Effective Remedies for Left Front Head Pain and Its Causes
Common Causes of Left Front Head Pain
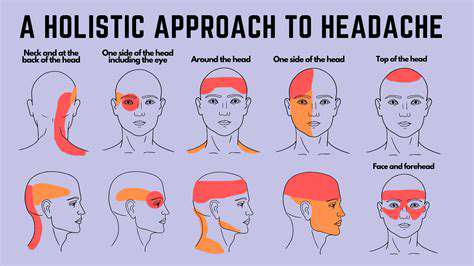
Stress and Tension Headaches
One of the primary causes of left front head pain is related to stress and tension. This type of headache often manifests as a tight band around the head or localized pressure. As individuals experience emotional or physical stress, the muscles in the neck and scalp can become tense, leading to discomfort.
Managing stress through relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga can be effective in alleviating these headaches. It is essential to identify stress triggers and adopt coping mechanisms to prevent future pain episodes. Regular physical activity can also play a significant role in reducing overall tension and improving mental well-being.
In addition, ensuring adequate hydration and nutrition can help prevent tension headaches. Dehydration or skipping meals can exacerbate the pain, making it crucial to maintain a healthy routine.
Sinus Issues and Allergies
Sinus issues and allergies are frequently linked to left front head pain. When the sinuses become inflamed due to allergies or infections, pressure builds in the facial area, contributing to headaches. The pain often intensifies when bending down or during sudden movements.
Identifying and managing allergens, such as pollen or dust mites, can significantly alleviate symptoms. Over-the-counter antihistamines or decongestants may provide relief by reducing inflammation and facilitating drainage of the sinuses.
In severe cases, consulting a healthcare provider for potential treatments such as nasal sprays or allergy shots might be necessary. Properly addressing underlying sinus conditions can greatly reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
Effective Remedies for Relief
Understanding the Causes of Left Front Head Pain
Left front head pain can be a result of various factors, including tension headaches, migraines, or even sinus issues. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment and relief. Stress and anxiety often exacerbate these types of headaches, leading to increased discomfort.
Additionally, lifestyle choices such as poor posture, inadequate hydration, and lack of sleep can contribute to the onset of pain in the head. Taking note of these factors can help you manage or prevent future occurrences. It’s essential to maintain a healthy routine to mitigate these risks.
In some cases, medical conditions such as cluster headaches or more serious concerns like a neurological disorder might be involved. Seeking professional medical advice is crucial for proper diagnosis and management of ongoing pain.
Natural Remedies for Immediate Relief
There are several natural remedies that individuals can utilize to alleviate left front head pain. For instance, essential oils like peppermint or lavender can be inhaled or applied topically to soothe headache symptoms. Mild massage techniques focused on the temples and neck can also promote relaxation and relieve tension.
Hydration is vital; ensuring adequate water intake throughout the day can prevent dehydration-related headaches. Herbal teas, such as chamomile or ginger, might provide calming effects and further assist in relieving pain.
Incorporating relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises may help reduce stress levels and, consequently, headache frequency. Establishing a calming bedtime routine can also promote better sleep quality, which is crucial for overall health.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many instances of left front head pain can be managed at home, there are signs that indicate a need for professional evaluation. If the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by symptoms such as visual disturbances or nausea, it's essential to seek medical help. A sudden onset of headaches that differs from your usual pattern warrants immediate attention.
Additionally, if headaches are interfering with daily life, affecting productivity, or causing significant distress, consulting with a healthcare provider is advisable. They can help determine whether medication or therapy is necessary for pain management.
Finally, individuals who experience neurological symptoms, such as weakness, confusion, or difficulty speaking, should seek emergency care. These symptoms could indicate a more serious underlying issue that needs immediate intervention.