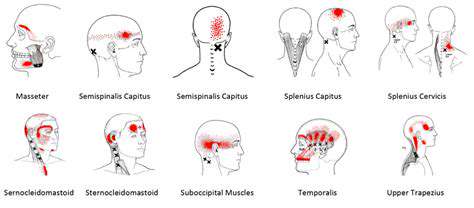
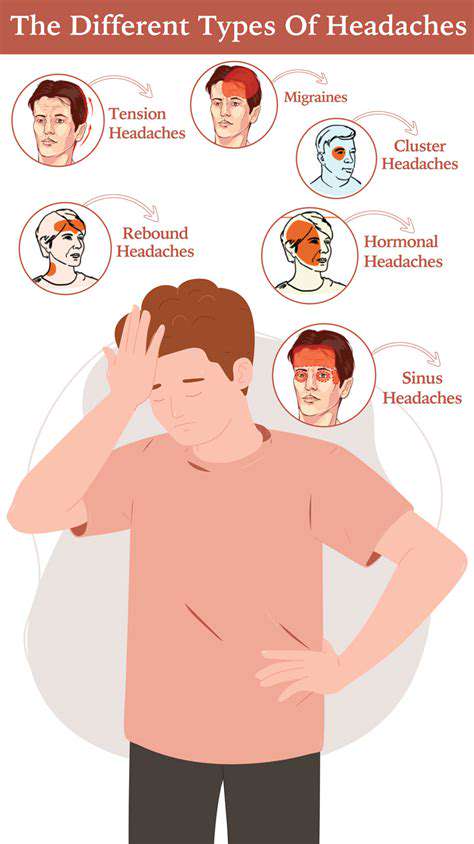
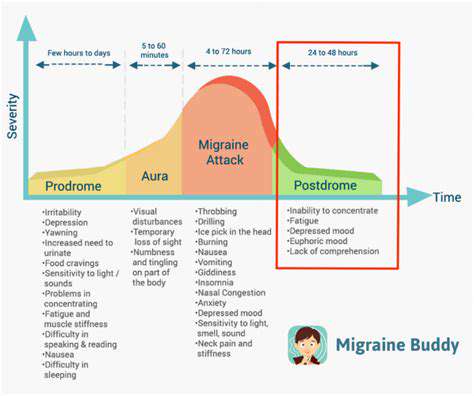
The Impact of Air Quality on Headaches and Migraines
The Mechanisms of Action: How Air Pollution Affects the Brain
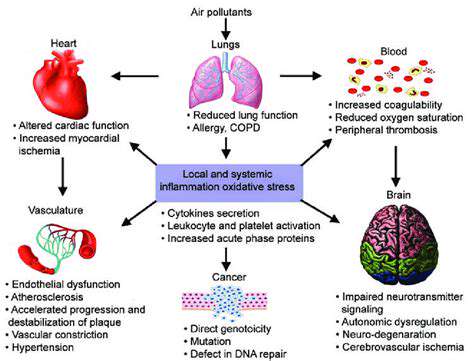
Air Pollution's Impact on Respiratory Systems
Breathing in polluted air exposes our lungs to a dangerous cocktail of gases and microscopic particles that can wreak havoc on respiratory health. When these contaminants enter our airways, they spark inflammatory reactions that can snowball into serious respiratory conditions. This inflammation throws off the respiratory system's delicate equilibrium, compromising lung efficiency. The alveoli - those tiny air sacs crucial for gas exchange - become swollen and irritated, hindering their oxygen-carbon dioxide transfer capabilities. Over time, this damage can manifest as chronic asthma, bronchitis, and heightened vulnerability to respiratory infections.
Pollutants don't just trigger inflammation; they physically erode the airway lining. This direct assault causes irritation and swelling while stimulating excessive mucus production - a double whammy that obstructs breathing passages. Years of exposure can permanently alter lung structure, gradually diminishing capacity and paving the way for severe respiratory complications.
Cardiovascular Effects of Air Pollution
Air pollution's destructive reach extends far beyond the lungs, striking at the heart of cardiovascular health. Microscopic particles in polluted air act like sandpaper on blood vessel walls, causing inflammation and arterial constriction that accelerates atherosclerosis. As plaque accumulates in narrowed arteries, blood pressure spikes and cardiac strain intensifies, dramatically elevating risks for heart attacks and strokes.
The inflammatory cascade triggered by air pollutants doesn't stop at blood vessels - it courses through the entire circulatory system. This systemic inflammation promotes dangerous blood clots that can trigger catastrophic cardiovascular events. Mounting evidence confirms that long-term exposure to dirty air substantially raises cardiovascular disease risks, making pollution control a critical public health priority.
Neurological Implications of Air Pollution
Groundbreaking studies are uncovering disturbing connections between air quality and brain health. Inhaled pollutants may disrupt neural pathways and neurotransmitter balance, potentially impairing cognitive functions like memory retention, focus, and information processing speed. Researchers suspect these microscopic invaders might breach the blood-brain barrier, directly interfering with neurological processes.
The inflammatory response to air pollution could also contribute to neurodegenerative conditions by damaging delicate brain tissue. While scientists continue unraveling the precise mechanisms, the correlation between pollution exposure and neurological disorders grows increasingly undeniable.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations
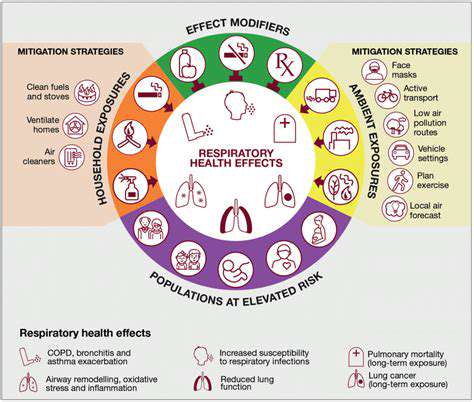
Certain groups bear the brunt of air pollution's harmful effects more severely than others. Children's developing lungs and faster breathing rates make them particularly susceptible to lasting damage. Pollution exposure during critical growth periods can permanently alter lung development, setting the stage for lifelong respiratory issues.
Elderly individuals face heightened risks due to age-related declines in lung function and overall resilience. Those with pre-existing heart or lung conditions experience amplified effects from pollution exposure. For these vulnerable groups, even short-term exposure can trigger dangerous health crises, underscoring the urgent need for protective measures.
Strategies for Prevention and Mitigation: Protecting Your Health
Strategies for Preventing Workplace Injuries
Workplace safety requires a proactive approach that prioritizes hazard identification, thorough risk analysis, and comprehensive training programs. Building a culture of safety through clear protocols and consistent reinforcement dramatically reduces accident rates. This involves establishing unambiguous safety standards and ensuring universal compliance through regular monitoring.
Effective safety programs thrive on open communication channels where employees feel empowered to report concerns. Timely hazard correction and equipment maintenance form the backbone of injury prevention strategies.
Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment
The foundation of workplace safety lies in systematically uncovering potential dangers through meticulous environmental scans. This process examines equipment, workflows, and physical spaces to flag risks ranging from simple trip hazards to complex chemical exposures. Documenting these findings creates a roadmap for targeted safety interventions.
Risk evaluation weighs both the probability and potential severity of identified hazards, allowing organizations to allocate resources strategically. This dynamic process requires regular updates to address evolving workplace conditions.
Employee Training and Education
Knowledge is the first line of defense against workplace injuries. Effective training programs equip staff with hazard recognition skills, emergency response knowledge, and proper equipment usage techniques. Role-specific instruction coupled with hands-on practice sessions dramatically improves safety compliance.
Refresher courses reinforce critical concepts while keeping pace with procedural updates. Interactive training methods enhance engagement and knowledge retention among diverse workforces.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Properly fitted and maintained PPE serves as a crucial barrier between workers and occupational hazards. From impact-resistant eyewear to respiratory protection, these specialized tools can mean the difference between minor incidents and life-altering injuries. Regular equipment inspections ensure continued effectiveness.
Engineering Controls and Safe Work Practices
Proactive hazard elimination through engineering solutions represents the gold standard in workplace safety. Machine guards, ventilation systems, and ergonomic designs address risks at their source, reducing reliance on individual protective measures. Complementing these physical controls with standardized safe work procedures creates multiple layers of protection.
Emergency Preparedness and Response
Comprehensive emergency plans transform chaotic crisis situations into managed responses. These protocols should detail accident reporting chains, first aid procedures, and evacuation routes. Regular drills ingrain these responses into muscle memory, ensuring calm, effective action during actual emergencies.
Continuous Improvement and Monitoring
Safety programs must evolve through ongoing evaluation and refinement. Analyzing incident patterns, soliciting employee feedback, and conducting routine audits create a feedback loop that progressively enhances protective measures. This iterative approach ensures safety systems remain effective amid changing workplace conditions.