Why Headache Symptoms May Worsen Over Time
Common Types of Headaches and Their Progression
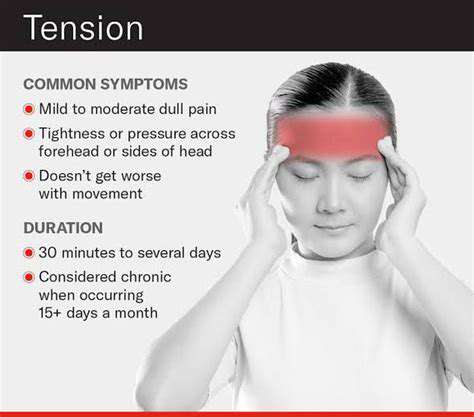
1. Tension Headaches
Tension headaches are among the most common types of headaches. They often begin as a dull ache around the forehead, temples, or back of the neck.
As the headache progresses, the pain may become more intense and widespread, leading to greater discomfort. Stress, poor posture, and inadequate hydration are common triggers that can exacerbate these symptoms over time.
Without proper management, tension headaches can become chronic, meaning individuals may experience them on a more regular basis, increasing their frequency and severity.
2. Migraines
Migraine headaches are characterized by intense, throbbing pain, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Initial episodes may be infrequent, but without intervention, they tend to increase in severity and frequency.
Hormonal changes, dietary factors, and stress can contribute to the worsening of migraine symptoms. As headaches recur, the brain's response to these triggers can intensify, leading to more debilitating episodes over time.
Many migraine sufferers report that their pain becomes increasingly harder to manage as they age, suggesting that successful treatment and preventive measures may be necessary to avoid chronic migraines.
3. Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches are one of the most severe types of headache, typically occurring in cyclical patterns or "clusters." These headaches strike suddenly and can cause excruciating pain around one eye or on one side of the head.
During a cluster period, individuals may experience recurrent headaches multiple times a day. As these episodes persist, they can lead to increased anxiety and distress, making the overall experience far more traumatic.
While the reasons for the worsening of cluster headaches may not be fully understood, changes in lifestyle or sudden stress can trigger more intense and frequent cycles.
4. Sinus Headaches
Sinus headaches occur when inflammation of the sinuses leads to pressure and pain, typically felt in the forehead, cheeks, and around the eyes. They often start mild but can escalate in severity if the underlying sinus issue is not treated.
As sinus conditions worsen—often due to allergies or infections—the headaches can become more persistent and debilitating, causing further discomfort that may interfere with daily activities.
Effective management of sinus health is crucial, as untreated sinus headaches can evolve and lead to chronic headaches, complicating the overall health condition.
5. Rebound Headaches
Rebound headaches, also known as medication-overuse headaches, occur when pain relief medications are taken too frequently. Initially, these headaches may respond well to treatment, but over time, they can become more intense and harder to alleviate.
The cycle of pain and relief can lead patients to increase their medication use, creating a vicious cycle that compounds the problem. This can result in a higher frequency of headaches, often leading to frustration and decreased quality of life.
Recognizing and breaking the cycle of rebound headaches is essential, as ongoing overuse of medication can worsen headache symptoms and overall health in the long run.
Factors Contributing to Worsening Headache Symptoms
Physical Health and Lifestyle Choices
One of the key factors that influence the worsening of headache symptoms is an individual's physical health. Poor nutrition, lack of exercise, and insufficient sleep can significantly impact how often and how severely headaches occur.
Inadequate hydration and prolonged stress are also critical contributors. When the body is not well-hydrated or under constant stress, it can lead to increased tension and exacerbate headache symptoms.
Environmental Triggers and Psychological Factors
Environmental factors, such as bright lights, loud noises, or strong odors, can also aggravate headache symptoms. For many individuals, exposure to these triggers can lead to more frequent and intense headaches.
Moreover, psychological factors such as anxiety and depression can play a significant role in the progression of headache disorders. Individuals dealing with these conditions may experience heightened sensitivity to pain, leading to more severe headache symptoms over time.
Methods for Managing Worsening Headache Symptoms
Understanding the Triggers of Headaches
Headaches can be triggered by a variety of factors, including stress, diet, and environmental changes. Identifying these triggers is essential for effective management.
For many, caffeine, alcohol, and certain foods can provoke headaches. Keeping a headache diary may help individuals pinpoint specific triggers.
The Role of Stress in Headache Development
Stress is a significant contributor to the frequency and severity of headaches. When the body is under stress, it releases chemicals that may lead to tension headaches.
Learning stress management techniques, such as mindfulness or meditation, can help alleviate headache symptoms. Regular exercise and adequate sleep also play a crucial role in reducing stress levels.
Treatment Options for Chronic Headaches
There are various treatment options available for chronic headache sufferers, including over-the-counter medications and prescription drugs. Non-pharmaceutical approaches, such as physical therapy and acupuncture, can also be beneficial.
It's important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan as every individual's experience with headaches can be different.
Impact of Lifestyle Changes on Headache Symptoms
Making changes to one's lifestyle can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of headaches. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and staying hydrated are simple yet effective strategies.
Sustaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can also support headache prevention. Avoiding skipping meals and eating at regular intervals can help maintain stable blood sugar levels, which may reduce headaches.
When to Seek Professional Help
It is essential to recognize when headache symptoms require medical attention. If headaches are accompanied by severe symptoms such as vision changes, confusion, or persistent vomiting, immediate medical care is crucial.
Additionally, if headaches worsen over time or do not respond to typical treatments, consulting a healthcare professional can lead to a more accurate diagnosis and effective management strategies.