激しい片頭痛で緊急治療が必要な場合
通常の頭痛を超えて:根本原因を理解する
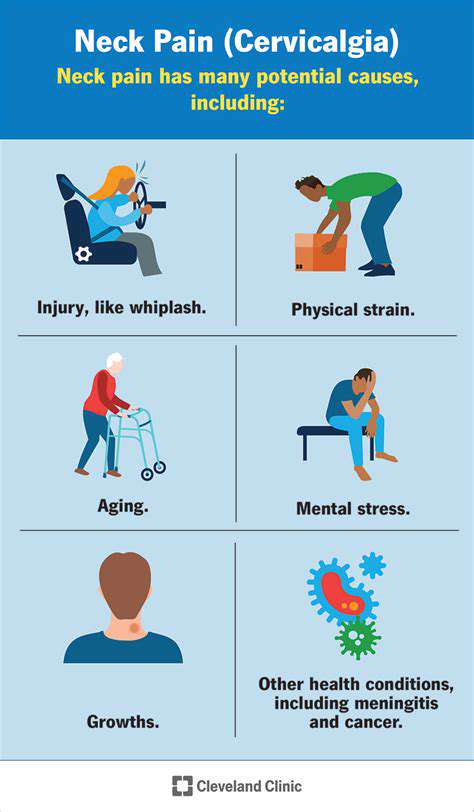
頭痛は、頻繁に軽微な不快感として片付けられることがありますが、場合によってはより深刻な健康問題を示している可能性があります。持続的なまたは非典型的な頭痛は、重大な健康問題につながる可能性があるため、決して無視すべきではありません。
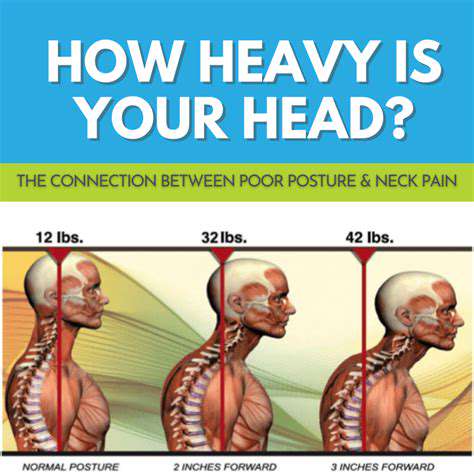
ストレスと生活習慣の役割
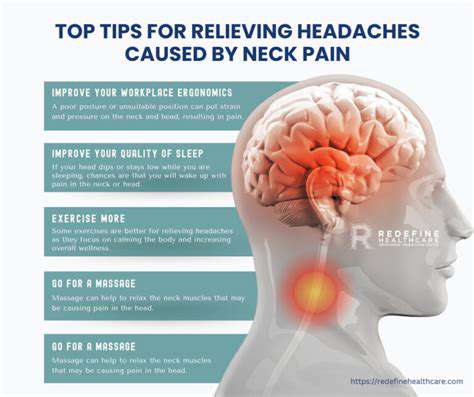
現代社会では避けられないストレスは、しばしば頭痛の発症に影響を与えます。持続的なストレスは、頭全体を締め付けるような、一定の鈍痛を特徴とする緊張型頭痛を引き起こす可能性があります。十分な睡眠、規則的な運動、バランスの取れた食事など、より健康的な習慣を取り入れることで、頭痛の発生を予防したり軽減したりすることができます。
食事と脱水の影響
栄養の選択と水分補給のレベルは、頭痛の発生と重症度に予想外の影響を与えます。カフェイン、加工食品、アルコール飲料など、特定の食品は、感受性のある人にとって頭痛を引き起こす可能性があります。新鮮な野菜や果物を含むバランスの取れた食事を維持し、
潜在的な医療上の状態とその症状
頭痛は、時により深刻な医療上の状態を示すことがあります。片頭痛、群発頭痛、さらには脳腫瘍を含む疾患は、頭痛の症状で現れる場合があります。これらの頭痛の独特のパターンと特徴を特定することは、迅速な対応にとって非常に重要です。
専門家の助けを求める:診断と治療
頭痛が日常生活の機能を妨げたり、潜在的な医療上の問題を懸念させたりする場合、専門家の相談が不可欠になります。医療従事者は包括的な評価を行い、病歴を検討し、頭痛の原因を特定します。この
神経学的指標としての視覚障害
視覚異常(ぼやけた視界から完全な失明まで)は、しばしば神経学的障害を示唆します。これらの症状は、視神経、視覚脳路、または視覚処理に影響を与える問題を示す傾向があります。
視覚症状を呈する神経学的疾患
いくつかの神経学的障害は、視覚経路の損傷を伴い、視覚障害を主要または二次的な症状として特徴づけます。例えば、脳卒中(脳血流の途絶によって特徴付けられる)は、視野欠損または皮質盲を引き起こす可能性があります。多発性硬化症は