Medication Safety
Adverse Reactions
HTML
Styling
Health
Medical Conditions
CSS
Navigeren door bijwerkingen van migrainemedicatie
Identificatie van potentiële bijwerkingen bij verschillende medicatie
Begrijpen van het spectrum van potentiële bijwerkingen
Bij het bekijken van medicatie is het essentieel om te begrijpen hoe deze medicatie verschillende mensen op verschillende manieren kan beïnvloeden. Potentiële bijwerkingen
Herkenning en Aanpak van Neurologische Bijwerkingen
Herkenning van de Tekenen van Neurologische Aandoeningen
Neurologische problemen beginnen vaak met subtiele veranderingen die mogelijk
Read more about Navigeren door bijwerkingen van migrainemedicatie
Chronische Stress en de Impact ervan op Spanning in Nek- en Schouderspieren
Oct 14, 2024
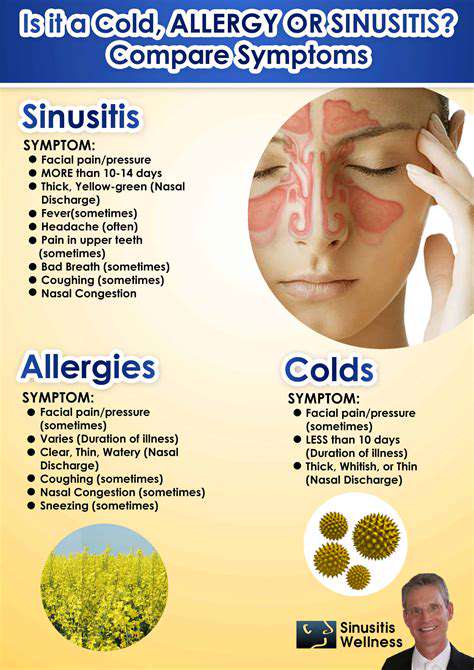
Het Begrijpen en Beheren van Symptomen van Druk in het Hoofd. Ontdek de complexiteit van symptomen van druk in het hoofd, inclusief veelvoorkomende oorzaken zoals sinusitis, spanningshoofdpijn en migraine. Deze uitgebreide gids legt de sensaties uit die verband houden met druk in het hoofd en biedt praktische huismiddeltjes voor verlichting, zoals hydratatie en ontspanningstechnieken. Leer wanneer je medische hulp moet zoeken en het belang van het herkennen van mogelijk ernstige onderliggende aandoeningen. Of je nu af en toe ongemak ervaart of chronische symptomen hebt, begrijp effectieve beheersstrategieën en het belang van het raadplegen van zorgprofessionals voor persoonlijke zorg. Verbeter je kwaliteit van leven door druk in het hoofd effectief aan te pakken met onze handige bronnen.
Nov 07, 2024
Het Belang van Vroege Opsporing in Gezondheidsmanagement: Ontdek het belang van vroege opsporing in de gezondheidszorg en leer hoe het vroeg herkennen van symptomen kan leiden tot betere gezondheidsuitkomsten, meer behandelingsopties en lagere gezondheidskosten. Deze gids schetst de veelvoorkomende signalen om in de gaten te houden, de rol van routinecontroles en het belang van professionele hulp zo nodig. Voorzie jezelf van kennis over proactief gezondheidsmanagement en neem de controle over je welzijn door vroege interventie.
Nov 19, 2024
Veelvoorkomende Oorzaken van Pijn aan de Achterkant van Je Hoofd Meta Beschrijving: Ontdek de veelvoorkomende oorzaken van pijn aan de achterkant van je hoofd, inclusief spierspanning, migraine, problemen met de cervicale wervelkolom en sinusinfecties. Leer hoe je symptomen kunt beheren en wanneer je medische hulp moet zoeken voor chronische ongemakken. Titel: Pijn aan de Achterkant van Je Hoofd Begrijpen Inhoudsoverzicht: Deze uitgebreide gids verkent de meest voorkomende oorzaken van pijn aan de achterkant van je hoofd en biedt inzichten in spierspanning, migraine, spanningshoofdpijn, problemen met de cervicale wervelkolom en sinusproblemen. Naast het identificeren van symptomen, gaat het artikel dieper in op behandelingsopties en zelfzorgstrategieën om ongemak te verlichten en het algehele welzijn te verbeteren. Belangrijke Secties: - Spierspanning en Spanning: Ontdek hoe houding en stress bijdragen aan nek- en schouderpijn. - Migraine en Spanningshoofdpijn: Leer over symptomen, triggers en effectieve beheertechnieken. - Problemen met de Cervicale Wervelkolom: Begrijp de impact van de gezondheidsstatus van de wervelkolom op hoofdpijn en nekpijn. - Sinusproblemen en Infecties: Identificeer de connectie tussen sinusongemakken en hoofdpijn en verken verlichtingsopties. - Andere Factoren: Uitdroging, omgevingsfactoren en stress spelen ook een cruciale rol bij de frequentie en ernst van hoofdpijn. - Medische Hulp Zoeken: Richtlijnen over wanneer je een zorgverlener moet raadplegen voor aanhoudende of ernstige symptomen. Oproep tot Actie: Als je last hebt van chronische pijn aan de achterkant van je hoofd of op zoek bent naar gepersonaliseerd advies over het omgaan met je symptomen, raadpleeg dan een zorgverlener voor gepersonaliseerde behandelingsplannen.
Dec 10, 2024
Stressreductietechnieken om hoofdpijn te voorkomen
May 05, 2025
Schermtijd en digitale oogvermoeidheid: een moderne trigger voor hoofdpijn?
May 06, 2025
Weersveranderingen: Voorbereiding op veranderingen in de luchtdruk
May 07, 2025
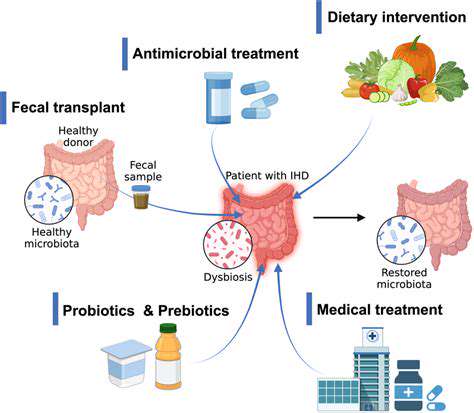
De darm-hersenenas: Hoe darmg gezondheid migraine beïnvloedt
May 08, 2025
Hormonaal hoofdpijn: Waarom het gebeurt en wat helpt
May 13, 2025
Muziektherapie voor ontspanning en pijnmanagement
May 29, 2025
Leefstijlveranderingen die de hoofdpijnbeheersing versterken
Jun 07, 2025
Wanneer u dringende zorg nodig heeft bij een ernstige migraine
Jun 27, 2025