Exploring the Impact of Blood Flow Changes and Blood Pressure Fluctuations on Health
Introduction to Blood Flow and Blood Pressure Dynamics
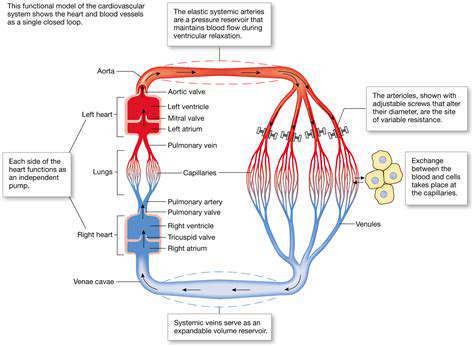
Understanding Blood Flow Mechanics
Blood flow is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues throughout the body. It is driven by the heart's pumping action and influenced by the resistance in blood vessels. Factors such as vessel diameter and blood viscosity can greatly affect how efficiently blood flows.
Understanding these mechanics is crucial for recognizing how different conditions, such as atherosclerosis or hypertension, can alter blood flow. These changes can lead to significant health issues if left unaddressed.
Factors Influencing Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is influenced by a myriad of factors, including physical activity, diet, and stress levels. Elevated blood pressure can strain the heart and lead to serious conditions like heart disease. Monitoring these influences is vital for maintaining cardiovascular health.
Additionally, lifestyle choices such as sodium intake and alcohol consumption can dramatically affect blood pressure levels. Being aware of these factors empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Consequences of Blood Flow Obstruction
Obstructed blood flow can lead to a variety of health complications, including ischemia and thrombosis. These conditions can result in damage to organs and tissues due to insufficient oxygen supply. Early detection and treatment are crucial for a favorable outcome.
Healthcare professionals often recommend regular check-ups and screenings to identify potential blood flow issues before they escalate. Strategies for prevention can include lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, medical interventions.
The Role of Exercise in Blood Health
Regular physical activity plays a significant role in improving blood circulation and regulating blood pressure. Exercise helps to strengthen the heart and can enhance the elasticity of blood vessels, promoting better blood flow.
Incorporating aerobic activities, strength training, and flexibility exercises can yield substantial benefits for overall cardiovascular health. These practices can help reduce the risks associated with high blood pressure and poor circulation.
Future Research Directions in Hemodynamics
Current research in hemodynamics is exploring innovative approaches to manage blood flow and pressure variations. Advanced technology, such as wearable monitors, is providing real-time data to help patients manage their conditions more effectively.
Future studies are likely to focus on personalized medicine and how individual variations can influence treatment. This research holds potential for developing tailored therapies that can improve health outcomes for patients with blood flow and pressure irregularities.
Common Causes of Changes in Blood Flow
Physiological Changes
Blood flow changes can be a natural response to various physiological conditions within the body. For instance, during physical activity, the body responds to the increased demand for oxygen by redirecting blood from less critical areas to muscles in action.
Additionally, factors such as temperature can influence blood flow. In warmer conditions, blood vessels dilate to help heat evaporate from the body, resulting in increased blood flow to the skin.
During rest or sleep, blood flow may decrease as the body's metabolic demands are lower. This shows how adaptable our circulatory system is to both active and resting states.
Hormonal changes, such as those occurring during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy, can also affect blood flow patterns. The increased levels of certain hormones can lead to vascular changes that enhance or reduce circulation in specific areas.
These physiological adjustments are essential for maintaining homeostasis, ensuring that organs and tissues receive adequate blood supply regardless of activity level.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions can significantly impact blood flow and pressure. For example, conditions such as atherosclerosis—where arteries become narrowed due to plaque build-up—can lead to decreased blood flow and increased blood pressure.
Heart disease is another critical factor; conditions like congestive heart failure can cause fluid buildup and impede efficient circulation, leading to various complications.
Diabetes can also affect blood flow by damaging blood vessels over time, leading to peripheral artery disease. This condition can result in severe pain and reduced circulation in extremities.
High blood pressure itself can be both a cause and a consequence of poor blood flow. It puts extra strain on the heart and arteries, increasing the risk of various cardiovascular events.
Consequently, monitoring and managing these health conditions is crucial to maintain optimal blood flow and pressure levels.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices significantly influence blood flow and pressure. Regular physical activity is positively correlated with improved circulation, as exercise strengthens the heart and promotes better vascular health.
On the other hand, a sedentary lifestyle can lead to decreased blood flow and increase the risk of developing conditions like varicose veins.
Diet also plays a crucial role; high-saturated fat and cholesterol diets can contribute to the narrowing of arteries, reducing blood flow and raising blood pressure.
Moreover, stress management is vital. Chronic stress can lead to the release of adrenaline, temporarily increasing blood pressure and potentially causing long-term damage to blood vessels.
Therefore, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and stress management techniques, can enhance blood flow and support overall cardiovascular health.
Medications and Treatments
Various medications are available to manage blood flow and pressure issues. For instance, antihypertensive drugs help lower blood pressure by relaxing blood vessels or reducing the heart's workload.
Anticoagulants are essential for individuals at risk of blood clots, as they help prevent clots from forming and promoting better blood flow.
Additionally, vasodilators, which widen blood vessels, can be prescribed to enhance circulation in certain medical conditions.
Besides pharmaceuticals, treatments such as physical therapy can also enhance blood flow, especially post-surgery or after an injury, by gradually improving circulation and promoting healing.
It is crucial for individuals to consult healthcare professionals before starting any medications or treatments, ensuring they are appropriate for their specific health conditions.
Impact of Age and Gender
As individuals age, blood vessel elasticity decreases, which can lead to increased blood pressure and reduced blood flow. Aging can also lead to heart diseases that further complicate circulation.
Gender differences also play a role in blood flow and pressure changes. Women may experience unique fluctuations in blood flow due to hormonal changes related to menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause.
Research suggests that men and women may experience symptoms of cardiovascular diseases differently, emphasizing the need for gender-specific approaches in treatment and management.
Additionally, older women are often found to have higher rates of hypertension, particularly after menopause, necessitating targeted preventative strategies.
Understanding these age and gender-related factors can help tailor health interventions aimed at maintaining optimal blood flow and pressure across different demographics.
The Role of Blood Pressure Fluctuations
The Importance of Consistent Blood Pressure Levels
Blood pressure is a critical indicator of cardiovascular health. Consistent levels are essential for the proper functioning of organs and systems throughout the body. When blood pressure remains stable, it ensures that tissues receive a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients.
Conversely, fluctuations in blood pressure can lead to various health issues, including heart disease and stroke. These fluctuations often stem from factors like stress, diet, and physical activity, all of which can influence overall wellbeing.
It's important to monitor blood pressure regularly to identify any significant changes. Consistent tracking allows for early intervention if numbers begin to rise or drop unexpectedly, which can prevent long-term health complications.
Healthcare providers often use guidelines based on age and risk factors to determine what constitutes a healthy blood pressure range. Understanding these parameters is crucial for maintaining long-term health.
Impact of High Blood Pressure on the Body
High blood pressure, or hypertension, can have severe implications for health. Over time, it can damage arteries and lead to a range of cardiovascular diseases. The strain on the heart can also result in heart failure, where the heart becomes less effective at pumping blood.
Additionally, hypertension can affect various organs. For example, it can lead to kidney damage or failure as the kidneys work harder to filter the blood. The eyes can also be affected, resulting in vision problems due to damage to the retina.
People with high blood pressure are at an increased risk of developing life-threatening conditions. That's why lifestyle adjustments, such as diet and exercise, are crucial in managing blood pressure levels effectively.
Regular check-ups and blood pressure monitoring can help in early detection and management of hypertension, which can significantly reduce the associated risks of organ damage and other serious health issues.
Managing Blood Pressure for Improved Health
Managing blood pressure is vital for overall health and can be achieved through lifestyle changes. Diet plays a fundamental role; incorporating fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while reducing sodium intake can help lower blood pressure.
Physical activity is another key component. Regular exercise strengthens the heart and improves its efficiency in pumping blood, which can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
Stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga, can also help keep blood pressure in check. These practices not only reduce stress but also contribute to overall emotional wellbeing.
Lastly, regular consultations with healthcare providers for medication management and monitoring blood pressure are essential steps in ensuring long-term health and preventing complications associated with fluctuating blood pressure levels.