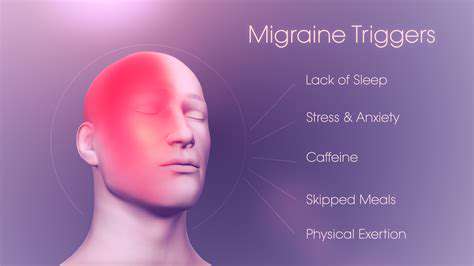
Chronic Daily Headaches: Causes and Coping Strategies
- Stress and anxiety
- Changes in sleep patterns
- Certain foods (aged cheeses, chocolate, processed meats)
- Bright lights or loud noises
The Role of Genetics in Migraine
If migraines run in your family, you’re more likely to experience them too. Research highlights a strong genetic link, though the specific genes involved are still under investigation. Knowing your family history helps doctors tailor prevention strategies, making it a key part of diagnosis and long-term management.
Exploring Treatment Options for Migraine
Treatment ranges from over-the-counter pain relievers (like ibuprofen) for mild attacks to prescription medications (such as triptans or CGRP inhibitors) for severe cases. Some drugs not only relieve pain but also prevent future episodes, offering a dual benefit for chronic sufferers.
Managing Lifestyle Factors for Migraine Prevention
Small lifestyle changes can make a big difference in migraine frequency and severity. Key strategies include:
- Stress management—try yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule.
- Eating balanced meals and staying hydrated.
- Regular exercise to reduce stress and boost overall health.
The Importance of Seeking Professional Help
Ignoring chronic headaches can lead to worsening symptoms and reduced quality of life. Early medical intervention is crucial—a healthcare provider can diagnose the issue accurately, rule out serious conditions, and create a personalized treatment plan. Don’t wait until headaches become debilitating; professional care is the best path to relief.
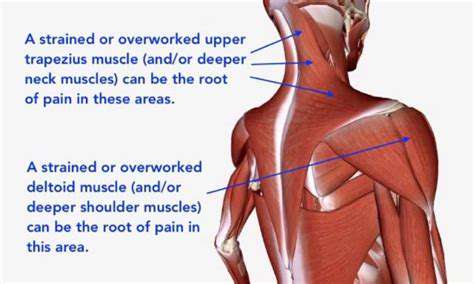
Tension headaches, often felt on the upper right side of the head, are frequently linked to stress or poor posture. The pain may feel like a tight band around the head, worsening with neck strain.
Exploring Underlying Medical Conditions
Understanding the Scope of Underlying Conditions
Underlying medical conditions span a wide range, from diabetes to rare disorders. Accurate diagnosis is the foundation of effective treatment, often requiring a team of specialists to coordinate care. A thorough evaluation—including medical history, exams, and tests—is essential.
The Impact of Underlying Conditions on Treatment
Pre-existing conditions can drastically alter treatment plans. For example, a patient with hypertension may need adjusted medications to avoid complications. Tailoring care to individual needs ensures safety and better outcomes.
Diagnostic Procedures for Identifying Underlying Conditions
From blood tests to advanced imaging, diagnostics play a pivotal role. Choosing the right tests depends on symptoms and risk factors, ensuring precise detection of underlying issues.
Management Strategies for Coexisting Conditions
Effective management requires personalized plans that address all health concerns. Regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments are key, along with strong patient-provider communication.
The Role of Prevention in Reducing Underlying Conditions
Healthy habits—like balanced diets and regular exercise—can prevent many chronic conditions. Public health initiatives are vital for spreading awareness and empowering individuals to take control of their health.
Developing Effective Coping Strategies for Chronic Daily Headaches

Identifying Triggers and Patterns
Tracking stress triggers through journals or apps helps uncover patterns, enabling proactive coping strategies.
Practicing Relaxation Techniques
Deep breathing, meditation, and muscle relaxation are proven methods to calm the mind and body, even in small daily doses.
Seeking Support Systems
Strong social connections buffer against stress, offering emotional relief and fresh perspectives. Don’t hesitate to lean on friends, family, or therapists.
Developing Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Sleep, nutrition, and exercise form the backbone of stress management. Prioritizing these boosts both physical and mental resilience.
Problem-Solving and Time Management Skills
Breaking tasks into smaller steps and using time-management tools can reduce overwhelm. Proactive problem-solving tackles stress at its root, fostering long-term relief.