The Impact of Sudden Diaphragm Contraction on Breathing and Health
What Causes Sudden Diaphragm Contraction?
Understanding the Diaphragm's Role in Breathing
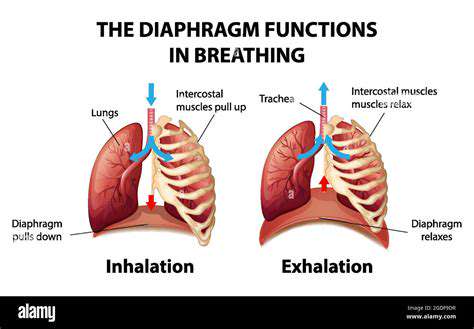
The diaphragm is a thin muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. It plays a critical role in the respiratory process by contracting and relaxing to allow air to flow in and out of the lungs.
When the diaphragm contracts, it creates a vacuum effect that helps draw air into the lungs. This contraction is essential for efficient breathing and maintaining adequate oxygen levels in the body.
Triggers for Sudden Diaphragm Contraction
Sudden diaphragm contraction can be triggered by various factors, including stress, anxiety, and physical exertion. These triggers can lead to involuntary spasms in the diaphragm, disrupting normal breathing patterns.
In some cases, a sudden contraction may occur due to respiratory illnesses or conditions affecting the lungs. Identifying these triggers is crucial for managing breathing difficulties effectively.
Effects on Health and Well-being
Experiencing sudden diaphragm contractions can lead to shortness of breath and feelings of tightness in the chest. This can contribute to a cycle of anxiety that exacerbates the situation, leading to further contractions.
Over time, frequent occurrences may impact overall health, especially for individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions. Addressing the underlying causes is vital to prevent long-term health issues.
Management and Treatment Strategies
Management of sudden diaphragm contractions often involves relaxation techniques and breathing exercises. Practices like yoga and deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress and promote better control over the diaphragm.
In cases where contractions are frequent or severe, consulting a healthcare provider is recommended. They may suggest therapies or medications tailored to alleviate symptoms and improve respiratory function.
The Physiological Effects of Diaphragm Contraction
The Mechanism of Diaphragm Contraction
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located at the base of the thoracic cavity, playing a crucial role in the breathing process. When the diaphragm contracts, it flattens and moves downward, creating negative pressure in the thoracic cavity. This action allows air to flow into the lungs, facilitating oxygen intake and carbon dioxide expulsion.
Contraction of the diaphragm is primarily initiated by the phrenic nerve, which signals the muscle to contract and relax. The timing of this contraction is vital; if it occurs suddenly or inappropriately, it can lead to hyperventilation or other respiratory issues.
Understanding the mechanics of diaphragm contraction can provide insights into various respiratory conditions and inform treatment strategies for optimal lung function.
The Role in Respiratory Diseases
Sudden contraction of the diaphragm can exacerbate respiratory diseases such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In patients with these conditions, irregular diaphragm movement can lead to difficulties in breathing and reduced oxygenation.
For individuals with asthma, sudden diaphragm contractions can trigger bronchospasms, making breathing more laborious and painful. This response underscores the importance of maintaining controlled breathing patterns, especially during asthma attacks.
For COPD patients, efficient diaphragm function is paramount, as compromised diaphragm integrity further complicates the overall respiratory process, leading to increased fatigue and discomfort.
Neurological Considerations
The diaphragm is not only a muscular structure but also has significant neurological connections that influence its function. The brainstem regulates breathing patterns, and any disruption to this control can result in abnormal diaphragm contractions.
Conditions like stroke or traumatic brain injury may affect the brain’s ability to send proper signals to the diaphragm. This can result in irregular breathing rhythms, which may further impact overall health and well-being.
Recognizing the neurological aspects of diaphragm control can assist healthcare providers in developing targeted therapies for patients with compromised respiratory function.
The Emotional and Psychological Factors
The diaphragm's function is also influenced by emotional states, such as anxiety or stress. During stressful situations, rapid or controlled diaphragm contractions can become challenging, leading to feelings of breathlessness.
People often experience “shortness of breath” during panic attacks, which is linked to sudden diaphragm contractions and the body’s fight-or-flight response. Addressing emotional health is crucial in managing breathing issues linked to diaphragm function.
Practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and breathing exercises can help regulate diaphragm movement and enhance overall respiratory health.
Therapeutic Techniques and Management
Various therapeutic techniques can be employed to enhance diaphragm function and improve respiratory health. Diaphragmatic breathing exercises, for instance, focus on strengthening diaphragm contractions while promoting relaxation.
Physical therapy also plays a significant role, as targeted exercises can enhance respiratory muscle performance and endurance. Individuals with respiratory issues are often encouraged to engage in regular exercise to maintain diaphragm strength and lung capacity.
Moreover, understanding how to manage diaphragm contractions through lifestyle modifications can lead to better health outcomes and reduced incidents of acute respiratory distress.
Managing Sudden Diaphragm Contraction
Understanding Sudden Diaphragm Contraction
Sudden diaphragm contraction, often experienced as a spasm or hiccup, can significantly disrupt regular breathing patterns. The diaphragm is a muscular structure that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity and plays a critical role in respiration. When it contracts suddenly, it can cause an involuntary intake of breath, leading to the characteristic sound of hiccups.
This involuntary contraction typically occurs during a variety of situations, such as eating too quickly, consuming carbonated beverages, or experiencing sudden changes in temperature. The spasm can provoke discomfort and even pain in some individuals, particularly if it persists for an extended period.
Understanding the mechanisms behind sudden diaphragm contraction requires an exploration of the neurological pathways involved. The phrenic nerve, which innervates the diaphragm, can be stimulated by various factors that trigger the contraction. Stress, excitement, or even certain medications can similarly influence diaphragm behaviour.
While most cases of sudden diaphragm contraction are harmless, frequent occurrences may signify an underlying health issue. Conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or respiratory diseases can contribute to the frequency and severity of these contractions. Therefore, further investigation may be warranted if symptoms persist.
To minimize the occurrence of sudden diaphragm contractions, individuals are encouraged to maintain a slow eating pace, stay hydrated, and monitor their intake of carbonated beverages. Mindful breathing techniques can also help alleviate the discomfort associated with these spasms.
Strategies for Managing Diaphragm Contractions
Managing sudden diaphragm contraction can often be achieved through lifestyle modifications and home remedies. One effective method is to drink water slowly. This helps stabilize the diaphragm and can often dispel hiccups by providing a controlled intake of fluid.
Another helpful strategy involves holding one’s breath for a short period. By taking a deep breath and holding it, you increase the carbon dioxide levels in the blood, which can prompt the diaphragm to relax. This technique is a common remedy for hiccups and aims to restore normal breathing patterns.
Utilizing grounding techniques such as distraction can also be beneficial. Engaging in conversation or focusing your mind on a different task can sometimes interrupt the cycle of diaphragm spasms. Creating mental distractions alleviates the stress response that might be triggering the contractions.
For those who experience frequent occurrences of diaphragm contraction, keeping a food diary can assist in identifying specific triggers, such as certain foods or eating habits. Adjusting your dietary choices accordingly may help mitigate these contractions.
In cases where discomfort is persistent or particularly bothersome, seeking advice from a healthcare professional is critical. They can recommend specific therapies or medications that may assist in managing the condition more effectively.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of sudden diaphragm contraction resolve with simple home remedies, there are circumstances when professional medical attention is necessary. If hiccups or diaphragm spasms persist for more than 48 hours, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for evaluation.
Additionally, should spikes in diaphragm contractions be accompanied by other symptoms such as chest pain, difficulty breathing, or severe abdominal pain, immediate medical attention is warranted. These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying health condition that requires prompt evaluation.
In some instances, recurrent diaphragm contractions could stem from neurological disorders. Conditions affecting the central nervous system can manifest through abnormal nerve responses, resulting in involuntary diaphragm spasms. Neurospecialists may need to conduct further investigations to rule out these concerns.
Sending a patient to a specialist might also include a comprehensive study of their respiratory health. Pulmonary diseases or structural abnormalities within the diaphragm itself may require targeted treatment strategies that go beyond basic lifestyle modifications.
Ultimately, being proactive about one’s health and recognizing abnormal patterns in diaphragm function can lead to better management of symptoms, resulting in improved overall well-being. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals can facilitate this process and ensure appropriate care is available as needed.