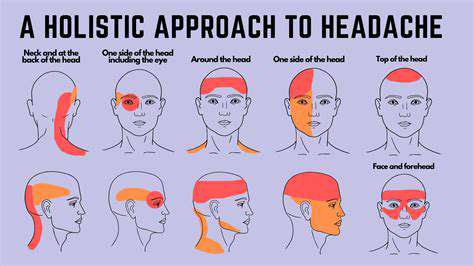
The Anti Inflammatory Diet: How It May Help Migraines
What is an Anti-Inflammatory Diet?

Understanding the Basics
An anti-inflammatory diet is a dietary approach focused on reducing inflammation in the body. Inflammation, while a natural response to injury or infection, can become chronic and contribute to various health issues, including heart disease, arthritis, and certain cancers. This approach emphasizes foods that are known to have anti-inflammatory properties, while limiting those that may promote inflammation.
By focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, an anti-inflammatory diet aims to provide the body with the nutrients it needs to support optimal health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. This includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean protein sources.
Key Dietary Components
A cornerstone of an anti-inflammatory diet is an abundance of fruits and vegetables. These colorful foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which help combat oxidative stress and reduce inflammation. Choosing a variety of colors ensures a diverse intake of beneficial nutrients.
Lean protein sources, such as fish, poultry, and beans, are also crucial. They provide essential amino acids for building and repairing tissues, while limiting red meat and processed meats can reduce inflammation-causing agents.
Foods to Include
The anti-inflammatory diet encourages the consumption of healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil. These fats contribute to healthy cell function and offer anti-inflammatory properties. Including foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon and flaxseeds, is particularly beneficial.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
Processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive amounts of saturated and unhealthy fats often contribute to inflammation. Reducing or eliminating these foods can significantly impact overall health and reduce inflammation markers. Trans fats, found in many commercially baked goods, are particularly detrimental.
Excessive consumption of refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and pasta, can also trigger inflammation. Consider replacing these with whole grains for a more balanced and anti-inflammatory approach.
Lifestyle Considerations
Beyond diet, lifestyle factors play a significant role in managing inflammation. Regular physical activity, stress management techniques, and sufficient sleep are all vital components of an anti-inflammatory lifestyle. Adequate hydration is also essential for overall bodily functions and reducing inflammation.
Potential Benefits and Considerations
Implementing an anti-inflammatory diet can offer numerous benefits, including improved cardiovascular health, reduced joint pain, and enhanced overall well-being. However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have any underlying health conditions. Individual needs and sensitivities should be taken into account.
This diet can be a powerful tool for managing inflammation, but it's not a cure-all. It's important to approach it as part of a broader health strategy that incorporates other lifestyle factors.
The Connection Between Diet and Migraine Frequency
The Role of Inflammation in Migraines
Inflammation plays a crucial role in the development and progression of migraines. While the exact mechanisms are still being researched, evidence suggests that chronic or recurring inflammation in the body can trigger or exacerbate migraine attacks. This inflammation can manifest in various ways, from localized inflammation in the brain to systemic inflammation throughout the body. Understanding the connection between inflammation and migraines is key to developing effective preventative strategies.
Dietary choices significantly impact the body's inflammatory response. Certain foods, particularly those high in processed sugars, saturated fats, and inflammatory compounds, can contribute to a pro-inflammatory environment. This, in turn, might increase the likelihood and intensity of migraine attacks. Conversely, an anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce inflammation, potentially lessening the frequency and severity of migraines.
Dietary Triggers for Migraines
Certain foods and beverages are known triggers for migraine attacks in many individuals. These include aged cheeses, processed meats, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, and foods containing nitrates and sulfites. The specific triggers can vary significantly from person to person, highlighting the importance of keeping a food diary to identify personal sensitivities.
Understanding your individual triggers is critical for managing migraine frequency. Pay close attention to how different foods and beverages affect you, and note any patterns or relationships between specific meals or drinks and subsequent migraine attacks.
The Power of Anti-inflammatory Foods
An anti-inflammatory diet emphasizes foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins. These nutrients have potent anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce the body's overall inflammatory response. Examples of these beneficial foods include fatty fish like salmon and tuna, leafy green vegetables, berries, and nuts.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can contribute to a healthier inflammatory balance, potentially reducing migraine triggers and lessening the frequency of attacks.
Hydration and Migraine Prevention
Proper hydration is essential for overall health and plays a significant role in migraine prevention. Dehydration can exacerbate existing inflammation and potentially trigger a migraine attack. Maintaining adequate water intake throughout the day is crucial for supporting bodily functions and reducing the risk of migraine occurrences.
The Importance of Regular Meals
Skipping meals or experiencing significant fluctuations in blood sugar levels can also trigger or worsen migraine attacks. Eating regular meals and maintaining stable blood sugar levels can help prevent these fluctuations, contributing to a more stable and less reactive inflammatory environment. A balanced diet with regular meals can help regulate blood sugar and reduce the likelihood of migraine occurrences.
Stress Management and Dietary Choices
Stress is a significant migraine trigger for many individuals. Stress can increase inflammation throughout the body, potentially leading to migraine attacks. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques into your daily routine, in conjunction with an anti-inflammatory diet, can provide a holistic approach to migraine management. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature can complement dietary changes to reduce stress and potentially lessen migraine frequency.
The Long-Term Impact of Dietary Choices
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet for migraine management is not a quick fix; it's a long-term commitment. By consistently making healthy dietary choices, you are not only reducing the frequency of migraine attacks but also improving your overall health and well-being. This approach can lead to significant long-term benefits, impacting not only migraine frequency but also general health and reducing inflammation throughout the body.
Lifestyle Considerations for Migraine Management
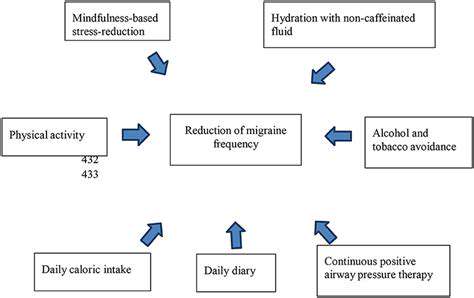
Dietary Changes
Maintaining a consistent and healthy diet is crucial for managing migraines. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients, promoting overall well-being and potentially reducing migraine frequency. It's also important to be mindful of trigger foods. Many individuals find that certain foods, such as aged cheeses, processed meats, chocolate, and caffeine-rich drinks, can exacerbate migraine symptoms. Careful monitoring of your dietary intake can help you identify potential triggers and make necessary adjustments.
Consider keeping a food diary to track your meals and any subsequent migraine episodes. This can help you identify patterns and pinpoint potential dietary triggers. Hydration is also a key element; staying adequately hydrated can help prevent migraines and alleviate symptoms. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is essential for overall health and can significantly impact migraine prevention.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress is a significant migraine trigger for many individuals. Chronic stress can wreak havoc on the body, leading to a cascade of physiological responses that can manifest as migraines. Effective stress management techniques can significantly reduce migraine frequency and severity. Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation can help manage stress levels and promote overall well-being.
Incorporating mindfulness practices into your daily routine can also be beneficial. Mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment without judgment. This can help reduce anxiety and stress, thus potentially decreasing the likelihood of migraines. Seeking support from a therapist or counselor can also be a valuable resource for developing coping mechanisms for stress and managing overall well-being.
Sleep Hygiene and Regularity
Adequate sleep is vital for overall health and well-being, and it plays a crucial role in managing migraine symptoms. A consistent sleep schedule helps regulate the body's natural rhythms, potentially reducing the risk of migraines. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to allow your body to rest and repair. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine can signal to your body that it's time to wind down, promoting better sleep quality. This might involve taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music.
Regular sleep patterns are just as important as the duration. Consistent sleep times and wake-up times, even on weekends, contribute to a healthy sleep-wake cycle. Making your bedroom conducive to sleep, such as ensuring it's dark, quiet, and cool, can also significantly improve the quality of your sleep and potentially reduce migraine episodes.