussion or other head injuries could result from a forceful impact. Regular monitoring and appropriate medical attention are crucial following any head trauma.
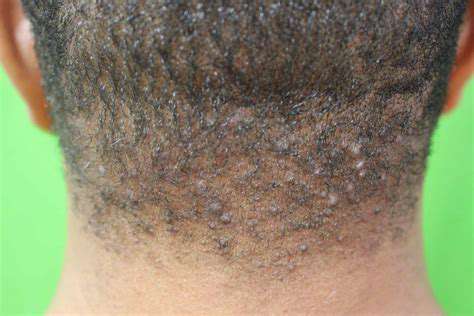
Cysts and Growths
Dermatological issues can also lead to bumps at the back of the head, such as sebaceous cysts or lipomas. These growths are usually benign and painless but may require medical evaluation if they become bothersome. They often arise from blocked sebaceous glands or fat accumulation in tissues.
In some instances, these cysts can become infected, leading to redness and tenderness. Treatment options range from observation to surgical removal, depending on symptoms and size.
Infections or Inflammatory Conditions
Infections that affect the scalp or the skin on the back of the head can lead to swelling and bumps. Conditions like folliculitis or even shingles may manifest as painful, elevated areas of skin. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications.
Inflammatory disorders such as dermatitis may also contribute to the formation of bumps. These can often be managed with topical treatments or lifestyle adjustments, depending on the underlying cause.
Symptoms Associated with a Bump on the Back of the Head
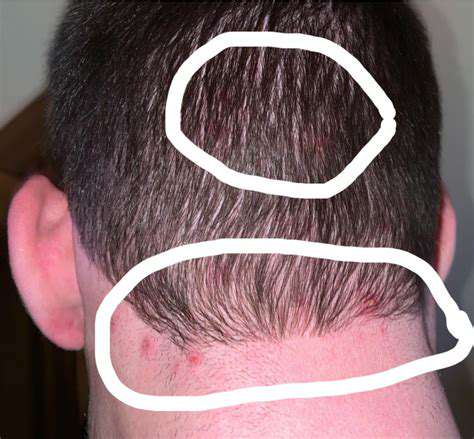
Common Symptoms to Look For
A bump on the back of the head can present various symptoms, which can help in identifying the underlying cause. Common symptoms may include swelling, tenderness, and pain in the affected area. These sensations can vary in intensity based on the injury or condition causing the bump.
In some cases, individuals may also experience headaches that can be mild to severe, depending on the injury's impact. It’s important to monitor these headaches, especially if they change in nature or severity over time.
Another often overlooked symptom is dizziness, which can accompany head trauma. Any form of dizziness after a bump may indicate a more serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Additionally, bruising or discoloration around the bump is common and can provide further insight into the severity of the injury. Observing these symptoms closely can guide appropriate treatment steps.
Serious Symptoms That Require Immediate Attention
While many bumps on the head can be benign, certain symptoms warrant urgent medical evaluation. If you experience confusion or a change in consciousness following a bump, it’s critical to seek help immediately.
Loss of coordination or difficulty walking are also serious symptoms. These can indicate potential brain injury and should never be ignored.
Furthermore, nausea or vomiting after sustaining a bump may suggest increased intracranial pressure and necessitates prompt medical intervention. It is vital to recognize these signs early.
Lastly, if there are visual disturbances, such as blurred vision or double vision, this could signal severe complications. Always err on the side of caution when it comes to head injuries, and consult a healthcare professional if any serious symptoms arise.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Understanding Symptoms to Monitor
When experiencing a bump on the back of the head, it's essential to observe any accompanying symptoms. Common indicators include swelling, bruising, and tenderness around the affected area. These symptoms can help in identifying the severity of the injury and guide further action.
Additionally, symptoms such as headache, dizziness, or nausea can signal a more serious issue. These should not be overlooked as they may indicate a concussion or other complications that could require immediate medical intervention.
Monitoring changes in behavior or cognitive function, such as confusion or difficulty concentrating, is equally important. If these symptoms develop after the bump occurs, seeking medical attention promptly is advisable to ensure appropriate care.
Identifying When to Call a Doctor
Determining the right time to seek medical help can be challenging. A good rule of thumb is to consult a healthcare professional if the bump is accompanied by severe pain or if the swelling does not subside after a few days. These could be signs of a more serious underlying injury.
Additionally, if the individual experiences vision changes, balance issues, or persistent vomiting, this may indicate serious brain injury, necessitating immediate medical evaluation. It's crucial to trust one's instincts; if something feels off, erring on the side of caution is wise.
For children, any significant head injury should always be evaluated by a doctor, as their symptoms can sometimes present differently compared to adults. Parental concern should never be dismissed, as their observations can be critical in ensuring timely care.
Home Remedies and First Aid
If the bump on the back of the head is minor and does not present serious symptoms, there are home remedy options that can provide relief. Applying a cold compress to the area can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. It is recommended to do this for 15-20 minutes at a time, ensuring a cloth separates the ice from direct skin contact.
An over-the-counter pain reliever, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may also be beneficial for managing discomfort. Always follow dosage instructions and consult with a pharmacist or doctor if there are any concerns regarding medication interactions.
Rest is crucial for recovery after a minor head injury. With proper care, most bumps can heal with time. However, ongoing observation of symptoms is necessary to ensure no delayed complications arise.
Preventative Measures to Consider
Preventing head injuries begins with awareness and precaution. Using proper protective gear during activities that pose a risk of head trauma—such as biking, skateboarding, or contact sports—is vital. Helmets and pads are essential for minimizing the impact during falls or accidents.
Additionally, ensuring that your living environment is safe can prevent falls that lead to head injuries. This involves removing clutter, ensuring adequate lighting, and using non-slip mats in areas prone to moisture.
Educating children about safe practices during play and encouraging them to be aware of their surroundings can greatly reduce the risk of injury. Teaching them to avoid standing on unstable surfaces or engaging in risky behavior can help instill a culture of safety and prevention.
Treatment Options for a Bump on the Back of the Head
Treatment Overview
When dealing with a bump on the back of the head, treatment often depends on the underlying cause. It's crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. Understanding whether the bump is due to trauma, infection, or another condition will guide the appropriate treatment pathways.
In many cases, rest and observation are enough if the bump is not associated with severe symptoms. Gentle ice application can help reduce swelling and alleviate minor pain.
However, if the bump is accompanied by symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, or neurological issues, immediate medical attention is required. Timely intervention can prevent serious complications.
In some instances, medical professionals may recommend imaging studies, such as an MRI or CT scan, to evaluate the condition of the underlying structures. These imaging methods provide crucial information for determining the best course of action.
Home Remedies
For minor bumps, several home remedies can provide relief and aid in recovery. Applying a cold compress to the area can help minimize swelling and soothe discomfort.
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can manage pain effectively. Always follow the recommended dosage instructions for safe use.
Rest is essential in recovery, especially if the bump was caused by a fall or impact. Ensure that you get plenty of sleep to support your body’s healing process.
Staying hydrated and maintaining a nutritious diet can also contribute positively to recovery. Foods rich in antioxidants can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many bumps on the head are benign, there are specific instances when seeking medical help is essential. If the bump is accompanied by severe headaches, visual disturbances, or persistent vomiting, it's important to seek emergency care.
Additionally, if the bump changes in size or color, or if any fluid drains from the site, it's critical to consult a healthcare professional. These changes could indicate infection or more serious conditions.
Do not ignore any neurological symptoms like confusion, difficulty speaking, or loss of balance, as these may signify a concussion or other serious injury. Prompt attention can be key to effective treatment.
Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider may be necessary for ongoing monitoring if the bump is linked to a chronic condition or after injury.
Preventative Measures
Taking steps to prevent bumps on the back of the head can help minimize risks associated with injuries. Wearing appropriate protective gear during physical activities, especially contact sports, is essential.
Creating a safe environment by removing obstacles and ensuring proper lighting can help prevent accidents that might lead to head trauma.
Education on safe practices during activities can significantly lower the chances of head injuries. Talk to children about the importance of being cautious during playtime.
Regular health check-ups can also play a proactive role in detecting underlying conditions that may predispose individuals to injuries or bumps.
Understanding Underlying Conditions
Several underlying conditions can cause bumps on the back of the head. Conditions such as cysts, lipomas, and dermatological issues like seborrheic keratosis can present as lumps under the skin.
Infection, such as folliculitis or cellulitis, can lead to swelling and bumps that require medical management. If left untreated, infections can escalate and cause more severe health issues.
In some cases, bumps may occur due to systemic conditions like hypertension or metabolic disorders. Understanding these potential links is vital for effective treatment and management.
Regular health screenings can help catch such underlying conditions early, ensuring timely and appropriate treatment options are explored.