Muscle Tension Can Result in a Range of Health Issues
What Causes Muscle Tension?
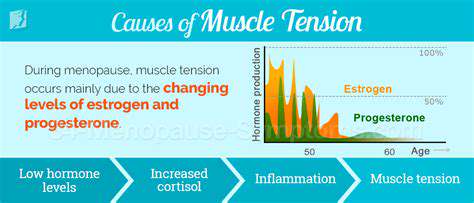
Physical Stress and Overexertion
One of the primary causes of muscle tension is physical stress, often resulting from overexertion during exercise or physical labor. When muscles are pushed beyond their limits, they can become tight and sore. This condition is exacerbated when individuals neglect proper warm-up and cool-down routines.
Moreover, repetitive motions or lifting heavy objects without proper technique can lead to chronic muscle tension. Such activities strain the muscles, causing them to tighten as a protective response.
Additionally, prolonged periods of poor posture can contribute to muscle tension over time. Sitting or standing incorrectly can place undue stress on specific muscle groups, leading to discomfort and tightness.
It's essential for individuals to listen to their bodies and rest when needed, as ignoring signs of overexertion can lead to more severe injuries. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises can help maintain muscle flexibility and prevent tension.
Overall, managing physical stress through appropriate techniques and awareness is crucial in mitigating muscle tension.
Emotional Stress and Anxiety
Emotional stress and anxiety significantly impact the muscles, often resulting in increased tension throughout the body. When a person experiences stress, the body enters a “fight or flight” mode, leading to muscle tightening as a natural response.
This heightened state of tension can cause discomfort, pain, and eventually chronic muscle tightness. Individuals facing emotional challenges may also neglect self-care, compounding the issue by failing to engage in relaxation techniques.
Furthermore, stress can lead to bad habits that worsen muscle tension, such as clenching jaws or hunching shoulders. These habits create a cycle of discomfort that can be difficult to break without intervention.
Recognizing the link between emotional well-being and physical health is crucial. Therapy, mindfulness practices, and stress management techniques can be beneficial in reducing emotional-induced muscle tension.
By addressing emotional stressors, one can often alleviate associated muscle tension effectively.
Medical Conditions and Injuries
Certain medical conditions and injuries also contribute to muscle tension. Conditions such as fibromyalgia, arthritis, and myofascial pain syndrome can lead to widespread muscle tightness and discomfort.
Additionally, injuries to muscles, tendons, or ligaments can result in localized tension as the body attempts to guard the affected area. This compensatory mechanism may lead to further tightness in surrounding muscle groups.
Chronic conditions like degenerative disc disease can also cause persistent muscle tension due to nerve compression and radiating pain. Understanding the underlying medical issues can help guide effective treatment.
Medical professionals often recommend personalized treatment plans for individuals with chronic muscle tension linked to health issues. These can include physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments tailored to alleviate symptoms.
Overall, awareness and proper management of medical conditions are vital in addressing the issue of muscle tension effectively.
The Consequences of Chronic Muscle Tension
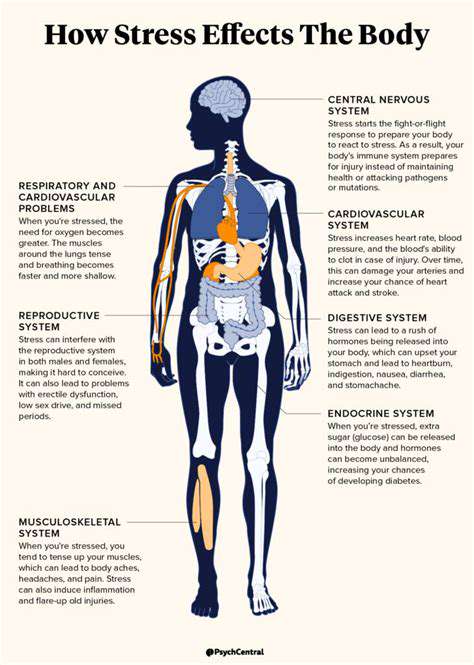
Understanding Chronic Muscle Tension
Chronic muscle tension refers to a prolonged state of muscular tightness or stiffness, often resulting from stress, poor posture, or repetitive movements. This condition can lead to discomfort and a decreased range of motion over time. Individuals may not even be aware that they have chronic tension until they experience pain or restricted mobility.
The muscles may become overly contracted, which can place additional strain on surrounding tissues and joints. As a result, this tension can contribute to various musculoskeletal disorders. Identifying the underlying causes of chronic tension is crucial for effective treatment and relief.
Many individuals engage in daily activities that exacerbate muscle tension, such as sitting for long hours without breaks. Addressing these habits can be the first step in alleviating chronic tension and promoting better overall health.
Physical Health Impacts
Chronic muscle tension can lead to a variety of physical health issues, including headaches, back pain, and neck pain. When muscles are in a constant state of contraction, they can compress nerves and blood vessels, leading to discomfort and a feeling of fatigue. This cycle can create a feedback loop of pain and tension.
Over time, the body’s natural healing processes can be hindered, leading to inflammation and chronic pain conditions. Muscles may lose elasticity, further limiting mobility and increasing the risk of injury. Recognizing the physical impacts of muscle tension is important for developing effective management strategies.
Common conditions associated with chronic muscle tension include fibromyalgia and myofascial pain syndrome. These conditions can significantly affect quality of life, underscoring the need for individuals to seek interventions and treatments when necessary.
Mental Health Considerations
The connection between physical muscle tension and mental health is well-documented. Chronic tension can be both a symptom and a contributor to anxiety and stress, creating a vicious cycle. Reducing muscle tension can lead to improvements in mental well-being.
Techniques such as mindfulness and meditation can help individuals manage stress and decrease muscle tension. Incorporating relaxation exercises into daily routines can significantly enhance both physical and psychological states. Understanding this link can empower individuals to take a holistic approach to their health.
Additionally, therapy and counseling can provide essential support for managing the mental aspects of chronic muscle tension. Recognizing and addressing the psychological factors at play can lead to better outcomes and a more comprehensive approach to treatment.
Strategies for Relief
There are various strategies to alleviate chronic muscle tension, ranging from physical therapies to lifestyle changes. Stretching and regular exercise are key components in reducing muscle tightness and improving flexibility. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation, such as yoga or tai chi, can be highly beneficial.
Incorporating ergonomic practices into daily life can help reduce strain on muscles, especially for those who work at desks or engage in repetitive motions. This may include adjusting chair heights, using supportive equipment, or taking regular breaks to move around. Awareness of one's posture can lead to significant improvements in muscle tension.
Additionally, seeking professional help from physiotherapists or massage therapists can provide targeted relief and help to identify specific problem areas. Treatment plans tailored to individual needs can pave the way for effective recovery from chronic muscle tension.
The Role of Nutrition and Hydration
Diet and hydration play critical roles in muscle health and tension levels. Consuming a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help mitigate the effects of chronic tension. Hydration is equally important, as muscles require adequate water to function properly.
Electrolyte balance is important for muscle function, so incorporating foods that provide essential minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium can also be beneficial. These minerals assist in muscle contraction and relaxation, thus aiding in reducing tension.
Additionally, avoiding excessive caffeine and processed sugars can help in managing both stress and inflammation levels in the body. Understanding the nutritional aspect of muscle health can lead to more effective tension relief and overall wellness.
Identifying Symptoms and Risk Factors
Common Symptoms of Muscle Tension
Muscle tension can manifest itself in various ways, and recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early intervention. Common signs include persistent aches, tightness, and discomfort in the affected areas. Individuals may also experience stiffness in the neck, shoulders, or back, which can limit mobility and cause pain during everyday activities.
In some cases, muscle tension can lead to headaches or migraines, as the tension in the neck and shoulder muscles can trigger discomfort that radiates to the head. Additionally, people suffering from muscle tension may notice fatigue, as the body expends extra energy to cope with the discomfort, leading to a feeling of overall tiredness and decreased productivity.
Risk Factors Associated with Muscle Tension
Several factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing muscle tension. These may include prolonged periods of poor posture, especially common in those who work at desks or use computers for extended periods. Stress and anxiety also play significant roles, as emotional tension can easily translate into physical muscle tightness.
Other potential risk factors include lack of regular physical activity, which can weaken muscles and make them more susceptible to strain. Additionally, aging can contribute to muscle tension, as the body naturally loses elasticity over time, making it more prone to stiffness and discomfort.
Effective Strategies to Relieve Muscle Tension

Understanding Muscle Tension
Muscle tension is a common condition that occurs when muscles remain in a state of contraction for an extended period.
This can happen due to various factors, including stress, poor posture, and lack of physical activity.
Over time, muscle tension can lead to discomfort and pain, impacting overall quality of life.
In addition to physical discomfort, tense muscles can contribute to emotional stress, creating a cycle that can be hard to break.
Recognizing the signs of muscle tension is crucial for timely intervention and relief.
Identifying the Causes of Muscle Tension
Muscle tension can be caused by both physical and emotional factors.
Physical causes may include repetitive movements, injuries, and prolonged sitting or standing. These factors can stress specific muscle groups, leading to chronic tension.
On the other hand, emotional stress is another major contributor, as it can cause muscles to tighten as a reaction to anxiety or frustration.
Understanding the root causes of muscle tension can help individuals make informed decisions when addressing the issue.
Keeping a diary of activities and stress levels can be a useful tool to identify triggers.
Effective Techniques for Muscle Relaxation
Implementing relaxation techniques can be an effective way to alleviate muscle tension.
Deep breathing exercises, for instance, can help calm the mind and release physical tension stored in the muscles.
Stretching is another powerful technique, as it directly targets the areas of tension and promotes flexibility. Regular stretching can also improve blood flow, which aids in recovery.
Other methods include yoga and meditation, both of which emphasize mindfulness and relaxation.
Engaging in these practices regularly can lead to long-lasting relief from muscle tension.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many instances of muscle tension can be managed at home, there are times when professional help is necessary.
If muscle tension is accompanied by persistent pain, numbness, or changes in mobility, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional.
They can provide a thorough evaluation to rule out any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the tension.
Physical therapy and massage therapy are effective treatments that can help muscle groups recover and function correctly. These interventions can provide targeted relief and promote overall wellness.
A professional can also guide you on the best techniques tailored to your specific needs, making recovery more effective.