The Future of Migraine Medication: What's on the Horizon?
Novel Therapeutic Targets for Migraine Relief

Targeting Inflammatory Pathways
Mounting evidence suggests inflammation significantly contributes to migraine development, with emerging therapies focusing on disrupting key inflammatory mediators. Selective inhibition of cytokines like TNF-alpha and interleukin-1beta shows particular promise for decreasing both attack severity and recurrence rates. Exciting new studies examining neuroglial cells' involvement in central nervous system inflammation may uncover additional treatment options by modifying these cells' activation patterns.
Current investigations prioritize mapping inflammatory cascades within the trigeminal system during migraine episodes. Identifying precise molecular sequences could enable creation of highly targeted drugs that interrupt pathological processes while sparing normal physiological functions, thereby reducing adverse effects.
Modulating Neuronal Hyperexcitability
Excessive neuronal firing represents a fundamental mechanism in migraine pathophysiology. This aberrant electrical activity initiates the complex sequence of events producing characteristic migraine symptoms. Novel pharmacological approaches aim to normalize neuronal function through precise modulation of specific ion channels and neurotransmitter systems. Potential strategies include potentiating inhibitory neurotransmission or selectively regulating channel kinetics.
Particular attention focuses on voltage-gated sodium channels, as their modulation may stabilize neuronal membranes and contain abnormal electrical discharges. Such targeted intervention could potentially shorten attack duration and lessen symptom intensity.
Trigeminal System Interventions
As the primary pain pathway in migraine, the trigeminal system offers multiple therapeutic opportunities. Deciphering the molecular mechanisms underlying trigeminal activation and sensitization remains critical for developing effective migraine-specific treatments. Current research explores both peripheral sensory neurons and their central connections with pain-processing brain regions.
Innovative approaches targeting trigeminal neuropeptide release or receptor modulation show particular promise. Such focused therapies could achieve significant pain relief while minimizing systemic effects by specifically addressing migraine-related pathways.
CGRP Pathway Exploration
The neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) continues to demonstrate central involvement in migraine mechanisms. While existing CGRP-targeted therapies show efficacy, ongoing research seeks to refine their specificity by characterizing receptor subtypes and downstream signaling pathways. Understanding CGRP's complex interactions with other neurotransmitter systems may yield even more precise therapeutic options with improved safety profiles.
Neurovascular Interactions
Migraine pathophysiology involves complex neurovascular coupling disturbances that contribute to characteristic symptoms. Investigating mediators like nitric oxide that regulate these interactions may reveal novel treatment targets. Restoring normal neurovascular function represents a promising therapeutic approach that could address multiple aspects of migraine pathology simultaneously. Current studies focus on identifying key regulatory points where targeted intervention might achieve optimal symptom control.
Gene Editing and Personalized Medicine in Migraine Management

Precision Gene Modification Technologies
CRISPR-Cas9 and related gene editing platforms have transformed biomedical research by enabling unprecedented DNA sequence precision. These tools surpass previous genetic modification methods in accuracy and versatility, offering potential treatments for numerous genetic disorders. Their capacity for individualized genetic corrections opens new frontiers in personalized therapeutic development.
These technologies facilitate groundbreaking investigations into genetic contributions to disease mechanisms. Researchers can now examine specific gene functions with remarkable precision, potentially enabling root-cause interventions for various conditions. This revolutionary approach may eventually allow permanent correction of genetic predispositions to migraine and other neurological disorders.
Tailored Treatment Paradigms
Personalized medicine represents a transformative shift toward customized healthcare based on individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Incorporating genomic data into clinical decision-making enables optimization of therapeutic efficacy while minimizing adverse reactions. This approach proves particularly valuable for conditions with heterogeneous presentations like migraine.
The convergence of gene editing with personalized medicine creates extraordinary opportunities for developing ultra-precise migraine therapies. By matching genetic profiles with targeted interventions, clinicians could achieve unprecedented treatment specificity for neurological conditions, potentially including migraine subtypes with distinct genetic components.
Ethical Dimensions and Future Prospects
These technological advances necessitate careful ethical consideration regarding safety, equitable access, and appropriate applications. Establishing robust ethical guidelines and regulatory oversight remains essential for responsible development of these powerful tools. Thoughtful governance can help maximize benefits while minimizing potential misuse.
Realizing the full potential of these technologies will require continued research, transparent public dialogue, and careful policy development. Addressing these challenges thoughtfully will help ensure these revolutionary approaches benefit all patients while respecting important ethical boundaries.
The Rise of Preventive Medications for Migraine Prophylaxis
Proactive Health Management
Preventive pharmacotherapy has emerged as a cornerstone of contemporary migraine management, emphasizing early intervention over reactive treatment. This paradigm shift recognizes the substantial benefits of reducing attack frequency before chronic patterns develop. Timely prophylactic intervention can significantly improve long-term outcomes and quality of life for migraine sufferers. Comprehensive prevention strategies incorporate both pharmacological and non-pharmacological elements.
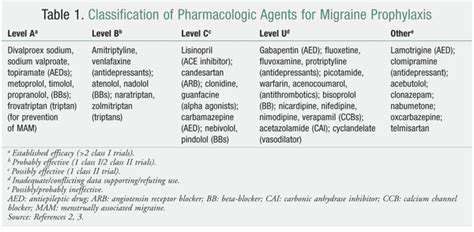
Innovative Pharmaceutical Development
Modern drug development has produced increasingly targeted preventive options addressing specific migraine mechanisms. These advances represent a quantum leap in migraine management, enabling more precise and effective prevention strategies. Ongoing research continues to identify novel molecular targets that may yield even more effective prophylactic options.
Integrated Lifestyle Approaches
Optimal migraine prevention combines medication with lifestyle modifications including dietary adjustments, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques. This multimodal approach often enhances treatment efficacy while minimizing required medication doses. For example, combining preventive drugs with consistent sleep patterns and relaxation practices frequently produces superior outcomes.
Personalized Prevention Strategies
Emerging personalized medicine approaches enable tailoring of preventive regimens based on individual genetic profiles, comorbidities, and treatment responses. This precision medicine paradigm promises to revolutionize migraine prevention by matching specific therapies to patients most likely to benefit. Genetic testing may eventually guide selection of optimal preventive medications.
Accessibility and Implementation
Widespread adoption of effective preventive strategies could substantially reduce the economic burden of migraine through decreased healthcare utilization and improved productivity. Ensuring equitable access to these advances remains a critical challenge for healthcare systems worldwide. Addressing cost and coverage barriers will be essential for maximizing population-level benefits.
The Role of Lifestyle Interventions and Complementary Therapies
Dietary and Activity Modifications
Lifestyle adjustments form a critical component of comprehensive migraine management, with dietary changes showing particular promise. Elimination of common triggers like aged cheeses, processed meats, and caffeine frequently reduces attack frequency. Regular aerobic exercise promotes endogenous pain modulation through endorphin release while improving overall health. Consistent sleep-wake cycles help stabilize neurological function and reduce migraine susceptibility.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Since stress represents a major migraine trigger, effective stress management proves essential for prevention. Mindfulness practices, yoga, and progressive relaxation techniques can significantly reduce stress-related migraine exacerbations. Regular practice enhances resilience to stress and may decrease central sensitization associated with chronic migraine.
Manual Therapies
Therapeutic massage demonstrates efficacy for reducing migraine-related muscular tension and improving circulation. Skilled practitioners can target specific muscle groups contributing to headache patterns, potentially decreasing both attack frequency and intensity. Some patients experience particular benefit from combined approaches incorporating massage with other modalities.
Traditional and Alternative Approaches
Acupuncture continues to show promise in migraine prevention, with some studies demonstrating reduced attack frequency. Certain herbal preparations like feverfew may offer adjunctive benefits, though professional guidance remains essential due to potential interactions. These approaches often work best when integrated into comprehensive management plans.
Nutritional Supplementation
Selected supplements including magnesium, riboflavin, and coenzyme Q10 have demonstrated prophylactic potential in clinical studies. While evidence varies, these natural compounds may provide additional support when used under medical supervision. Individual response patterns necessitate personalized approaches to supplementation.
Comprehensive Care Models
Optimal migraine management typically combines multiple evidence-based strategies tailored to individual needs and preferences. This integrative approach addresses the multifactorial nature of migraine while empowering patients through active participation in their care. Consistent implementation and patience are essential for achieving lasting benefits from lifestyle and complementary interventions.