Common Symptoms of Stiffness, Discomfort, and Difficulty in Movement
Recognizing the Signs of Mobility Issues
Understanding Stiffness and Discomfort
Stiffness in the muscles and joints is a common symptom experienced by individuals of all ages, but it becomes particularly prevalent with aging or certain medical conditions. This sensation can vary from mild tightness to severe pain that restricts movement, often making daily activities challenging.
Discomfort associated with stiffness can be due to a variety of factors, including overuse of muscles, prolonged inactivity, or underlying health issues such as arthritis or fibromyalgia. Recognizing these symptoms early can help in managing them effectively through appropriate treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
Identifying Difficulty in Movement
Difficulty in movement often manifests as struggles with coordination or the ability to perform simple tasks like walking or climbing stairs. People may experience an unsteady gait or a reduced range of motion in joints, which affects their overall quality of life.
This symptom can be linked to neurological conditions, musculoskeletal disorders, or even injury recovery. It's important to identify the root cause and seek professional advice to address not only the symptoms but also the underlying condition contributing to these mobility issues.
Impact on Daily Life
Mobility issues can have a significant impact on an individual's daily life, affecting everything from personal care to social activities. Stiffness and discomfort may limit participation in hobbies, leading to feelings of frustration or isolation.
Beyond physical barriers, these symptoms can also influence mental health, causing anxiety or depression as one grapples with the changes in their mobility. Addressing these concerns through supportive therapies, regular exercise, and seeking social support can help maintain a positive outlook while managing mobility challenges.
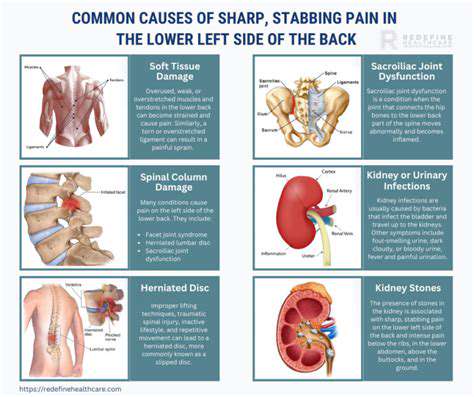
Potential Causes of Stiffness and Discomfort
Muscle Strain and Overuse
Muscle strain often occurs when muscles are stretched beyond their normal capacity, leading to stiffness and discomfort. Increased physical activity without proper warm-up can exacerbate these symptoms.
Overuse injuries can develop gradually, manifesting as persistent discomfort in the affected muscles. It's essential to allow adequate recovery time to prevent further strain and promote healing.
Arthritis and Related Conditions
Arthritis is a common cause of stiffness, particularly in older adults. Conditions such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can lead to chronic discomfort and restricted movement joints. These conditions often require medical evaluation for proper management.
Inflammation surrounding the joints can result in swelling and reduced mobility. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve quality of life.
Nerve Compression and Neurological Factors
Nerve compression, such as that caused by a herniated disc or sciatica, can lead to pain and stiffness in various body parts. The sensation of numbness or tingling can accompany these symptoms, indicating potential nerve involvement.
Neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis or Parkinson's disease, can also contribute to motor difficulties. Understanding and addressing the underlying neurological factors is crucial for effective treatment.
Inactivity and Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle can lead to muscle atrophy and stiffness due to lack of movement. Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining flexibility and overall musculoskeletal health.
Prolonged periods of inactivity can result in tight muscles, making it difficult to perform daily activities. Incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises can help alleviate stiffness and improve mobility.
The Impact of Sedentary Lifestyles
The Dangers of Prolonged Inactivity
Prolonged periods of inactivity can lead to a multitude of physical health issues. One of the most significant risks is the stiffness that can develop in muscles and joints. When the body is not regularly engaged in movement, flexibility decreases and discomfort can become a constant companion in daily activities.
Moreover, a sedentary lifestyle can exacerbate existing conditions like arthritis or chronic back pain. Individuals may find that their previously manageable symptoms become more pronounced as they spend more time sitting. This cascade effect can turn minor discomfort into significant mobility issues.
Additionally, long hours spent in one position can also lead to poor posture, ultimately contributing to pain in the neck, shoulders, and lower back. Adjusting one’s lifestyle to incorporate more movement could be crucial in mitigating these negative effects.
The Psychological Effects of Inactivity
Inactivity doesn't only affect the body it can also impact mental health. People leading sedentary lifestyles often report feelings of lethargy and low motivation. The lack of physical activity can trigger or worsen anxiety and depression, creating a vicious cycle of inactivity and mental distress.
Adding regular movement into one’s routine can have remarkably positive effects on mood. Exercise releases endorphins, which can help counteract feelings of sadness or anxiety. Even short bursts of physical activity can elevate one's spirit and boost energy levels.
Staying active also fosters social connections, whether through group exercises or recreational activities. These interactions enhance emotional wellbeing by providing a sense of community and support, thus helping to counteract the isolation that often accompanies a sedentary lifestyle.
Practical Strategies to Combat Sedentarism
To combat the detrimental effects of a sedentary lifestyle, individuals should consider integrating more movement into their daily routines. Simple changes, like taking the stairs instead of the elevator, can make a significant difference. Additionally, standing desks or adjustable workstations can encourage standing throughout the workday.
Setting reminders to take short breaks to stretch or walk can also be beneficial. Every hour, taking just a few minutes to move around can help ease stiffness and improve circulation. This not only combats discomfort but can also enhance productivity and focus.
Lastly, engaging in regular physical activities that you enjoy can make exercise feel less daunting. Whether it’s dancing, swimming, or cycling, finding enjoyable forms of movement is key to sustaining an active lifestyle and improving overall health.
Managing Symptoms Effectively
Understanding the Causes of Stiffness
Stiffness in the body can arise from a variety of underlying conditions, including arthritis, muscle strain, or even sedentary lifestyles. Understanding the specific cause of stiffness is crucial for effective management. For instance, degenerative joint diseases like osteoarthritis lead to the gradual breakdown of cartilage, resulting in pain and stiffness, particularly in weight-bearing joints.
In many cases, muscle stiffness can be the result of overuse or injury. Engaging in strenuous physical activities without adequate warm-up can lead to muscle tightness, making movement feel uncomfortable. Additionally, conditions such as fibromyalgia can cause widespread stiffness, emphasizing the need for a tailored approach to treatment that considers the individual's specific circumstances.
Effective Home Remedies
Many individuals find relief from stiffness and discomfort through simple home remedies. Applying heat, such as warm baths or heating pads, can help relax tight muscles and improve blood circulation to affected areas. Cold therapy, conversely, may alleviate inflammation and reduce swelling, especially after acute injuries.
Gentle stretching exercises play a significant role in managing stiffness. Regularly incorporating activities like yoga or tai chi can enhance flexibility and strength, subsequently reducing discomfort experienced during movement. These low-impact exercises also promote relaxation and can improve overall mental well-being.
When to Seek Professional Help
While mild stiffness can often be managed at home, it is important to recognize when professional help is needed. If stiffness persists for an extended period, worsens, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as swelling, fever, or severe pain, consulting a healthcare provider is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Medical professionals may recommend physical therapy, medications, or other interventions based on the severity and cause of the symptoms. Early intervention can prevent further complications and enhance the quality of life, making it critical to address concerns promptly.
When to Seek Professional Help
Understanding the Severity of Symptoms
When experiencing stiffness, discomfort, or difficulty in movement, it's essential to assess the severity of the symptoms. Mild cases may result from temporary strain or overexertion, often alleviated with rest or home remedies. However, persistent or worsening symptoms could indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires attention.
Keep track of any accompanying symptoms, such as swelling, redness, or limited range of motion. These could be signs of inflammation or injury. Additionally, note how long the symptoms have persisted and if they interfere with daily activities, as this information can be crucial when consulting a healthcare professional.
If the stiffness or discomfort significantly affects your quality of life or daily functioning, it is advisable to seek professional advice. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to further complications and prolonged discomfort.
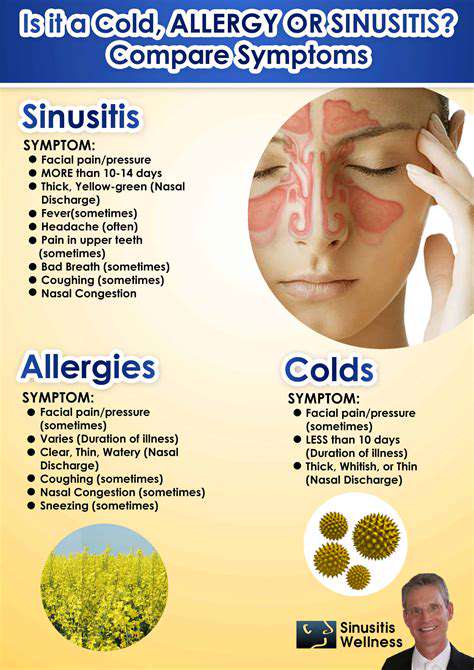
Evaluating Associated Symptoms
In some cases, stiffness and difficulty in movement may be linked to other symptoms, such as fatigue, fever, or nausea. This combination can provide important clues regarding the underlying cause. For instance, stiffness accompanied by fever may suggest an infection or inflammatory condition, while fatigue and pain might point towards an autoimmune disorder.
It's also crucial to consider any recent changes in lifestyle or activities. New exercises, job ergonomics, or even stress factors can contribute to physical discomfort. Documenting these changes helps healthcare providers identify potential triggers and tailor appropriate treatment plans.
As a general rule of thumb, if you notice a sudden onset of stiffness or any unusual symptoms that are severe or persistent, it’s recommended to consult a healthcare professional. Timely intervention can facilitate quicker recovery and prevent further issues.