Head Pain When Walking: Causes and Relief Options
- Worsen progressively with each walk
- Occur with nausea/vomiting
- Follow head trauma
Changes in Barometric Pressure
Weather-sensitive individuals often experience pressure headaches when walking outdoors. The inner ear detects atmospheric changes that can trigger vascular responses. Planning walks during stable weather periods or using indoor tracks during pressure fluctuations may help.
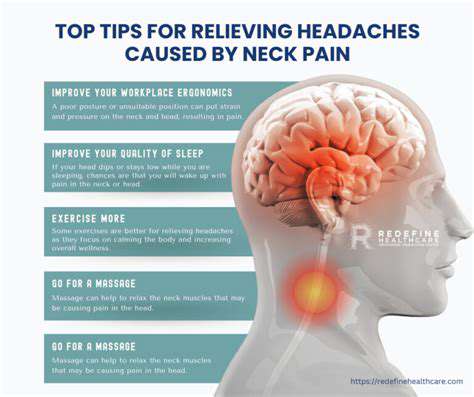
Muscle Strain and Tension Headaches
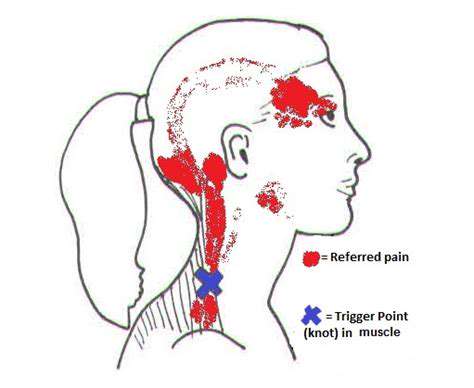
Understanding Muscle Strain
Muscle overuse creates microscopic tears that stimulate pain receptors. The trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles commonly refer pain to the head. Many sufferers describe a band-like pressure around their forehead or base of skull. Gentle neck rotations before walking prepare these muscles for activity.
The Role of Muscle Tension in Headaches
Chronic muscle tension alters pain perception thresholds in the brain. Over time, even normal muscle activity can trigger headache responses. Stress-induced muscle guarding creates a vicious cycle - tension causes pain which increases tension. Breaking this cycle requires both physical and psychological approaches.
Treatment and Prevention Strategies
Effective management combines:
- Postural retraining with a physical therapist
- Targeted stretching of pectoral and suboccipital muscles
- Stress reduction techniques like diaphragmatic breathing
Underlying Medical Conditions

Underlying Cardiovascular Issues
Vascular abnormalities often first manifest during exercise when circulatory demands increase. Conditions like vertebral artery stenosis may only cause symptoms when head movement during walking compromises blood flow. A simple pulse check at the wrist and neck during headache episodes can reveal important clues.
Metabolic Syndrome
Insulin resistance creates systemic inflammation that sensitizes pain pathways. Many patients report headache improvement after adopting anti-inflammatory diets, even before significant weight loss occurs. The connection between metabolic health and pain perception is increasingly recognized.
Diabetes
Diabetic neuropathy can paradoxically cause both numbness and pain during activity. Foot numbness alters gait mechanics, creating compensatory strain in upper body muscles. Regular podiatric evaluations help prevent these secondary effects.
Rheumatological Diseases
Inflammatory arthritis often involves the cervical spine, making head movement during walking painful. Morning stiffness lasting over 30 minutes strongly suggests inflammatory rather than mechanical pain. Early rheumatologic consultation prevents irreversible joint damage.
Autoimmune Disorders
Conditions like giant cell arteritis cause exercise-limiting headaches through vessel inflammation. New headaches after age 50 with jaw pain during chewing require urgent evaluation. These temporal symptoms often precede vision-threatening complications.
Infections and Chronic Pain
Post-viral syndromes frequently include exercise intolerance with headache. Recent illness preceding headache onset should be reported to healthcare providers. Even mild infections can trigger lasting pain sensitivity changes.