HTML element
CSS class
HTML
Styling
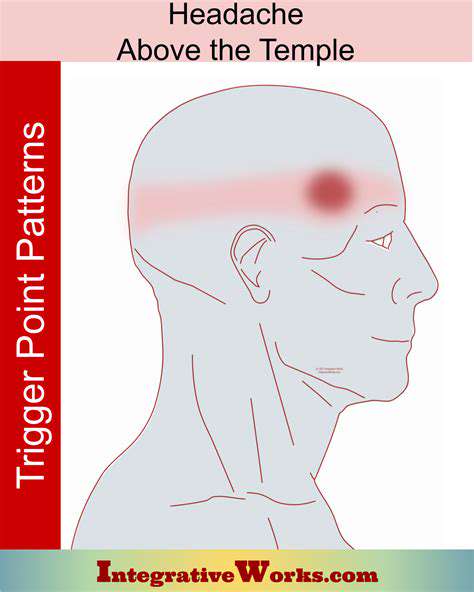
Headache
Neurology
Đau đầu từng cơn: Nhận biết các dấu hiệu của cơn đau dữ dội
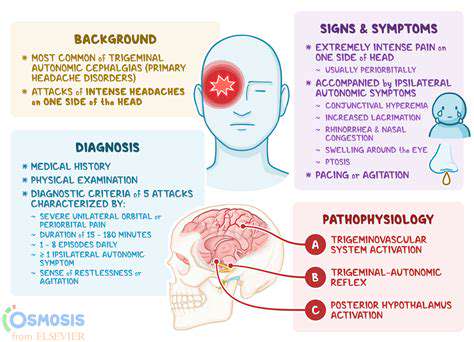

Bản chất tuần hoàn của cơn đau nửa đầu từng cụm
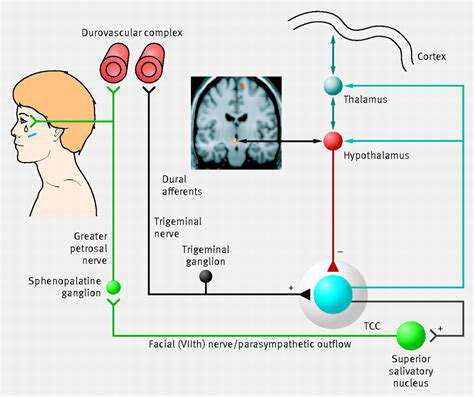
Hiểu về khái niệm cốt lõi
Trong mạng cảm biến không dây, các trạm gốc hoạt động theo một mô hình tuần hoàn riêng biệt, một đặc điểm không phải là tình cờ
Quản lý và ngăn ngừa đau đầu từng cụm
Hiểu về đau đầu từng cụm
Đau đầu từng cụm là một loại đau đầu đặc biệt dữ dội, với cơn đau dữ dội thường tập trung gần mắt hoặc thái dương. Các đợt đau có thể kéo dài từ 15 phút
Read more about Đau đầu từng cơn: Nhận biết các dấu hiệu của cơn đau dữ dội
Mối liên hệ giữa ho và đau đầuKhám phá mối quan hệ phức tạp giữa ho và đau đầu trong hướng dẫn toàn diện của chúng tôi. Tìm hiểu cách cơ chế sinh lý của một cơn ho có thể dẫn đến căng cơ, đau đầu do căng thẳng và bệnh migraine. Chúng tôi đi sâu vào các tình trạng phổ biến như viêm xoang, viêm phế quản và dị ứng làm trầm trọng thêm các triệu chứng, cùng với những vấn đề tiềm ẩn cần được chẩn đoán y tế. Trang này cung cấp cái nhìn sâu sắc về các kỹ thuật quản lý hiệu quả, các phương pháp chữa bệnh tại nhà và các biện pháp phòng ngừa để giảm bớt các triệu chứng và nâng cao chất lượng cuộc sống của bạn. Hãy tìm hiểu khi nào cần tìm sự giúp đỡ nếu cơn ho và cơn đau đầu liên quan của bạn kéo dài hoặc xấu đi. Hiểu rõ hơn về sức khỏe của bạn với kiến thức giúp bạn giao tiếp hiệu quả với các nhà cung cấp dịch vụ chăm sóc sức khỏe.
Dec 31, 2024
Nguyên nhân, phòng ngừa và điều trị
Apr 05, 2025
Đau Miệng Bên Trái: Hiểu về các triệu chứng và phương pháp điều trị
May 01, 2025
Khám phá những điều chỉnh lối sống hiệu quả để ngăn ngừa đau nửa đầu và giảm bớt các triệu chứng. Học cách nhận biết các dấu hiệu cảnh báo sớm, bao gồm tiền triệu đau nửa đầu, để giúp quản lý và giảm các cơn đau nửa đầu. Hướng dẫn toàn diện này bao gồm...
May 04, 2025
Tạo không gian tối và yên tĩnh để giảm đau nửa đầu
May 05, 2025
Đau đầu ở trẻ em: Khi nào cần lo lắng và những cách giúp đỡ nào?
May 07, 2025
Đau đầu hàng ngày mãn tính: Nguyên nhân và chiến lược đối phó
May 16, 2025
Gánh nặng tài chính của chứng đau nửa đầu: Nguồn lực và lời khuyên
May 24, 2025
Khôi phục cuộc sống từ chứng đau đầu mãn tính
May 26, 2025
Vượt qua định kiến liên quan đến chứng đau nửa đầu
Jun 02, 2025
Có an toàn khi dùng thuốc đau nửa đầu trong thời gian dài không?
Jun 05, 2025
Làm thế nào để hỗ trợ người thân yêu bị đau nửa đầu?
Jun 09, 2025