Common Causes and Treatments for Left Side Pain
Possible Causes of Left Side Pain
Musculoskeletal Issues
Musculoskeletal problems are among the most common causes of left side pain. This can include conditions like strained muscles, torn ligaments, or inflammation of the joints. Such injuries often result from physical activities that put undue stress on the body. Regularly engaging in proper warm-up and stretching exercises can significantly reduce the risk of these ailments.
Conditions such as fibromyalgia can also lead to chronic pain on the left side. This syndrome affects the muscles and soft tissues, causing widespread pain throughout the body. Patients often report a combination of pain, fatigue, and cognitive issues, which can worsen over time. Seeking medical attention is crucial for proper diagnosis and management.
Another musculoskeletal issue can arise from poor posture, particularly in individuals who spend long hours sitting. Over time, improper alignment can lead to muscular imbalances, causing pain on one side of the body. Addressing posture through ergonomic adjustments and conscious awareness can alleviate discomfort.
In some cases, inflammation of the muscles or connective tissues can also manifest as left side pain. This can be a result of overexertion or an underlying medical condition. Appropriate treatment may include physical therapy and anti-inflammatory medications to promote healing.
Digestive Disorders
Various digestive disorders can lead to pain on the left side of the abdomen. Conditions such as gastritis, pancreatitis, or diverticulitis may present with sharp, cramping pain. Identifying the specific disorder is essential for effective treatment. A healthcare provider will often conduct tests to determine the underlying issue.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is another condition that can cause discomfort in the left side. This occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, leading to heartburn and pain that may radiate to adjacent areas. Lifestyle changes and medications are usually recommended for management.
The spleen, located on the left side of the body, can also be a source of pain if it becomes enlarged or injured. Splenomegaly can occur due to various factors, including infections and liver disease. In severe cases, surgical intervention might be necessary to address the cause of the pain.
Crohn's disease is another inflammatory bowel condition that can lead to localized pain on the left side. Individuals suffering from this illness often experience abdominal cramps and other digestive issues. It is crucial for affected individuals to work closely with a gastroenterologist for effective management.
Cardiovascular Concerns
Pain on the left side of the chest may indicate underlying cardiovascular issues, such as angina or a heart attack. Angina often manifests as a feeling of pressure or tightness in the chest, which can radiate to the left side. Recognizing these symptoms early can be life-saving. Seeking immediate medical attention is essential in such cases.
Other cardiovascular conditions, such as pericarditis, can also cause discomfort on the left side. This condition involves inflammation of the lining surrounding the heart and can produce sharp pains, particularly when coughing or lying down. Treatment typically includes anti-inflammatory medications and rest.
Aortic dissection is a less common but very serious cause of left side pain that requires urgent care. This condition involves a tear in the wall of the aorta and can lead to severe complications. Understanding the severity of chest pain or discomfort is imperative, as it can be a warning sign of major health concerns.
Regular check-ups and monitoring of heart health are crucial, especially for individuals with risk factors such as hypertension or a family history of heart disease. Lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Nerve-Related Issues
Nerve-related problems can also lead to left side pain, particularly conditions like sciatica or herniated discs. These issues often cause sharp pain that radiates along the path of the affected nerve. Individuals with these conditions may also experience numbness or tingling sensations. Consulting with a neurologist for proper evaluation and treatment is vital for recovery.
Shingles, caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, can lead to intense, localized pain on one side of the body, including the left. This pain often accompanies a rash and can be debilitating. Prompt medical intervention can help manage the symptoms effectively.
Other nerve disorders, such as peripheral neuropathy, can result in left side pain due to nerve damage in the extremities. This often leads to a burning sensation or extreme sensitivity. Effective management typically involves identifying the underlying cause and treatment options to alleviate the symptoms.
In some cases, nerve impingement from structural issues can also present as discomfort on the left side. Treatment might involve physical therapy, medications, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention to relieve pressure on the affected nerve.
Reproductive System Issues
In women, left side pain can be related to reproductive health issues, such as ovarian cysts or ectopic pregnancies. Ovarian cysts may cause pressure or sharp pain on one side of the abdomen, especially if they rupture. Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to more effective treatment options.
Endometriosis is another condition that can cause chronic pain on the left side. This happens when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside it, leading to severe cramps and discomfort. Treatment options may include hormonal therapy or surgery in more severe cases.
Men can also experience left side pain related to reproductive health, such as testicular torsion or varicocele. Testicular torsion is a medical emergency that requires immediate intervention to prevent loss of the testicle. Regular check-ups are essential for early detection and treatment of these issues.
Overall, understanding the potential reproductive health concerns is crucial for both men and women. Regular medical evaluations and addressing any unusual pain can prevent more serious complications and provide peace of mind.
Psychological Factors
Pain on the left side may not always have a physical cause; psychological factors can also play a significant role. Stress, anxiety, and depression can manifest as physical pain, commonly known as psychosomatic pain. Addressing mental health is just as important as treating physical discomfort. Professional therapy and mindfulness practices may help alleviate these symptoms.
Somatic symptom disorder is another condition where individuals experience significant pain that has no apparent physical cause. This could lead to chronic left side pain, further compounding the person's emotional distress. Comprehensive management often includes psychological support and medication.
Chronic stress can lead to muscle tension in the body, especially on one side. Over time, this tension can result in pain that is both physical and psychological in nature. Exploring relaxation techniques or stress management strategies can yield long-term benefits.
In many cases, addressing underlying psychological factors may lead to significant improvement in physical symptoms. Supporting mental health through therapy, support groups, or self-care practices is essential for holistic well-being.
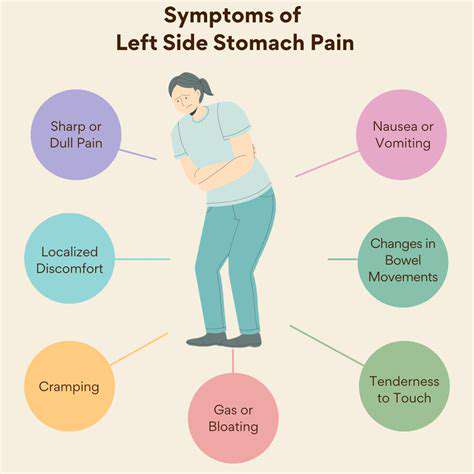
Symptoms Associated with Left Side Pain
Identifying Symptoms of Left Side Pain
Left side pain can manifest in various ways, and understanding these symptoms is crucial for determining the underlying cause. Common symptoms include sharp or dull aching sensations, radiating pain, or localized discomfort. The intensity of the pain may vary, sometimes becoming severe and impairing daily activities.
In some cases, patients may experience additional symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, or sweating, which could indicate a more serious condition, especially if accompanied by chest pain. Monitoring these symptoms closely can assist healthcare providers in making accurate diagnoses and formulating treatment plans.
Furthermore, the duration of the pain, ranging from sudden acute episodes to chronic ongoing discomfort, can help identify the nature of the issue. It is essential to document when symptoms occur and any triggers, as this information can be vital for medical evaluation.
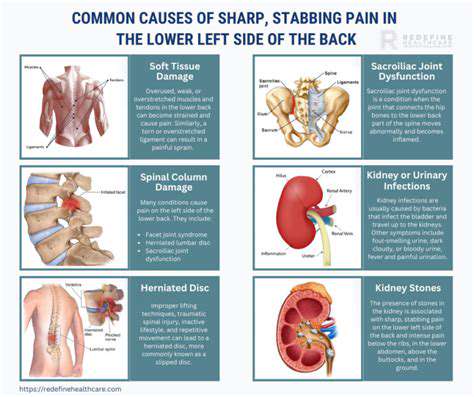
Potential Underlying Conditions
Left side pain can result from a variety of medical conditions, some of which may require immediate attention. Common issues include musculoskeletal problems, such as muscle strains or rib fractures, which can cause localized pain that intensifies with movement. Conditions affecting the digestive organs, like gastritis or pancreatitis, can also lead to left-sided pain, often accompanied by gastrointestinal distress.
Other potential causes include cardiac issues, such as angina or heart attacks, where pain may radiate to the left side and be mistaken for less serious ailments. Conditions such as pneumonia or pleurisy may cause pain in the left side of the chest, prompting a thorough examination to rule out respiratory infections.
Recognizing and understanding these underlying conditions can aid in early interventions. It is crucial for individuals to seek medical advice if they experience unexplained or persistent left side pain to prevent complications.
Treatment Options for Left Side Pain
Treatment for left side pain varies widely based on the underlying cause, ranging from conservative approaches to more aggressive therapies. Generally, pain relief can include over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, which can help alleviate discomfort while the underlying issue is assessed.
For musculoskeletal conditions, physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. In cases where digestive disorders are the cause, dietary modifications or medications to manage symptoms such as acid reflux may be effective.
In more serious cases, where conditions such as heart disease or acute pancreatitis are involved, hospitalization may be necessary. Treatment could involve more specialized approaches, including intravenous medications or surgery, depending on the diagnosis. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Treatment Options for Left Side Pain
Medications for Pain Relief
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications are often the first line of treatment for individuals experiencing left side pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen can reduce inflammation, making them effective for pain management.
For more severe pain, healthcare professionals may prescribe stronger medications. Opioids may be considered in cases of acute pain, but their use is monitored due to the risk of dependency.
In addition to traditional pain relievers, alternative medications such as muscle relaxants or nerve pain medications can also be beneficial. These should always be used under medical supervision to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Physical Therapy and Lifestyle Changes
Physical therapy is an essential treatment option for those suffering from chronic left side pain. A qualified physical therapist can design a personalized regimen that includes exercises focused on strength, flexibility, and stability.
In addition to physical therapy, lifestyle changes can significantly impact pain management. Incorporating regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing good posture can alleviate pressure on the left side and reduce pain over time.
Complementary therapies like yoga, Pilates, or acupuncture can also help relieve left side pain. These practices promote relaxation, improve body awareness, and often lead to enhanced physical function and pain reduction.