Exploring the Connection Between Muscle Tension and Inflammation
The Mechanics of Muscle Tension
The Physiology of Muscle Tension
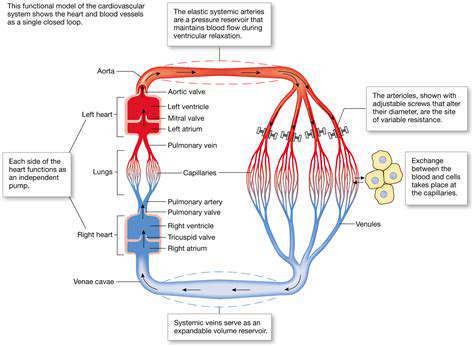
Muscle tension is a physiological response that occurs when muscle fibers contract. This contraction can be voluntary, as seen in exercises, or involuntary, such as reflex actions. The interaction of actin and myosin filaments within the muscle fibers is what facilitates this contraction. Understanding this process is crucial for comprehending how muscle tension can impact inflammation.
When muscles are engaged in intense activity or under prolonged stress, they generate not only motion but also metabolic byproducts. These byproducts, including lactic acid, can accumulate and lead to discomfort and increased muscle tension. The body recognizes this build-up as a signal to increase blood flow to the area, which is an initial inflammatory response aimed at alleviating discomfort.
Moreover, muscle tension affects neighboring tissues, potentially causing a ripple effect that can lead to widespread tension and strain in surrounding areas. This interconnectedness of muscle groups highlights the importance of addressing tension both locally and throughout the body.
In summary, the physiology of muscle tension is closely tied to how muscles work and the systemic responses that arise from their activity. Recognizing these connections allows for better management of both muscle tension and inflammation over time.
The Role of Inflammation in Muscle Health
Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injury or stress, and it plays a complex role in muscle health. While acute inflammation can promote healing, chronic inflammation may lead to issues such as muscle degeneration and chronic pain syndromes. Understanding the balance between these two types of inflammation is critical for maintaining healthy muscle function.
Chronic inflammation can be exacerbated by inadequate recovery from exercise, overtraining, or poor nutrition. When muscles do not receive the necessary nutrients or rest periods, inflammatory markers increase, leading to a cycle of pain and dysfunction. This cycle often manifests as extended muscle soreness, stiffness, and a reduced range of motion.
Additionally, systemic inflammation can stem from lifestyle factors such as sedentary behavior, poor diet, and high-stress levels. Addressing these factors can help reduce overall inflammation and subsequently improve muscle recovery and health.
Thus, recognizing the effects of inflammation on muscle health not only raises awareness of the importance of balanced exercise and nutrition but also emphasizes the need for proactive recovery strategies to maintain overall muscle function.
Strategies for Managing Muscle Tension
Managing muscle tension effectively requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates both physical and mental strategies. Regular physical activity is one of the best ways to reduce muscle tension. Exercise encourages blood flow and enhances the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, thereby reducing the likelihood of tension-related inflammation.
Stretching and flexibility exercises are also crucial in managing muscle tension. Incorporating practices such as yoga or Pilates can help improve flexibility and promote relaxation within the muscle tissues, easing existing tension and preventing its recurrence.
Additionally, mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises, can play a significant role in alleviating muscle tension. These practices help reduce stress and promote relaxation, which can mitigate the involuntary muscle contractions that contribute to tension.
Combining these strategies into a comprehensive plan can lead to better management of muscle tension, enhancing overall physical health and reducing the risk of inflammation-related complications.
The Impact of Nutrition on Muscle Tension and Inflammation
Nutritional choices can significantly influence muscle tension and inflammation. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help combat chronic inflammation and promote better muscle health. These foods provide essential vitamins and minerals that support muscle recovery and function.
Additionally, hydration is key to preventing muscle tension. Dehydrated muscles can lead to cramping and increased tension, making it essential to maintain adequate fluid intake, especially during physical activities. Electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, also play a crucial role in muscle contraction and relaxation.
Moreover, post-exercise nutrition is vital for recovery. Consuming a blend of protein and carbohydrates after intense workouts can aid in muscle repair and reduce inflammation, helping to shorten the recovery time and maintain healthy muscle function.
In conclusion, understanding the connections between nutrition, muscle tension, and inflammation can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices that enhance muscle health and overall well-being.
The Role of Inflammation in Muscle Health
Understanding Inflammation and Muscle Function
Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injury or stress, playing a crucial role in muscle function and recovery. When muscle tissue is damaged, inflammatory processes are activated to help repair the affected areas. This involves the release of cytokines and other signaling molecules that promote healing and regeneration.
While inflammation is essential for recovery, excessive or chronic inflammation can be detrimental to muscle health. It can lead to a condition known as muscle wasting, where the body breaks down muscle tissue faster than it can be rebuilt. Understanding this balance is key for athletes and individuals engaged in regular physical activity.
Moreover, one of the significant challenges in muscle recovery is distinguishing between normal post-exercise inflammation and that which indicates overtraining or injury. Too much inflammation can hinder performance and recovery, leading to a cycle of fatigue and reduced muscle quality.
To mitigate the negative effects of inflammation, several strategies can be employed, including proper nutrition, hydration, and rest. Anti-inflammatory foods such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants can help manage the body’s inflammatory response, promoting better muscle health overall.
The Impact of Chronic Inflammation on Muscle Recovery
Chronic inflammation can severely impact muscle recovery, influencing the rate at which muscle tissue heals after exercise. Persistent inflammation often results from factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, or underlying health issues. Identifying and addressing these factors is essential for optimal muscle repair and function.
Research has shown that chronic inflammation can impair the activation of satellite cells, which are crucial for muscle growth and repair. This impairment means that the muscle cannot fully recover after intense workouts, leading to decreased muscle strength and endurance over time.
Additionally, athletes may experience prolonged soreness and increased risk of injury when chronic inflammation is present. This situation can lead to decreased training volume and performance, ultimately affecting an athlete’s success in their respective sports.
Effective approaches to reduce chronic inflammation include adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, incorporating regular low-impact exercises, and ensuring adequate sleep. Finding a balanced regimen helps maintain a healthy inflammatory response, promoting efficient muscle recovery and overall performance in physical activities.
Common Causes of Muscle Tension and Inflammation
Understanding Muscle Tension
Muscle tension is a common physical response to various stimuli, including stress, overexertion, and injury. When our muscles are under strain, they can contract and become tight, leading to discomfort and reduced mobility. This tension can also interfere with the body's natural balance, potentially resulting in a cycle of inflammation.
Chronic muscle tension can develop from several lifestyle factors. Poor posture, for instance, can lead to an uneven distribution of pressure across different muscle groups. Over time, this can create persistent tension that triggers inflammation in surrounding tissues.
Additionally, prolonged periods of stress can lead to the body's fight-or-flight response being engaged for too long. This response causes muscles to remain in a state of contraction, which can become detrimental if not addressed through relaxation techniques or physical therapy.
Understanding muscle tension is important because it sets the stage for addressing its underlying causes and developing effective treatment strategies. Awareness of muscle tension can empower individuals to take proactive steps toward alleviating discomfort and preventing further complications.
The Role of Inflammation in Muscle Health
Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or stress, signaling the immune system to begin healing. However, chronic inflammation can have adverse effects on muscle health, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced function. When muscle tissue becomes inflamed, it can impede recovery, making it vital to understand how to manage both muscle tension and inflammation.
One key factor in inflammation is the release of inflammatory substances by the body, often triggered by muscle injury or ongoing tension. These substances can lead to swelling and increase the sensitivity of nerves, contributing to the sensation of pain. Consequently, managing inflammation is crucial for overall muscle recovery and function.
Furthermore, there is a symbiotic relationship between muscle tension and inflammation; prolonged muscle tension can lead to inflammation, and vice versa. This interconnection necessitates a holistic approach for individuals experiencing symptoms related to both muscle tension and inflammation.
Subsequently, understanding how to effectively reduce inflammation—through methods such as properly timed rest, ergonomic adjustments, and anti-inflammatory diets—can significantly improve muscle health and alleviate tension-related symptoms.
Effective Strategies for Relief
To mitigate muscle tension and inflammation, incorporating a well-rounded approach is essential. Regular physical activity is one of the best ways to promote muscle relaxation and blood circulation, reducing the likelihood of tension buildup. Activities such as stretching, yoga, and low-impact exercises can keep muscles supple and minimize inflammation.
In addition to exercise, stress management techniques play a crucial role in alleviating muscle tension. Methods like mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help calm the nervous system, reducing prolonged muscle contractions and promoting relaxation.
Dietary changes can also be beneficial in this regard. Consuming a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods—such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids—can help combat inflammation and support overall muscle health.
Finally, seeking professional help through physical therapy or massage therapy can provide targeted relief. Therapists can assist in identifying muscle groups that are chronically tense and develop personalized treatment plans to improve muscle function and decrease inflammation.
Effective Strategies for Relief

Understanding Muscle Tension and Its Causes
Muscle tension is a common physical condition that affects many individuals, often resulting from physical strain, stress, or poor posture. Identifying the root causes of muscle tension is crucial for effective relief and management. Chronic muscle tension can lead to inflammation, which complicates the healing process and enhances discomfort.
Common causes of muscle tension include overexertion during exercise, prolonged periods of sitting, and stress from daily life. The impact of stress on muscle tension cannot be overstated, as it often results in a cycle of pain and discomfort. Additionally, factors such as dehydration and inadequate nutrition can contribute significantly to the development of muscle tension.
Understanding individual lifestyle choices can help in pinpointing specific triggers for muscle tension. Regular physical activity, stretching, and mindfulness can mitigate these issues and promote healthier muscle function. Addressing muscle tension early on can prevent it from leading to more serious health concerns.
In summary, recognizing the common causes of muscle tension is the first step toward developing effective relief strategies. By being proactive about one's health, individuals can reduce discomfort and improve overall well-being.
Inflammation: A Consequence of Muscle Tension
Muscle inflammation occurs when muscle fibers are damaged or strained, leading to a cascade of biological responses. This response is characterized by swelling, pain, and stiffness in the affected area, making movement difficult. Understanding the link between muscle tension and inflammation can empower individuals to seek proactive treatments.
Chronic inflammation can evolve from untreated muscle tension, leading to long-term pain and mobility issues. This condition can significantly impact one’s quality of life, making it essential to address both muscle tension and inflammation concurrently. Regular assessment of muscle health is vital to prevent such negative outcomes.
Certain lifestyle factors can exacerbate inflammation, including poor diet, lack of exercise, and insufficient sleep. Integrating anti-inflammatory foods and regular physical activity into one's routine can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Ensuring proper hydration and rest is also crucial in this process.
In summary, muscle tension can lead to inflammation, which necessitates a comprehensive approach to treatment. Tackling both conditions can help individuals regain mobility and enhance their quality of life.
Effective Techniques for Relieving Muscle Tension and Inflammation
There are several effective techniques for relieving muscle tension and inflammation, ranging from physical therapy to at-home remedies. Professional treatments, such as massage therapy and chiropractic adjustments, can help restore balance in the musculoskeletal system. Implementing a structured exercise program tailored to individual needs can significantly reduce tension and inflammation.
At home, applying heat or cold to the affected areas can provide immediate relief. Heat stimulates blood flow and relaxes tight muscles, while cold therapy reduces swelling and numbs pain. Additionally, stretching exercises can help to alleviate tightness and improve flexibility.
Mindfulness practices, including meditation and deep-breathing exercises, can also play a role in managing muscle tension. Reducing stress levels in conjunction with physical treatments can enhance recovery. Incorporating relaxation techniques into daily life can lead to long-term benefits.
Ultimately, a combined approach to relieve muscle tension and inflammation is recommended. Combining professional treatment with personal wellness practices can greatly improve overall muscle health and reduce the risk of future complications.