Source Credibility
Author Expertise
HTML
Styling
CSS
Health
Alternative Medicine
Betrouwbare online bronnen vinden voor informatie over migraine
Betrouwbare bronnen voor migraineverlichting identificeren

Read more about Betrouwbare online bronnen vinden voor informatie over migraine
Begrijpen hoe hoesten hoofdpijn veroorzaakt
Meta beschrijving: Ontdek hoe hoesten leidt tot hoofdpijn, de soorten hoofdpijn die het kan veroorzaken en effectieve beheersstrategieën. Leer over de onderliggende aandoeningen en wanneer je medische hulp moet zoeken voor aanhoudende hoest en hoofdpijn.--- Overzicht
Verken de verbinding tussen hoesten en hoofdpijn, inclusief de mechanismen die betrokken zijn, de soorten hoofdpijn die worden veroorzaakt en effectieve strategieën om mee om te gaan. Deze pagina biedt inzichten in de lichamelijke belasting van hoesten en de effecten ervan op het algehele welzijn.
Belangrijke Onderwerpen
- Het mechanisme begrijpen: Leer hoe hoesten spierspanning veroorzaakt, wat leidt tot hoofdpijn.
- Soorten hoofdpijn: Ontdek spanningshoofdpijn en “hoesthoofdpijn”.
- Onderliggende aandoeningen: Identificeer luchtweginfecties, allergieën en sinusitis die de symptomen kunnen verergeren.
- Beheersstrategieën: Vind huisremedies en medische adviezen voor het verlichten van hoofdpijn veroorzaakt door hoesten.
Conclusie
Blijf geïnformeerd over hoe je de impact van hoesten op hoofdpijn kunt beheren om je kwaliteit van leven te verbeteren. Als de symptomen aanhouden, is het essentieel om een zorgprofessional te raadplegen voor een effectieve behandeling.
Oct 22, 2024
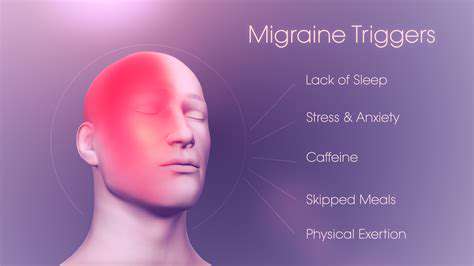
Veelvoorkomende Oorzaken en Remedies voor Tempel Pijn — Ontdek de verschillende oorzaken van tempel pijn, zoals spanningshoofdpijn, migraine en sinusdruk, evenals de rol van levensstijlkeuzes. Ontdek effectieve strategieën voor het verlichten van ongemakken, waaronder huismiddeltjes, medicijnen zonder recept en aanpassingen in de levensstijl. Leer over het belang van het herkennen van triggers voor hoofdpijn en wanneer het cruciaal is om medische hulp te zoeken voor aanhoudende of ernstige symptomen. Blijf geïnformeerd en neem de controle over uw gezondheid met onze uitgebreide gids voor het beheren van tempel pijn en het verbeteren van uw algehele welzijn.
Nov 04, 2024
Begrip van spierverrekking tijdens het hoesten: Oorzaken, symptomen en verlichtingsstrategieënMeta Beschrijving: Ontdek de oorzaken van spierverrekking door hoesten, veel voorkomende symptomen en effectieve verlichtingsstrategieën. Leer hoe je spierverrekking kunt voorkomen en beheren voor een betere ademhalingsgezondheid.---Wat veroorzaakt spierverrekking tijdens het hoesten? Hoesten is een natuurlijke reflex die bedoeld is om de luchtwegen te reinigen, maar kan leiden tot spierverrekking, vooral in de borst en de buik. Dit artikel verkent de mechanismen achter spierverrekking tijdens het hoesten, veelvoorkomende verergerende factoren en de essentiële rol van de algehele spiergezondheid. Symptomen van spierverrekking door hoesten Leer hoe je symptomen kunt herkennen zoals plaatselijke pijn, stijfheid en zwelling. Het begrijpen van deze tekenen is cruciaal voor het beheren van ongemak en het voorkomen van chronische problemen. Preventieve maatregelen en verlichtingsstrategieën Ontdek praktische tips om spierverrekking door hoesten te voorkomen, waaronder het behouden van een goede ademhalingsgezondheid, hydratatie en goede ademhalingstechnieken. Ontdek effectieve verlichtingsmethoden, zoals warmte- en koudebehandeling, zachte rekken en wanneer je medische hulp moet zoeken. Versterk je gezondheid Neem proactieve stappen in het beheren van je gezondheid door de relatie tussen hoesten en spierverrekking te begrijpen. Raadpleeg zorgprofessionals en neem deel aan oefeningen om je spieren te versterken voor een betere veerkracht. Voor meer inzichten over het voorkomen en beheren van spierverrekkingen tijdens het hoesten, bezoek onze volledige gids!
Dec 31, 2024
Ontdek de veelvoorkomende oorzaken van pijn aan de voorkant van het hoofd die optreden tijdens het hoesten. Deze uitgebreide gids verkent de anatomie van hoofdpijn en benadrukt hoe verschillende medische aandoeningen zoals sinusitis, spanningshoofdpijn en migraine zich kunnen manifesteren tijdens hoestepisodes. Het gaat in op de rol van externe irriterende stoffen en preventieve maatregelen om ongemak te verlichten, en biedt effectieve huismiddeltjes en wanneer medische hulp te zoeken. Verhoog uw begrip van uw symptomen en leer proactieve strategieën voor het beheren van pijn aan de voorkant van het hoofd die verband houdt met hoesten. Sleutelwoorden: pijn aan het voorhoofd, hoesten, sinusitis, spanningshoofdpijn, migraine, medische adviezen, preventieve maatregelen, huismiddeltjes.
Mar 09, 2025
Neuskortikosteroïden en zoutoplossing-sprays kunnen de druk in de sinussen verlichten en de afvoer bevorderen. Allergiebeheer: Antihistaminica kunnen helpen bij het beheersen van allergische reacties en het verminderen van verstopte neus. Vrij verkrijgbare verlichting: Vrij verkrijgbare pijnstillers zoals ibuprofen kunnen effectief hoofdpijn behandelen. Raadpleging van Professionals: Nauwe samenwerking met zorgverleners is cruciaal om een behandelingsstrategie op maat voor uw specifieke symptomen te ontwikkelen. Concluderend, als u hoofdpijn ervaart bij het neusblazen, is het essentieel om de mogelijke oorzaken en symptomen te begrijpen. Neem de juiste preventieve maatregelen en raadpleeg professionals voor effectieve behandeling om uw algehele welzijn te verbeteren.
Mar 29, 2025
Kop pijn bij het snuiten: Oorzaken en oplossingen
Apr 30, 2025
Mijn hoofd doet pijn als ik mijn neus ophaal: Wat je moet weten
May 01, 2025
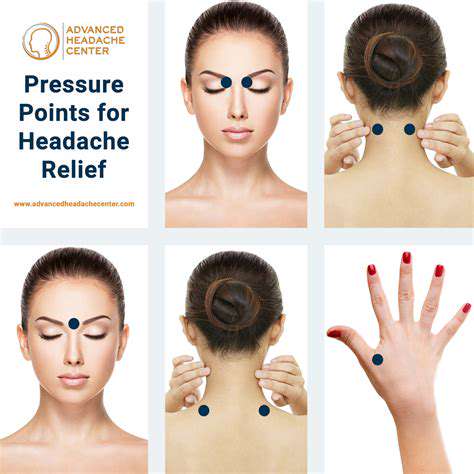
Massagetherapie voor het verlichten van spanningshoofdpijn
May 12, 2025
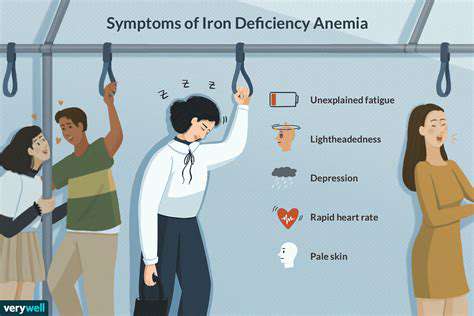
IJzertekortanemie en hoofdpijn: Wat u moet weten
May 24, 2025
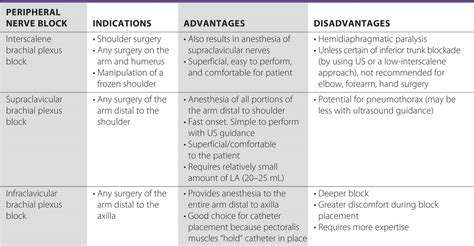
Zenuwblokkades voor hoofdpijnbehandeling: Wat u moet weten
May 24, 2025
Wat zijn vestibulaire migraine? De link tussen duizeligheid en migraine
May 30, 2025