Migraine Pain on Left Side of Head: Understanding Symptoms
Possible Causes of Left-Sided Migraine Pain

Common Triggers for Left-Sided Migraines
Many individuals experience migraines that can often be triggered by specific external factors. Understanding these triggers can help in managing migraine occurrences. Common triggers include stress, hormonal changes, and certain food items. Foods such as aged cheese, alcohol, and processed meats are often noted as potential culprits. Maintaining a migraine diary can be beneficial for identifying personal triggers.
Environmental factors such as strong odors, bright lights, and loud noises may also play a role. People who suffer from migraines should try to minimize their exposure to these stimuli. This can significantly reduce the frequency of left-sided migraines. Additionally, changes in weather, particularly barometric pressure changes, can exacerbate migraine symptoms as well.
Overexerting oneself, whether through physical activity or mental strain, can also lead to the onset of migraines. It's crucial to find the right balance between work and relaxation. Taking regular breaks and practicing stress-relief techniques can prove helpful.
Sleep patterns are another critical factor in managing migraines. Insufficient sleep or sleeping too much can trigger migraine episodes. Developing a consistent sleep schedule is essential for migraine prevention.
Hydration is vital as well; dehydration can lead to the onset of a migraine. Drinking enough water throughout the day can help maintain your body's optimal functioning. Simple lifestyle adjustments can make a significant difference in reducing Left-Sided Migraine Pain.
Symptoms Unique to Left-Sided Migraines
The symptoms associated with left-sided migraines can vary, but some common ones include intense pain localized to the left side of the head. This pain can be throbbing or pulsating and often worsens with physical activity. Understanding the nuances of these symptoms can help in seeking timely medical assistance. Some individuals may also experience nausea and vomiting.
Left-sided migraines may be accompanied by sensitivity to light and sound, further complicating the experience. This sensitivity can make daily activities challenging, necessitating a quiet and dark environment during an episode. Many sufferers also report visual disturbances known as aura, which can involve seeing spots or flashing lights.
Another common symptom associated with left-sided migraines is tingling or numbness on one side of the body. This can be alarming, as it may mimic other medical conditions. It's important to differentiate these symptoms to respond appropriately.
Emotional symptoms such as irritability and anxiety may also accompany migraines. Understanding this emotional aspect can aid individuals in preparing for potential migraines. Keeping track of mood changes can be beneficial for those suffering from chronic migraines.
Lastly, the duration of left-sided migraines varies widely, ranging from a few hours to several days. Understanding how long symptoms typically last can help individuals manage their expectations and plan accordingly. Seeking medical advice for persistent or severe symptoms is crucial.
Diagnosis of Left-Sided Migraine Pain
Diagnosing left-sided migraine pain typically involves a comprehensive medical history review and a physical examination. Patients are often asked to describe their symptoms, onset, and frequency of episodes. Clear communication about these experiences can significantly aid the diagnostic process.
Healthcare professionals might also conduct neurological examinations to rule out other conditions that may present similar symptoms. Diagnostic imaging, such as MRI or CT scans, could be recommended to exclude serious underlying issues. However, these tests are usually not necessary for straightforward migraine cases.
Keeping a migraine diary is greatly encouraged for those experiencing left-sided migraines. Documenting details such as duration, intensity, triggers, and associated symptoms can provide vital information. This record can be instrumental during medical consultations for more tailored treatment approaches.
Sometimes, additional tests may include blood tests to check for conditions like anemia or thyroid issues that can contribute to headache symptoms. Identifying any underlying health problems can be a crucial step toward effective treatment.
Once diagnosed, a healthcare provider can design a personalized treatment plan that may include lifestyle changes, medications, or alternative therapies. Following through with recommended treatments can lead to a better quality of life for migraine sufferers.
Treatment Options for Left-Sided Migraines
Treatment for left-sided migraines often involves both acute and preventive strategies. Acute treatments aim to alleviate symptoms during an attack and may include over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or prescription medications like triptans. Effective acute treatment can significantly improve the experience of a migraine episode.
Preventive measures are designed to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines. These may include daily medications such as beta-blockers, anticonvulsants, or antidepressants. Consultation with a healthcare professional can ensure the best preventive strategy tailored to individual needs.
Lifestyle modifications encompass a wide range of options, including dietary changes, regular exercise, and stress management techniques. Techniques like yoga or meditation can lower stress levels and may lead to a reduction in migraine occurrences. Consistent adherence to these changes can yield long-lasting benefits.
Alternative therapies such as acupuncture or biofeedback may also be beneficial in managing left-sided migraine pain. Many individuals find these holistic approaches to be effective complements to traditional treatment regimens. Exploring various therapies can help individuals discover what works best for them.
In chronic cases, it may be useful to explore options such as Botox injections, which have shown effectiveness for some migraine sufferers. Discussing all potential treatment avenues with a healthcare professional will aid in creating a comprehensive approach to migraine management.
Long-term Management Strategies
Long-term management of left-sided migraines focuses on identifying and avoiding triggers while maintaining overall well-being. Creating a supportive environment that minimizes trigger exposure can foster better health outcomes. Engaging in regular follow-ups with healthcare providers can help in adjusting treatment plans as needed.
Developing a personalized health plan that incorporates medication, lifestyle changes, and coping strategies is crucial for lasting management. Regular exercise and a balanced diet contribute significantly to overall health and can help mitigate migraine frequency. Keeping up with a routine is often beneficial.
Regular hydration and sleep patterns can support long-term migraine management. Individuals should aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and stay adequately hydrated throughout the day. These fundamental aspects often lay the groundwork for migraine prevention.
Tracking migraines over time can reveal patterns that aid in future management. Using apps or diaries to log symptoms and associated factors can provide valuable insights into personal migraine profiles. This tool is vital for developing informed strategies for long-term management.
Lastly, educating oneself about migraines can empower individuals to take control of their condition. Participating in support groups or engaging with online communities can provide additional resources. Being proactive in managing migraines can improve the quality of life overall.
Recognizing Symptoms Associated with Left-Sided Migraines
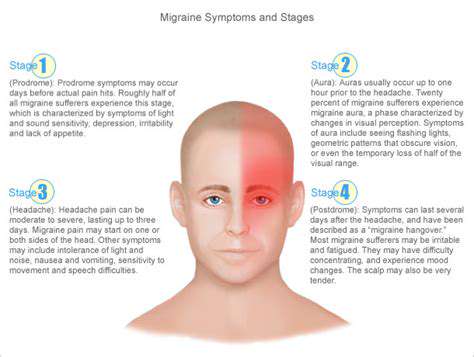
Common Symptoms of Left-Sided Migraines
Left-sided migraines are often characterized by intense, throbbing pain located primarily on the left side of the head. Individuals experiencing this type of migraine may also suffer from nausea and sensitivity to light. Other common symptoms can include blurred vision and dizziness, which can exacerbate the discomfort of the headache.
In some cases, migraines can also be accompanied by visual disturbances, known as aura. These auras may appear as flashing lights or zigzag patterns and can serve as an early warning sign of an impending migraine attack. Recognizing these symptoms can be crucial for effective management and treatment.
It's also important to understand that each migraine episode can differ in its presentation, making it essential for sufferers to keep track of their symptoms. Identification of these symptoms allows individuals to better prepare for and manage their migraine episodes.
Triggers of Left-Sided Migraines
A variety of factors can trigger migraines on the left side of the head, and these triggers can vary greatly between individuals. Common triggers include stress, hormonal changes, and certain foods, such as aged cheeses or processed meats. Identifying personal triggers can greatly assist in reducing the frequency of migraine attacks.
Environmental factors such as bright lights, strong odors, and loud noises can also provoke migraines. Individuals should consider keeping a diary to track their triggers and patterns to better understand their specific migraine profile.
In addition to external triggers, dehydration and lack of sleep are significant contributors to migraine frequency. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and staying adequately hydrated are practical steps that may help alleviate symptoms.
Impact on Daily Life
Left-sided migraines can significantly disrupt daily activities, affecting both personal and professional responsibilities. Many individuals find it challenging to concentrate or perform tasks during a migraine attack. This not only impacts productivity but also can affect personal relationships and social interactions.
For some, the unpredictability of migraine attacks can lead to anxiety and depression, further complicating their overall well-being. Those suffering from chronic migraines may find themselves altering their lifestyle to accommodate their condition, which can lead to feelings of isolation.
Implementing coping strategies and seeking supportive environments can help individuals manage their migraines more effectively. Having a support system in place can provide emotional relief and greater understanding from those around them.
Medicinal and Non-Medicinal Treatments
When it comes to managing left-sided migraines, a combination of medicinal and non-medicinal treatments is often recommended. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can be effective for mild to moderate migraine pain. However, many individuals find that prescription medications, such as triptans, are necessary for severe migraine episodes.
In addition to medication, alternative therapies like acupuncture and yoga are becoming increasingly popular for migraine management. These non-medicinal approaches can alleviate stress and promote relaxation, potentially reducing the frequency of migraine attacks.
It’s essential for sufferers to consult healthcare professionals regarding suitable treatment plans tailored to their specific needs. Education about the condition and treatment options empowers individuals to take control of their migraine management.
Long-Term Strategies for Management
Living with left-sided migraines often requires implementing long-term strategies for effective management. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and consistent hydration are fundamental components that contribute to overall well-being and may reduce migraine occurrences. Establishing a routine can help maintain predictable patterns that may minimize triggers.
Mindfulness and stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises, can also play a vital role in long-term management. Practicing these techniques consistently can lead to improved mental resilience against migraine triggers.
Finally, regularly consulting with a healthcare provider for updated treatment options and coping strategies is crucial for maintaining an effective management plan. Being proactive in one’s health care can lead to improved outcomes and a better quality of life.
Effective Relief Strategies for Left-Sided Migraine Pain
Identifying Symptoms of Left-Sided Migraine Pain
Migraine pain can manifest in various forms, and when it affects the left side of the head, it often presents specific symptoms that can help in identification. One hallmark symptom is throbbing or pulsing pain, which can be intermittent or persistent for several hours or even days.
Many individuals experience sensitivity to light and sound during a migraine attack. This sensitivity can exacerbate the discomfort associated with the left-sided pain and compel individuals to seek a quiet, dark space for relief.
Nausea and vomiting are additional symptoms commonly observed during a left-sided migraine. These symptoms may not occur for everyone, but they can significantly affect a person's quality of life and ability to perform daily tasks.
Visual disturbances, known as aura, often precede a migraine attack. These can include flashes of light, zigzag patterns, or partial loss of vision, which can uniquely affect individuals experiencing left-sided pain.
Lastly, left-sided migraine pain may sometimes be accompanied by numbness or tingling sensations in other parts of the body, offering a potential indication of a migraine's neurological nature.
Understanding Triggers of Left-Sided Migraines
Understanding the triggers that can lead to left-sided migraine pain is crucial for effective management. Common triggers include specific dietary choices, where certain foods like aged cheese, processed meats, and alcoholic beverages can provoke an attack.
Stress is another significant trigger for many individuals. High-pressure situations at work or personal life stressors can contribute to the onset of migraines, particularly on one side of the head.
Changes in sleep patterns, whether too much or too little sleep, can also trigger migraines. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule is essential to reducing the likelihood of incurring left-sided migraine pain.
Environmental factors, such as bright lights, strong smells, or changes in weather, can also act as triggers. It’s important to be mindful of the surroundings and take proactive measures, such as wearing sunglasses or avoiding strong odors.
Finally, hormonal changes, particularly in women, can play a pivotal role in triggering migraines. Changes in menstrual cycles, pregnancy, or menopause can all influence migraine frequency and intensity.
Effective Treatment Options for Managing Left-Sided Migraine Pain
Managing left-sided migraine pain can involve a variety of treatment approaches tailored to individual needs. Over-the-counter pain relief medications, such as ibuprofen or aspirin, may offer relief for mild to moderate attacks.
For more severe migraines, prescription medications, including triptans, can be effective. These specific medications target and alleviate migraine symptoms and are often advised when over-the-counter options fail.
Preventative strategies, including lifestyle modifications, can also significantly reduce the frequency of migraines. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate hydration contribute to overall well-being and help mitigate migraine episodes.
Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or aromatherapy, can provide complementary approaches to traditional medicine. These methods may help alleviate stress and tension, acting as preventative measures for migraines.
Lastly, maintaining a migraine diary can be beneficial. Recording symptoms, frequency, triggers, and treatments can provide valuable insights for both the individual and healthcare providers, leading to more effective management plans.



