HTML
Styling
CSS
Migraine Management
Medication Effectiveness
Medicamentos anticonvulsivantes usados para a prevenção da enxaqueca
Como os ASM visam a enxaqueca>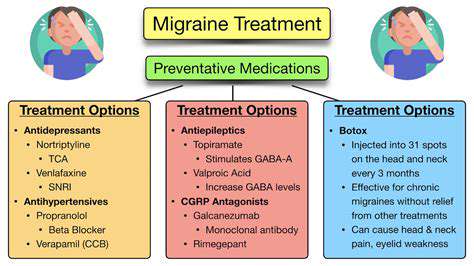

Eficácia e Efeitos Colaterais dos Ansiolíticos no Tratamento da Migrânea
Eficácia dos Ansiolíticos no Tratamento da Migrânea
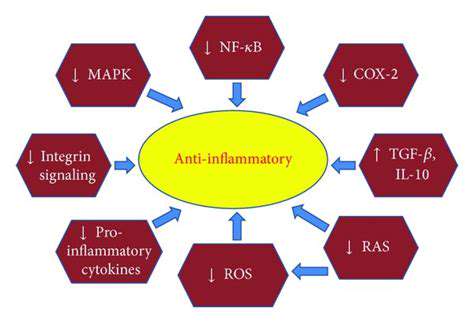
Os medicamentos anticonvulsivantes (Ansiolíticos) demonstraram potencial no manejo da migrânea, particularmente para aqueles que experimentam enxaquecas crônicas ou cefaléias por uso excessivo de medicamentos. Embora não sejam o tratamento de primeira linha para
Read more about Medicamentos anticonvulsivantes usados para a prevenção da enxaqueca
Gatilhos da Enxaqueca e Estratégias de Gestão
Descubra as complexidades dos gatilhos da enxaqueca e as estratégias de gestão eficazes em nosso guia abrangente. Aprenda sobre gatilhos comuns, como estresse, fatores alimentares e alterações hormonais que podem afetar a frequência e a gravidade das enxaquecas. Entenda como identificar seus gatilhos únicos através de métodos práticos, como manter um diário de enxaqueca. Explore ajustes no estilo de vida, incluindo técnicas de gerenciamento de estresse, mudanças na dieta e a importância da higiene do sono, para ajudar a reduzir episódios de enxaqueca. Saiba quando buscar ajuda profissional para enxaquecas persistentes e como medidas proativas podem melhorar sua qualidade de vida. Comece hoje mesmo o caminho para uma melhor gestão da enxaqueca!
Nov 21, 2024
Dor de cabeça ao assoar o nariz: Causas e remédios
Apr 30, 2025
Enxaquecas Induzidas por Exercício: Prevenção e Gestão
May 03, 2025
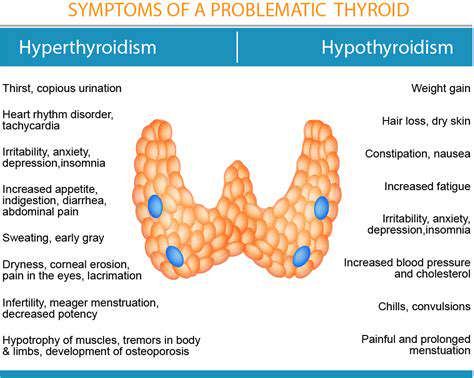
A Conexão Entre Distúrbios da Tireóide e Cefaleias
May 04, 2025
Criando um espaço escuro e silencioso para alívio da enxaqueca
May 05, 2025
Explorando a Dieta Cetogênica para Prevenção de Migrenas
May 11, 2025
Cefaleia diária persistente nova (NDPH): O que você precisa saber
May 14, 2025
O Potencial do Gengibre para os Sintomas de Enxaqueca
May 15, 2025
O Clima Realmente Pode Causar Dor de Cabeça? Explorando as Evidências
May 19, 2025
Construindo Resiliência Vivendo com Migrañas
May 21, 2025
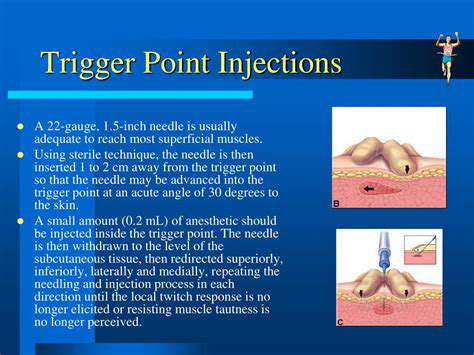
Injeções de Ponto-gatilho para Cefaleias de Tensão e Cervicogênicas
Jun 09, 2025