Essential Guide to Preventing and Treating Muscle Strain
What is a Muscle Strain?
Understanding the Mechanics of Muscle Strains
A muscle strain, often referred to as a pulled muscle, occurs when muscle fibers are overstretched or torn. This injury can happen during various activities, from sports to everyday tasks, and understanding the mechanics behind it is crucial for prevention.
Strains primarily affect the muscles and the tendons, which connect muscles to bones. The severity of a strain can vary, categorized as mild, moderate, or severe based on the extent of the damage. A mild strain may involve only a few muscle fibers, while a severe strain can result in complete tears.
Common factors contributing to muscle strains include lack of flexibility, inadequate warm-up before activities, and sudden increases in physical intensity. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises can significantly reduce the risk of developing a strain.
Moreover, muscle strains can occur in any muscle group, but areas like the back, hamstrings, and quadriceps are particularly vulnerable. Being aware of these at-risk areas can help individuals take extra precautions.
Recognizing the early signs of a muscle strain, such as tightness or discomfort, can lead to timely treatment and better outcomes.
Prevention Strategies for Muscle Strains
Preventing muscle strains is often more effective than treating them after they occur. Individuals can adopt several strategies to minimize the risk of injury. One of the most crucial is incorporating a proper warm-up routine before engaging in physical exercise or sports.
Warming up increases blood flow to the muscles and enhances flexibility, preparing the body for more intense activity. Dynamic stretches that mimic the movements of the exercise can be particularly beneficial in this regard.
Incorporating strength training into your weekly routine can also help protect against strains. Stronger muscles are better equipped to handle stress and absorb impact during physical activities, reducing the likelihood of injury.
Staying hydrated and maintaining proper nutrition supports muscle function and overall performance. Dehydration can lead to muscle cramps and increases the risk of strains.
Finally, listening to your body is key. Pushing through pain can lead to further injury, so it's essential to rest and recover when needed.
Recognizing Symptoms of Muscle Strain
Recognizing the symptoms of a muscle strain is vital for timely intervention and preventing further damage. Common signs include sudden pain in the affected muscle, swelling, and bruising. Individuals may also experience muscle spasms or reduced range of motion.
If the muscle strain is severe, there might be a noticeable muscle deformity, or the individual may feel a “pop” at the time of injury. These symptoms warrant immediate medical attention, as they may indicate a partial or complete tear.
Active people might also notice difficulty in using the affected muscle in daily activities. For instance, someone with a hamstring strain may struggle to walk, while a shoulder strain might hinder overhead movements.
In some cases, symptoms can appear gradually, especially with overuse injuries. Pay attention to persistent discomfort or tightness that worsens with activity, as it could signal an impending strain.
Recognizing these symptoms early enables individuals to seek treatment promptly, which can significantly aid recovery and prevent long-term complications.
Treatment Options for Muscle Strains
When it comes to treatment, the R.I.C.E. method is widely recommended for muscle strains. R.I.C.E. stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Resting the affected muscle helps in preventing further injury.
Icing the area can reduce swelling and numb the pain. It’s essential to apply ice for 15-20 minutes every hour for the first couple of days post-injury. Compression using elastic bandages can help decrease swelling and provide support.
Elevation of the injured area above heart level also aids in reducing swelling. This is particularly effective during the initial stages of recovery.
Pain relief medications, such as NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), may also be recommended to manage pain and inflammation.
For more severe strains, physical therapy can play a crucial role in recovery. A physical therapist can guide individuals through rehabilitation exercises, helping to restore strength and flexibility to the affected muscle.
Common Causes of Muscle Strain
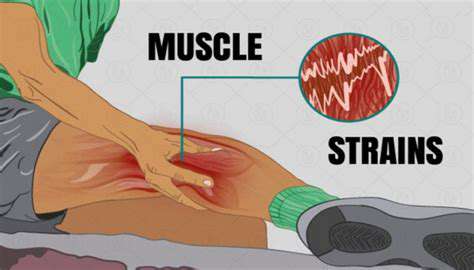
Understanding Muscle Anatomy
To effectively prevent and treat muscle strain, it is vital to first understand the muscle anatomy involved. Muscles are made up of fibers that contract and relax, allowing for movement and stability.
When these fibers are overstretched or torn, muscle strain occurs, resulting in pain and discomfort. The severity of the strain can vary, leading to different levels of injury.
Anatomy knowledge can help in identifying which muscles are at risk during certain activities. For instance, the hamstrings are often strained during sports that involve sprinting or sudden stops.
Issues with muscle coordination and balance can also contribute to strains, highlighting the importance of muscle awareness and control. Understanding these aspects can provide a foundation for effective prevention strategies.
Risk Factors for Muscle Strain
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing a muscle strain. These include age, as muscle elasticity tends to decrease over time, making injuries more common.
Another significant risk factor is poor conditioning. Athletes or individuals who suddenly increase their physical activity without proper training are more susceptible to strains.
Muscle imbalances and previous injuries also play a crucial role in the likelihood of strains. If one muscle group is stronger or more flexible than its counterpart, the weaker muscle may face excess stress.
Finally, inadequate warm-up or cool-down routines can contribute to muscle strain. Ensuring that the body is properly prepared for activity can help mitigate these risks.
Preventing Muscle Strain
Preventive measures are essential for safeguarding against muscle strains. One of the most effective strategies is to engage in regular flexibility and strength training exercises.
Incorporating a proper warm-up routine before physical activity allows muscles to prepare for exertion. This includes dynamic stretching to increase blood flow and mobility.
Maintaining good hydration levels is also crucial, as dehydration can impair muscle function and increase injury risk. Additionally, paying attention to proper technique during physical activities can prevent undue strain on muscles.
Listening to one’s body and honoring the need for rest is another vital aspect of prevention. Overexertion can lead to muscle fatigue, making strains more likely.
Treating Muscle Strain Effectively
When a muscle strain occurs, immediate treatment is essential for recovery. The R.I.C.E. method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is the first line of treatment to reduce inflammation and pain.
Resting the affected muscle allows it to heal and prevents further injury. Applying ice can help diminish swelling and provide pain relief in the acute phase.
Compression through bandages or wraps can also alleviate swelling and support the muscle. Furthermore, elevating the injured area above heart level assists in reducing inflammation.
As the muscle begins to heal, gentle stretching and strengthening exercises may be introduced gradually. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate rehabilitation plan.
Signs and Symptoms of Muscle Strain
Common Signs of Muscle Strain
Recognizing the signs of muscle strain is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. One of the most common indicators is acute pain that occurs immediately following an injury. This pain may be sharp and localized to the muscle that has been strained, making it easy to identify the affected area.
Swelling is another frequent symptom associated with muscle strains. When the muscle fibers are damaged, the body responds with inflammation, which can lead to visible swelling around the affected area. This may also contribute to the muscle feeling tighter or more tense than usual.
In addition to pain and swelling, bruising may also appear as a result of underlying blood vessels being damaged during the strain. This discoloration can vary in severity and might take several days to fully manifest on the surface of the skin.
Lastly, a reduced range of motion is a significant sign of a muscle strain. Individuals may experience difficulty moving the affected muscle or joint without discomfort, which can hinder daily activities and sports performance.
Treatment Options for Muscle Strain
Immediate treatment for a muscle strain typically follows the RICE protocol: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. This approach helps reduce pain and swelling in the early stages of injury. Resting the affected muscle allows it to recover without further damage.
Applying ice to the strained area can significantly alleviate swelling and numb sharp pain. It's important to use ice wrapped in a cloth or towel for about 15-20 minutes every hour, especially within the first 48 hours after the injury.
Compression with elastic bandages or wraps can also help minimize swelling and provide support to the injured muscle. It’s essential to ensure that the compression is firm but not so tight that it restricts blood flow.
After allowing sufficient time for initial healing, rehabilitation exercises can be introduced to strengthen the muscle and restore flexibility. Consulting a healthcare professional for personalized exercises can lead to a more effective recovery and prevent future strains.
Prevention Strategies for Muscle Strain
Understanding the Causes of Muscle Strain
Muscle strain, often referred to as a pulled muscle, occurs when fibers in the muscle are overstretched or torn. This injury commonly results from physical activities that involve lifting, twisting, or sudden movements. Understanding the specific causes can aid in preventing such injuries.
One significant risk factor for muscle strain is inadequate warm-up before engaging in strenuous activities. Warming up prepares the muscles by increasing blood flow and flexibility, reducing the likelihood of injury. Neglecting this crucial step can leave muscles vulnerable to strain.
Another contributing factor is muscle fatigue. When muscles are tired, they are less capable of handling the stress of physical activity. Incorporating rest days into your fitness routine can help prevent fatigue-related injuries.
Lastly, not using proper techniques during physical activities, such as lifting heavy objects, can lead to muscle strain. Educating oneself on the correct posture and lifting techniques is essential to minimize the risk of injury.
Effective Treatment Options for Muscle Strain
When you experience a muscle strain, immediate treatment can significantly influence the healing process. The R.I.C.E. method, which stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation, is often recommended for managing muscle injuries.
Resting the affected muscle is crucial for recovery. Engaging in activities that put stress on the injured area can exacerbate the damage and prolong the healing process. Taking a break from physical activities allows the tissue to repair itself.
Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce swelling and pain. Ideally, ice should be applied in 15 to 20-minute intervals several times a day during the first 48 hours post-injury. It's important to wrap the ice pack in a cloth to prevent skin damage.
Compression and elevation also play essential roles in recovery. Wrapping the injured area with an elastic bandage can help minimize swelling, while elevating the affected limb can further reduce inflammation. Seeking medical attention for severe strains is crucial and may require physical therapy for rehabilitation.
Treatment Options for Muscle Strain

Treatment Options for Muscle Strain
When dealing with a muscle strain, the first step is to assess the severity of the injury. Understanding whether the strain is mild, moderate, or severe can guide the appropriate treatment path. For minor strains, self-care measures can often suffice, while more serious injuries may require medical intervention.
Rest is crucial following a muscle strain. It allows the affected area to recover and reduces the risk of aggravating the injury. Taking a break from activities that stress the muscle is essential for proper healing. Ice therapy can also help in reducing swelling and pain during the initial recovery period.
Physical therapy plays an important role in the rehabilitation of muscle strains. A qualified therapist can provide exercises tailored to the specific injury, fostering strength and flexibility in the affected area. Regular sessions can significantly expedite the healing process and prevent future injuries.
Home Remedies for Muscle Strain
Home remedies can supplement professional treatment and help alleviate symptoms of muscle strain. Applying heat after the first few days can enhance blood flow and relax the muscle, promoting healing. Additionally, over-the-counter pain relief medications can provide temporary relief from discomfort.
Gentle stretching and mobility exercises should be initiated once the acute pain subsides. Engaging in these activities can help restore range of motion and strengthen the muscle fibers. It is important to listen to your body during this phase to avoid overexertion.
Hydration and nutrition also play indispensable roles in recovery. Staying well-hydrated helps the muscles function optimally, while a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports healing. Incorporating protein into meals can promote muscle repair, making it a vital aspect of recovery.
Preventative Measures for Muscle Strain
Prevention is an effective strategy when it comes to muscle strains. Engaging in a proper warm-up routine before activities is essential to prepare the muscles for exertion. Stretching and dynamic movements can significantly reduce the risk of strains.
Maintaining overall fitness levels can also be a preventive measure. Regular strength training exercises not only enhance muscle tone but also improve coordination and agility. This comprehensive approach minimizes the risk of injuries during physical activities.
Lastly, listening to your body is key in preventing muscle strains. Taking breaks when feeling fatigued or when experiencing discomfort can prevent overuse injuries. Being mindful of your body's limits can help ensure long-term health and prevent potentially serious injuries.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing Symptoms of Muscle Strain
Understanding the symptoms of muscle strain is crucial for determining whether medical attention is necessary. Common symptoms include localized pain and tenderness that worsen with movement. Many individuals also experience swelling in the affected area. These symptoms can significantly hinder daily activities and affect overall well-being.
A pulled muscle may also lead to stiffness, which can make it difficult to use the affected limb. The range of motion is often compromised, and in some severe cases, bruising may occur. Being aware of these symptoms can help individuals decide when to seek professional help.
It's important to note that symptoms can vary in intensity based on the severity of the strain. A mild strain may simply involve tightness in the muscle, while a severe strain may result in an inability to use the muscle at all. If symptoms persist or worsen, it's advisable to consult a healthcare provider.
Keeping a close eye on how the body responds to pain and activity can provide valuable insights. Individuals should take note if the pain is sharp, persistent, or accompanies other concerning symptoms, as these may warrant immediate medical evaluation.
Factors That Indicate Serious Injury
While many muscle strains can be treated at home, certain factors can indicate a more serious condition that requires medical attention. If the pain is severe and does not improve with rest and basic home care, it could suggest a more significant injury, such as a complete muscle tear.
Other red flags include a noticeable deformation of the muscle or joint, which may indicate a dislocation or fracture. Additionally, if there is significant swelling or bruising that spreads beyond the initial injury site, this warrants a professional assessment.
Another critical factor is the presence of numbness or tingling, especially if it radiates into the limbs or is accompanied by weakness. These symptoms may indicate nerve involvement or a more complex injury, suggesting the need for medical imaging or specialized treatment.
Finally, if the injured individual has difficulty walking or using the affected muscle even after several days of rest and home treatment, seeking medical attention is strongly advised to rule out serious complications.
All About Treatment Options
When it comes to treating muscle strain, a variety of options are available depending on the severity of the injury. Initial treatment typically involves the RICE method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. This approach can help reduce swelling and pain in the early stages after an injury.
Over-the-counter pain relief medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may also be recommended to alleviate discomfort and minimize inflammation. It's important for individuals to follow the appropriate dosages and guidelines for these medications.
For more severe strains, physical therapy may be necessary to regain strength and flexibility in the affected muscle. A physical therapist can develop personalized exercises and recovery plans that promote healing and help prevent future injuries.
In some instances, corticosteroid injections may be considered for persistent pain and inflammation. These should be used judiciously, as they come with potential side effects. Overall, a tailored approach that considers the individual's specific needs and severity of the injury is crucial for effective recovery.