The Long Term Effects of Stress on Mental and Physical Health
Introduction to Stress

1. Understanding Stress: Definition and Types
Stress can be defined as a physiological and psychological response to external pressures, often referred to as stressors. These stressors can be both positive and negative, ranging from life changes like marriage to chronic situations like unemployment. Understanding the types of stress—acute, episodic acute, and chronic—is essential for recognizing how it affects individuals.
Acute stress is short-term and can arise from specific incidents, while episodic acute stress is frequent stress experienced due to various life situations. Chronic stress, on the other hand, can last for extended periods and can be detrimental to both mental and physical health.
Identifying stressors is crucial for effective management, and it often requires self-reflection and awareness of one's surroundings and experiences. Recognizing what causes stress can encourage individuals to adopt healthier coping mechanisms.
A thorough understanding of stress and its effects sets the foundation for exploring its long-term repercussions on mental and physical health.
2. The Biological Impact of Stress
The body reacts to stress through the release of hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, triggering the "fight or flight" response. Prolonged exposure to high levels of these hormones can lead to significant health issues, including heart disease and obesity.
This biological response triggers various changes in bodily functions, increasing heart rate and blood pressure. Over time, these changes can become habitual, contributing to chronic health conditions that may not be immediately apparent.
Furthermore, stress affects the immune system, making the body more susceptible to illnesses. Continuous stress can result in systemic inflammation, which has been linked to a plethora of diseases.
Recognizing the biological underpinnings of stress can help individuals understand why managing stress is vital for maintaining overall health.
3. Psychological Effects of Long-Term Stress
Long-term stress can significantly impact mental health, contributing to conditions such as anxiety, depression, and burnout. Chronic stress diminishes the capacity of the brain to manage emotions and can lead to cognitive decline.
Individuals may find themselves in a cycle of negative thinking, which can exacerbate feelings of hopelessness and despair. The link between stress and mental health issues underlines the importance of addressing stressors head-on.
Moreover, long-term stress can decrease motivation and self-esteem, making it challenging to engage in everyday activities or pursue personal goals. This psychological toll can create a self-fulfilling prophecy, as stress feeds into further negative experiences.
4. The Connection Between Stress and Lifestyle Choices
Stress often influences lifestyle choices, creating a vicious cycle that can further deteriorate health. People under significant stress may turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as overeating, smoking, or substance abuse as a means of relief.
Additionally, stress can hinder one’s willingness to engage in physical activity or healthy eating, which are essential for maintaining good health. This shift in behavior can result in weight gain and increased health risks over time.
Social support systems may also be adversely affected, as stressed individuals often withdraw from social interactions. This isolation can lead to a greater sense of stress, ultimately affecting both mental and physical health.
By understanding this connection, individuals can work to create healthier habits that counteract the negative effects of stress instead of succumbing to them.
5. Strategies for Managing Long-Term Stress
Effective stress management techniques are vital for mitigating the long-term effects of stress on health. Stress-reduction strategies may include mindfulness practices, regular exercise, and healthy eating, all of which contribute positively to health.
Therapeutic options such as cognitive-behavioral therapy can help individuals reframe their thoughts and develop coping strategies. These therapies promote resilience in the face of stressors and foster a healthier outlook on life.
Additionally, establishing a robust support network of friends, family, or support groups can provide comfort and reduce feelings of isolation. Connecting with others can help in sharing experiences and learning new coping strategies.
Incorporating relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation can also create a profound impact on stress levels, improving both mental and physical health over time.
The Physiology of Stress
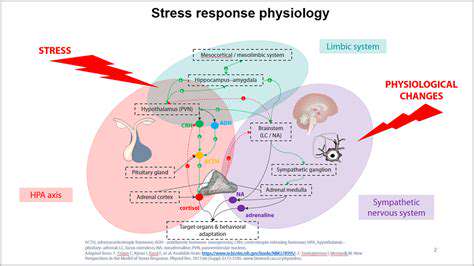
The Body's Response to Stress
When faced with stress, the body activates its fight or flight response, a survival mechanism that prepares individuals to deal with perceived threats. This response triggers the release of hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol, which accelerate heart rate and increase blood flow. These physiological changes are intended to provide a burst of energy and focus.
However, when stress is chronic, the continued production of these hormones can lead to numerous health problems. For instance, elevated cortisol levels may interfere with metabolic processes, impacting weight gain and overall energy levels. This long-term hormonal imbalance can severely affect both mental and physical health.
Moreover, stress can lead to a weakened immune system, making the body more susceptible to illnesses. Frequent colds and infections can become common occurrences for those under prolonged stress. The body's inability to fight off pathogens can result in frequent medical visits and increased healthcare costs.
On a psychological level, the body's response to stress can lead to anxiety and depression. As stress levels skyrocket, individuals may find it challenging to manage their emotions, leading to feelings of overwhelm and hopelessness. This emotional turmoil is often compounded by the physical symptoms associated with stress.
Ultimately, understanding the body's response to stress is critical for managing it effectively. Recognizing these physiological changes can empower individuals to seek assistance or employ coping strategies that mitigate the effects of stress on their health.
Chronic Stress and Its Implications
Chronic stress can have profound implications on mental health, often leading to psychological disorders. Individuals experiencing long-term stress are at a heightened risk for anxiety disorders, depression, and even post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These conditions can severely impact daily functioning and quality of life.
Physically, chronic stress is linked to lifestyle diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and gastrointestinal disorders. The ongoing strain can lead to chronic conditions that require long-term management and can significantly alter an individual's health trajectory. Additionally, chronic stress can contribute to unhealthy coping mechanisms, including substance abuse and overeating.
Social implications are also noteworthy; individuals under constant stress may find it challenging to maintain relationships. The combination of irritability, withdrawal, and mood swings can lead to conflicts and isolation from friends and family. This social isolation can further exacerbate feelings of loneliness and anxiety.
Furthermore, the workplace can become a breeding ground for chronic stress. High-pressure environments with unrealistic deadlines can perpetuate a cycle of stress that impacts productivity and job satisfaction. Employees may experience burnout, leading to increased absenteeism and turnover rates.
Recognizing the symptoms and long-term effects of chronic stress is essential for proactive management. Seeking help through counseling, stress management programs, or lifestyle changes can significantly improve one’s overall well-being and reduce the chances of serious health complications.
Impact on Mental Health
Connection Between Chronic Stress and Anxiety Disorders
Chronic stress has been identified as a significant risk factor for the development of anxiety disorders. When individuals experience prolonged stress, their bodies constantly produce stress hormones such as cortisol, which can alter brain function over time. This alteration can lead to heightened levels of anxiety and the development of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and panic disorder.
Moreover, individuals dealing with chronic stress often struggle with feelings of helplessness and uncertainty, which can exacerbate anxiety symptoms. The continuous cycle of stress and anxiety can also lead to avoidance behaviors, where individuals may withdraw from social situations or activities they once enjoyed, further compounding their mental health issues.
It is important to address chronic stress early on through coping strategies such as therapy, mindfulness, and stress management techniques. By doing so, individuals may be able to break the cycle of stress and anxiety, promoting better mental well-being.
In summary, the link between chronic stress and anxiety disorders highlights the need for proactive mental health care, especially for individuals experiencing long-term stress. Early intervention can help prevent the escalation of symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
Impact on Cognitive Function
Chronic stress has a profound impact on cognitive functioning, with research indicating that prolonged exposure to stress hormones can impair memory and learning abilities. One of the key areas affected is the hippocampus, a brain region crucial for memory formation and spatial navigation. Increased cortisol levels can lead to hippocampal atrophy, which may result in difficulties in forming new memories or recalling past experiences.
Additionally, chronic stress can impact attention and concentration, making it challenging for individuals to focus on tasks or engage in problem-solving activities. This decline in cognitive function can have far-reaching effects on daily life, from poorer academic performance to decreased productivity in the workplace.
Furthermore, the detrimental effects of stress on cognitive health can also lead to a cycle of increased stress, where difficulties in cognition cause frustration and anxiety. This, in turn, can perpetuate the feeling of being overwhelmed, creating a feedback loop that is difficult to break.
To combat the adverse effects of stress on cognition, implementing strategies such as regular exercise, mindfulness practices, and adequate sleep can be beneficial. These practices not only help manage stress but also support brain health, cognitive function, and overall mental well-being.
Stress and Lifestyle Choices
Impact of Stress on Eating Habits
Stress can significantly alter an individual's eating patterns, leading to either overeating or undereating. When faced with high levels of stress, many people turn to comfort food—often high in sugar and fat—as a way to cope with their emotions. This form of emotional eating can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of obesity-related health issues.
Conversely, some individuals may find that stress suppresses their appetite, causing them to skip meals or reduce their food intake. This can result in nutritional deficiencies and a range of other health problems over time, such as fatigue or weakened immune function.
The Relationship Between Stress and Exercise
Stress can either motivate individuals to engage in physical activity as a means of alleviation or discourage them from exercising altogether. For some, a stressful day might lead to a vigorous workout as a form of stress relief, which can boost mood and improve overall health.
On the other hand, persistent stress can lead to a cycle of inactivity, where individuals feel too overwhelmed to prioritize exercise. This lack of physical activity can contribute to long-term health issues, including cardiovascular disease and deterioration of mental health, further exacerbating the stress cycle.
Stress Management Techniques for Better Health
Implementing effective stress management techniques is essential for maintaining both mental and physical health. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and regular physical activity can help reduce stress levels. These methods promote relaxation, improve mood, and enhance overall well-being.
Additionally, cultivating strong social connections and engaging in hobbies can serve as effective buffers against stress. By developing a support network and finding joy in leisure activities, individuals can better manage stress, leading to improved health outcomes in the long run.
Coping Strategies for Stress Management

Understanding the Importance of Stress Management
Stress management is a crucial aspect of maintaining both mental and physical health. Effective coping strategies can significantly reduce the adverse effects of stress. Learning how to manage stress can lead to improved emotional well-being and a greater sense of control over one's life. In today’s fast-paced world, individuals encounter a variety of stressors, from work to personal relationships. Recognizing the need for proactive stress management is essential for long-term health.
When stress becomes chronic, it can lead to various health issues, including anxiety disorders, depression, and physical ailments such as heart disease. Therefore, engaging in stress management practices is not just beneficial but necessary. Developing a personalized coping plan can empower individuals to address stress before it becomes overwhelming. Incorporating stress management techniques into daily routines helps build resilience against future stressors.
Moreover, understanding one’s unique stress triggers is a foundational step in developing effective coping mechanisms. This awareness allows individuals to tailor their strategies and find what works best for them. Regular mindfulness practices, physical exercise, and social support are all proven methods to help mitigate stress. Taking the time to implement these strategies can lead to a happier and healthier lifestyle.
Practical Strategies for Managing Stress
There are numerous practical strategies that individuals can adopt for effective stress management. One of the most popular methods is engaging in physical activity, which has been shown to release endorphins and improve mood. Regular exercise not only helps alleviate stress but also boosts overall physical health. Finding an enjoyable form of exercise, such as dancing, biking, or yoga, can make this process more appealing.
Mindfulness and meditation have become increasingly popular in recent years as effective stress relief methods. These practices encourage individuals to focus on the present moment, which can help diminish feelings of anxiety about the future. Simple mindfulness exercises can be practiced anywhere and only require a few minutes of focused breathing. Regular incorporation of these techniques can train the mind to respond better to stressors.
In addition to physical and mental techniques, building a strong support system is vital for effective stress management. Connecting with friends and family can provide emotional support and shared experiences that alleviate stress. Seeking professional help through therapy or counseling can offer additional strategies tailored to individual needs. Cultivating relationships with those who understand and share similar experiences is essential for reducing feelings of isolation.