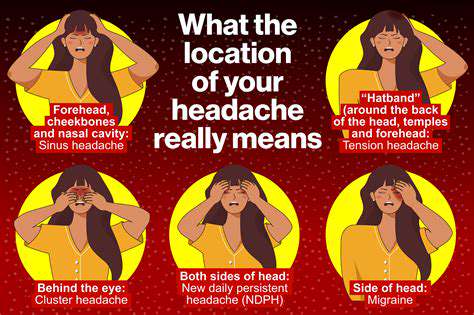
Headaches
Preventive Strategies
Sleep Hygiene
Circadian Rhythm
empty
invalid
Health
Wellbeing
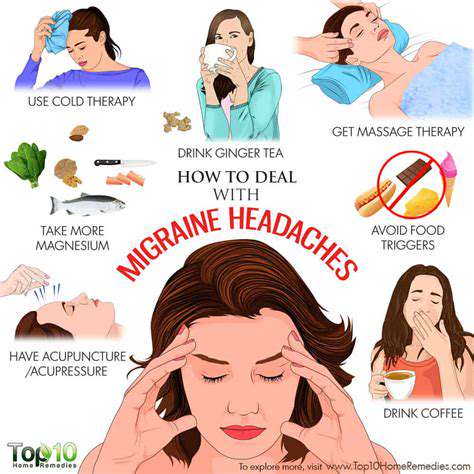
Migraines
De kracht van routine bij het voorkomen van migraine
De basis van een routine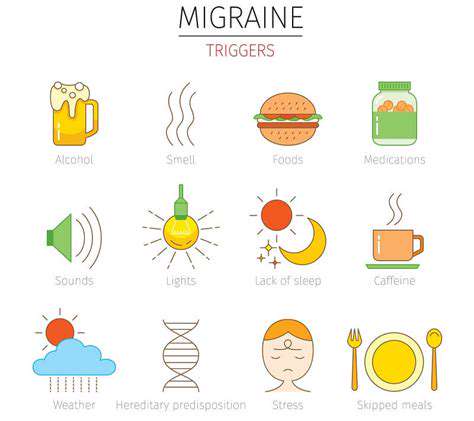

View Blog>>

De oorzaken begrijpen
Migraine-triggers zijn zeer divers
Slaap optimaliseren voor migrainepreventie: Consistentie is de sleutel
Een consistent slaapschema vaststellen
Regelmatige slaappatronen helpen bij het reguleren van circadiane ritmes, wat de kwaliteit van de slaap verbetert en mogelijk migraine-triggers vermindert. Het aanhouden van
Stress beheren voor migraineverlichting: een stressbestendige routine opbouwen

Het verband tussen stress en migraine begrijpen
Hydratatie en beweging: essentiële elementen van een migrainepreventieve routine Voldoende hydratatie ondersteunt de algehele gezondheid en helpt migraine te voorkomen. Uitdroging beïnvloedt de circulatie en de elektrolytenbalans.
Hydratatie: de basis van welzijn
Read more about De kracht van routine bij het voorkomen van migraine
Verken een uitgebreide gids over pijnstillers, met de nadruk op verschillende beschikbare soorten voor het beheer van chronische pijn, inclusief vrij verkrijgbare en op recept verkrijgbare opties. Leer meer over niet-steroïdale ontstekingsremmers (NSAID's), opioïden en adjuvante medicatie zoals antidepressiva en antiepileptica. Ontdek de verschillen tussen topische analgetica en natuurlijke remedies zoals aromatherapie en massage therapie, terwijl u ook de risico's en voordelen begrijpt die aan elke behandelingsoptie zijn verbonden. Betrek personaliseerde pijnmanagementstrategieën die levensstijlveranderingen en opkomende therapieën voor optimale resultaten integreren. Raadpleeg zorgverleners om de beste pijnverlichtingsoplossingen te vinden die zijn afgestemd op uw behoeften.
Oct 15, 2024
Begrijpen van Kloppende Pijn aan de Linkerzijde van het Hoofd Verken de complexiteit van kloppende pijn aan de linkerkant van het hoofd, met inzichten in de symptomen, veelvoorkomende oorzaken zoals spanningshoofdpijn en migraine, en effectieve behandelingsopties. Deze uitgebreide gids duikt in de kenmerken van kloppende pijn, inclusief het kloppende gevoel en de intermitterende aard, samen met mogelijke begeleidende symptomen zoals misselijkheid en gevoeligheid voor licht. Ontdek hoe levensstijlfactoren, milieudrukkers en onderliggende medische aandoeningen kunnen bijdragen aan dit ongemak. Leer over veelvoorkomende oorzaken zoals migraine, clusterhoofdpijn en arteritis temporalis, en begrijp wanneer je medische hulp moet inroepen voor ernstige symptomen. De pagina benadrukt ook verschillende beheersstrategieën, waaronder medicatiet opties, dieetoverwegingen en levensstijlaanpassingen om pijn te verlichten. Geef jezelf de kennis om kloppende pijn effectief te beheersen en je algehele welzijn te verbeteren.
Nov 09, 2024
Hoesten en hoofdpijn komen vaak samen voor, maar het begrijpen van hun verbinding kan leiden tot een betere beheersing en verlichting. Deze uitgebreide gids verkent de fysiologie achter hoesten, veelvoorkomende aandoeningen die hoestgerelateerde hoofdpijn kunnen veroorzaken en effectieve preventiemaatregelen. Ontdek hoe stress en spanning een rol spelen, de verschillende soorten hoesten en hun impact, evenals natuurlijke remedies en aanpassingen in de levensstijl om ongemak te verlichten. Leer wanneer het essentieel is om medische hulp te zoeken en geef jezelf de kennis om deze symptomen effectiever te beheren.
Nov 16, 2024
De Mechanismen Achter Hoesten Ontdek de essentiële rol van hoesten in de luchtweggezondheid met onze uitgebreide gids. Ontdek het complexe hoestreflexproces dat door irriterende stoffen wordt gestart, leer de verschillen tussen productieve en non-productieve hoest en begrijp wanneer een hoest ernstige gezondheidsproblemen kan signaleren. Verken de fysiologische voordelen van hoesten, waaronder de beschermende en immuunversterkende effecten op het ademhalingssysteem. Deze bron biedt waardevolle inzichten in verschillende soorten hoest, triggers en het belang om medische hulp te zoeken wanneer dat nodig is. Vergroot uw kennis over hoesten en de implicaties ervan voor betere ademhalingszorg.
Nov 16, 2024
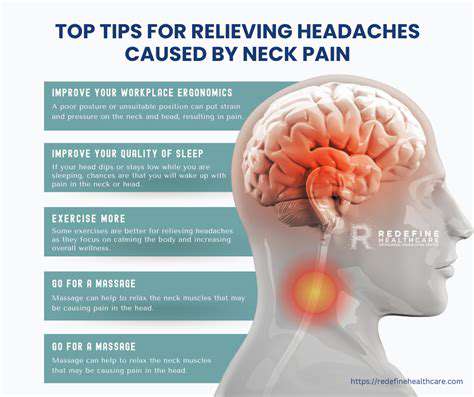
Pijn aan de rechterkant van de nek en het hoofd begrijpen
Meta Beschrijving: Verken de mogelijke oorzaken van pijn aan de rechterkant van de nek en het hoofd, waaronder spierspanning, cervicale wervelkolomstoornissen, zenuwcompressie, hoofdpijn en effectieve behandelingen. Ontdek tips voor preventie en verlichting.--- OverzichtAls je pijn voelt aan de rechterkant van je nek en hoofd, dan ben je niet alleen. Veel mensen ondervinden vergelijkbaar ongemak door verschillende onderliggende aandoeningen. Het begrijpen van deze oorzaken is de eerste stap naar effectieve beheersing en verlichting. Veelvoorkomende Oorzaken van Pijn Spierspanning en StressSpierspanning door een slechte houding of repetitieve bewegingen is een veelvoorkomende reden voor deze pijn. Stress en angst kunnen de spierspanning verergeren, wat leidt tot voortdurende ongemakken. Regelmatige pauzes en goede ergonomische praktijken kunnen helpen de symptomen te verlichten. Cervicale WervelkolomstoornissenAandoeningen zoals hernia's en artritis kunnen leiden tot uitstralende pijn in de nek en het hoofd. Diagnostische beeldvorming kan de situatie verduidelijken, terwijl behandelingsopties fysiotherapie en medicatie kunnen omvatten. Zenuwcompressie of -beschadigingZenuwcompressie, zoals cervicale radiculopathie, kan zich uiten als scherpe pijn die naar het hoofd kan uitstralen, samen met symptomen zoals gevoelloosheid of zwakte. Tijdige medische hulp wordt aanbevolen voor zenuwletsels. Effectieve Remedies en Behandelingen- Nekverstuiking of -letsel: RICE (Rust, IJs, Compressie, Elevatie) wordt aanbevolen voor behandeling, samen met vrij verkrijgbare pijnstillers. - Hoofdpijn en Migraine: Onderzoek levensstijlaanpassingen en natuurlijke remedies naast traditionele pijnbeheersingsmethoden. - Andere Mogelijke Oorzaken: Behandel samengeknepen zenuwen, hernia's of botsporen met geschikte medische interventies.Voor meer inzicht in het beheersen en behandelen van pijn aan de rechterkant van je nek en hoofd, raadpleeg een zorgverlener.
Jan 01, 2025
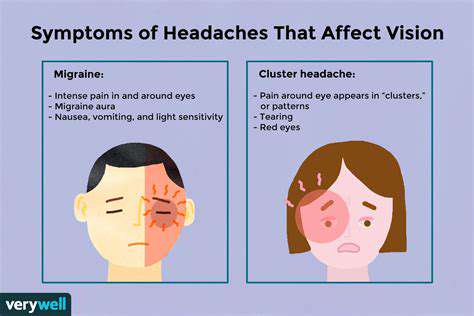
Oorzaken en Verlichtingsstrategieën Verken de veelvoorkomende oorzaken van oog- en hoofdpijn, waaronder oogvermoeidheid, migraine, sinuspijn en meer. Leer hoe stress deze aandoeningen beïnvloedt en ontdek effectieve symptomen om op te letten. Begrijp de connectie tussen oogpijn en hoofdpijn, zoals spanningshoofdpijn en migraine. Deze gids schetst uitvoerbare strategieën voor verlichting, van natuurlijke remedies zoals de 20-20-20 regel tot medische behandelingen, waaronder voorgeschreven medicijnen en gespecialiseerde interventies. Het is cruciaal om te herkennen wanneer je professionele hulp moet zoeken om je algehele gezondheid te behouden. Verbeter je welzijn door de complexe relatie tussen ooggezondheid en hoofdpijn te begrijpen. Lees verder om je comfort en welzijn vandaag nog te verbeteren!
Jan 04, 2025
Spieren spanning en verstuiking begrijpenVerken de oorzaken van spierspanning en verstuiking, inclusief fysiologische reacties op stress, overbelasting en slechte houding. Deze uitgebreide gids bespreekt preventieve maatregelen zoals juiste hydratatie, effectieve rekoefeningen en de voordelen van warmte- en koudetherapie. Leer over directe verlichtingstrategieën zoals massage en mindfulness-oefeningen, evenals langetermijnstrategieën voor spiergezondheid. Herken symptomen vroegtijdig en breng zelfzorgtechnieken in de praktijk om ongemakken aan te pakken en herstel te bevorderen. Of je nu een atleet bent, een fitnessliefhebber of een zittende persoon, het begrijpen van spierspanning kan leiden tot een betere gezondheid en het voorkomen van blessures.
Jan 13, 2025
Oorzaken, symptomen en behandelingEen hoofdpijn na hoesten kan zowel ongemakkelijk als zorgwekkend zijn. Het begrijpen van de oorzaken, symptomen en behandelmethoden kan helpen deze aandoening effectief te beheersen. Deze uitgebreide
Mar 29, 2025
Symptomen, Oorzaken en Behandeling
Inzicht in hoofdpijn aan de linkerzijde is cruciaal voor effectieve behandeling en beheer. Deze informatieve gids onderzoekt de aard van linkerhoofdpijn, veelvoorkomende symptomen, potentiele oorzaken en aanbevolen acties om verlichting te vinden.
Links Hoofdpijn Begrijpen
Hoofdpijn aan de linkerzijde kan enorm variëren in intensiteit en kwaliteit, waarbij individuen de pijn vaak beschrijven als pulserend of als constante druk. Deze onderscheidingen zijn van vitaal belang voor zorgprofessionals om passende behandelstrategieën te ontwikkelen. Onderzoek heeft aangetoond dat hoofdpijn aan de linkerzijde in verband kan worden gebracht met verschillende aandoeningen zoals migraine, en beïnvloed wordt door levensstijlfactoren zoals stress en slaapstoornissen.
Veelvoorkomende Symptomen
Symptomen die vaak gepaard gaan met hoofdpijn aan de linkerzijde zijn onder andere gevoeligheid voor licht of geluid, misselijkheid en visuele stoornissen. Het bijhouden van een hoofdpijndagboek dat het begin, de duur en de bijbehorende symptomen bijhoudt, kan helpen bij het identificeren van specifieke triggers en het informeren van behandelingsbenaderingen.
Potentiele Oorzaken
1. Primaire Hoofdpijnen: Deze op zichzelf staande hoofdpijen omvatten migraine, spanningshoofdpijn en clusterhoofdpijnen. Migraine staat bekend om eenzijdige pijn en kan bijkomende symptomen zoals misselijkheid en lichtgevoeligheid omvatten. Spanningshoofdpijn ontstaat meestal uit stress of een slechte houding en gaat vaak niet gepaard met misselijkheid.
2. Secundaire Hoofdpijnen: Deze zijn symptomatisch voor onderliggende aandoeningen, zoals sinusinfecties, die kunnen leiden tot uitstralende pijn aan de linkerkant van het hoofd. Zelden kunnen ernstigere aandoeningen, zoals beroertes, zich ook manifesteren als gelokaliseerde hoofdpijn.
3. Levensstijl Factoren: Emotionele stress, musculoskeletale problemen, en overmatig medicijngebruik kunnen als triggers optreden. Het handhaven van een goede houding en het verminderen van stress door middel van ontspanningstechnieken kan de frequentie van hoofdpijn verminderen.
Wanneer Hulp Te Zoeken
Herkennen wanneer medische hulp nodig is, is cruciaal. Plotselinge opkomende hoofdpijn, neurologische symptomen, of aanhoudende pijn vereisen onmiddellijke professionele evaluatie. Bovendien, als vrij verkrijgbare medicijnen geen verlichting bieden, kan het raadplegen van een zorgprofessional leiden tot een meer gepersonaliseerd behandelplan.
Effectieve Verlichtingsstrategieën
Preventieve Maatregelen
Het implementeren van een gebalanceerde levensstijl—regelmatige lichaamsbeweging, een passend dieet, voldoende hydratatie, en effectief stressmanagement—kan de frequentie en intensiteit van hoofdpijn aan de linkerzijde aanzienlijk verminderen.
Behandelopties
Vrij verkrijgbare medicijnen zoals ibuprofen of paracetamol dienen als een eerste verdedigingslinie, maar voorzichtigheid is geboden om rebound-hoofdpijn door overmatig gebruik te voorkomen. Alternatieve therapieën, waaronder acupunctuur en mindfulness-oefeningen, kunnen ook aanzienlijke voordelen bieden.
Conclusie
Het begrijpen van hoofdpijn aan de linkerzijde is cruciaal voor effectieve verlichting en beheer. Door symptomen te herkennen, potentiële triggers te identificeren en te weten wanneer medische hulp moet worden ingeroepen, kunnen individuen hun kwaliteit van leven aanzienlijk verbeteren. Of het nu gaat om levensstijlveranderingen of professionele behandelingen, het aanpakken van deze hoofdpijn kan leiden tot een gezonder, meer vervullend bestaan.
Voor meer gedetailleerde begeleiding, duik dieper in onderwerpen zoals [hoe hoofdpijn triggers te identificeren]() of leer over [wanneer medische hulp te zoeken]().
Apr 18, 2025
Kruidenthee die mogelijk hoofdpijn kan verlichten
May 08, 2025
Verschillende soorten hoofdpijn dagboeken en trackers vergelijken
May 12, 2025
De rol van hydratatiebijhouden bij hoofdpijnbehandeling
May 18, 2025