Bump on Back of Head Hurts: What You Need to Know
Common Causes of a Bump on the Back of the Head
1. Trauma or Injury
A Bump on the back of the head is often caused by trauma or an injury. This might happen due to falls, sports accidents, or any situation where the head is subjected to a sudden impact. When the soft tissue in that area experiences a force, it can swell, resulting in a noticeable bump.
It’s important to assess the severity of the injury. If the bump is accompanied by other symptoms such as dizziness, vision changes, or persistent headaches, it may indicate a more serious underlying issue, like a concussion.
In case of a head injury, it’s advisable to rest and monitor symptoms closely. Applying ice to the area can help reduce swelling. However, if there are any alarming symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial.
In summary, trauma is a common cause of bumps on the back of the head, and understanding the circumstances surrounding the injury can help determine the appropriate response.
2. Cysts and Lipomas
Another reason for a bump on the back of the head could be benign growths like sebaceous cysts or lipomas. Sebaceous cysts are small lumps beneath the skin that can feel like a hard ball. They are caused by blocked sebaceous glands.
Lipomas, on the other hand, are soft, fatty lumps that form slowly and are usually painless. They occur due to an overgrowth of fat cells and can appear anywhere on the body, including the head.
While these conditions are generally harmless and do not lead to serious complications, they may cause discomfort or self-consciousness, prompting individuals to seek removal. A healthcare provider can evaluate these growths to determine the best course of action.
Identifying the nature of the bump is essential. If it changes in size, becomes painful, or shows signs of infection, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional.
3. Infections or Inflammatory Conditions
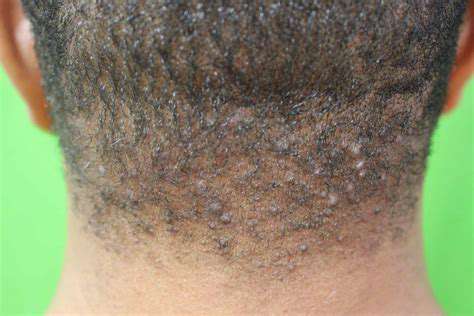
Infections or inflammatory conditions can also result in bumps on the back of the head. Conditions like folliculitis, which is an infection of hair follicles, can produce small, painful lumps that can swell and become red.
Another possible condition is scalp acne, which occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oils and dead skin cells. This can lead to inflammation and the formation of bumps on the scalp, including the back of the head.
In rarer cases, conditions such as osteomyelitis (an infection of the bone) may also lead to swelling and pain in the area. Symptoms can include fever, warmth over the site, and increasing pain.
When dealing with infections or inflammatory conditions, treatment may involve antibiotics or other medications to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. Consulting a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis is crucial.
Symptoms Associated with a Bump on the Back of the Head
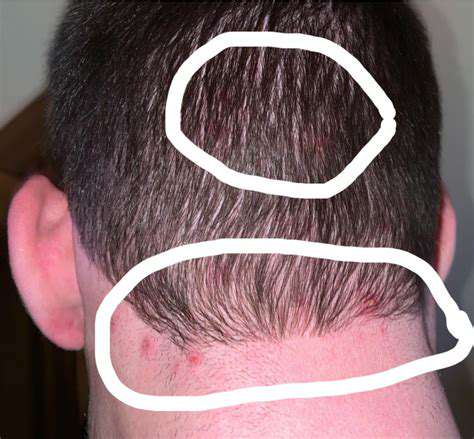
Common Symptoms Indicating a Bump on the Back of the Head
When experiencing a bump on the back of the head, patients often report various symptoms. Common symptoms may include Tenderness at the site of the bump. This tenderness can vary from mild discomfort to severe pain, depending on the underlying cause.
In addition to tenderness, swelling around the bump may also be observed. This swelling could be a result of inflammation or injury to the surrounding tissues.
In some cases, patients might experience headaches or dizziness, which could indicate complications or a more serious underlying issue.
Potential Causes of Pain in the Bump Area
Several factors can contribute to the development of a bump on the back of the head. Trauma is one of the most common causes, often resulting from falls or accidents.
Infections or cysts can also lead to bumps in this area. These conditions may cause inflammation and pain, necessitating medical evaluation.
Other potential causes include dermatological issues such as skin infections, which could require topical or systemic treatment.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is essential to monitor any bumps that appear on the back of the head for changes. If a bump persists or grows in size, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider.
Additionally, if the pain becomes severe or is accompanied by other worrying symptoms, such as fever or nausea, immediate medical attention is warranted.
Seeking help early can prevent complications and ensure that any serious conditions are addressed promptly.
Diagnosis of Bumps and Associated Symptoms
The diagnosis process typically involves a physical examination and patient history. Doctors may ask about the onset of the bump and any associated symptoms to gather relevant information.
In some instances, imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, may be necessary to assess deeper structures and rule out serious conditions.
Understanding the underlying cause is critical for determining the appropriate treatment plan and ensuring effective recovery.
Treatment Options for Bumps on the Back of the Head
Treatment largely depends on the identified cause of the bump. For minor injuries, rest and over-the-counter pain relief may suffice.
In cases of infection, antibiotics or other medications may be prescribed. Your healthcare provider will determine the best course of action based on the specifics of your condition.
For larger cysts or persistent bumps, surgical intervention may be considered necessary to remove them and alleviate symptoms.
Treatment Options for Pain from a Bump on the Back of the Head
Home Remedies to Alleviate Pain
When experiencing pain from a bump on the back of the head, several Home Remedies can provide relief. Applying a cold compress to the affected area can help reduce swelling and numb the pain. Simply wrap ice in a cloth and hold it against the bump for 15-20 minutes multiple times a day.
Additionally, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be effective for managing discomfort. Always follow the recommended dosage and consult with a healthcare provider if you're unsure about which medication is suitable for you.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While minor bumps can often be treated at home, there are signs that warrant a visit to a healthcare professional. If the pain worsens or persists over a few days, it’s crucial to get it evaluated. Symptoms such as severe headache, confusion, dizziness, or vision changes could indicate a more serious condition.
Similarly, if you notice any fluid or blood leaking from your ears or nose, or if you experience nausea and vomiting, seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms could suggest a concussion or other significant head injury that requires expert evaluation.
Diagnostic Evaluations and Imaging
If the bump on the back of the head is significant or accompanied by troubling symptoms, your doctor may recommend diagnostic imaging. A CT scan or MRI can help visualize internal structures and rule out any fractures or serious brain injuries that might not be apparent through a physical examination.
During the evaluation, your doctor will likely ask about your medical history and any other related symptoms. Providing detailed information can aid in a more accurate diagnosis and treatment plan, ensuring that any necessary interventions are identified early on.
Preventative Measures for Future Injuries
Taking steps to prevent future bumps on the head is essential, especially if you're prone to falls or engaging in sports. Wearing protective headgear during activities such as biking, skateboarding, or contact sports can significantly reduce the risk of injury.
In addition, maintaining a tidy living space, particularly in areas where one tends to walk or play, can help prevent accidental bumps. Ensuring good lighting and removing trip hazards can make a big difference in preventing head injuries at home.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Head
To better comprehend the implications of a bump on the back of the head, it's helpful to have a basic understanding of the head's anatomy. The occipital bone, located at the lower back of the skull, is particularly vulnerable to trauma, and bumps here can vary in severity from minor bruises to more serious injuries.
Understanding the structure of the skull and its surrounding tissues can provide insight into the importance of any pain or discomfort experienced. It’s always recommended to monitor your symptoms closely and keep track of any changes over time for proper assessment.