My Left Temple Hurts: Understanding Symptoms and Remedies
Many people experience tension headaches, which are among the most frequently reported types of headaches globally. These headaches typically present as a persistent, dull ache that can vary from slight discomfort to more pronounced pain. The sensation is often likened to a tight band encircling the head, and while not usually severe, the discomfort can significantly interfere with daily routines. Grasping the full picture of tension headaches is vital for proper handling and avoidance.
Stress, anxiety, and improper posture are frequently at the root of these headaches. Pinpointing and tackling these root causes is essential for stopping future occurrences. Noticing the trends linked to your tension headaches enables you to adopt forward-thinking methods for easing pain and boosting general health.
Contributing Factors and Triggers
Several elements can lead to the onset of tension headaches. Emotional and physical stress are common culprits. Maintaining poor posture for extended periods, particularly when sitting with rounded shoulders, can strain muscles in the neck and head, resulting in tension headaches.
Daily habits and nutrition choices also have a notable impact. Insufficient water intake, sleep deprivation, and specific foods or drinks can intensify headache symptoms. Recognizing these triggers allows for customized approaches to control and avert subsequent headaches.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Although tension headaches are often identified by their symptoms, a comprehensive assessment by a medical expert is necessary to eliminate other possible sources of head pain. This process might include a physical check-up, reviewing medical background, and possibly imaging tests if needed.
Precise diagnosis is fundamental for crafting the most suitable treatment strategy. A healthcare provider can assist in identifying the particular triggers and contributing elements for your headaches, paving the way for a tailored pain management plan.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Various treatments exist for tension headaches, from readily available pain medications to more specialized therapies. Common pain relievers can offer short-term respite from discomfort. Practices like controlled breathing and mindfulness can aid in stress reduction, potentially decreasing both the occurrence and severity of headaches.
Adjusting daily routines, such as correcting posture, managing stress, and staying hydrated, often forms the backbone of lasting headache control. Consistent physical activity and a nutritious diet support overall health and may lessen the chances of tension headaches developing.
Alternative Therapies and Complementary Approaches
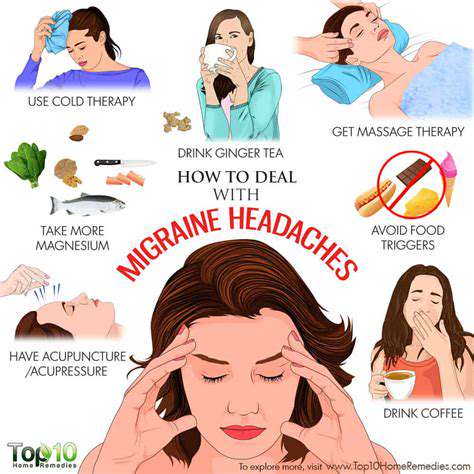
In addition to standard treatments, several alternative and complementary methods might provide relief for tension headaches. Techniques like acupuncture, therapeutic massage, and biofeedback could help reduce pain and encourage relaxation. These approaches can be combined with conventional treatments for a more comprehensive headache management plan.
While these methods may offer supplementary advantages, consulting a healthcare professional before trying them is advisable. This ensures they're safe and appropriate for your specific health situation and requirements.
Prevention and Proactive Measures
Taking preventive steps is key to handling and avoiding tension headaches. Spotting and managing potential triggers, like stress and posture problems, can substantially lower how often headaches occur. Leading a healthy lifestyle, which includes regular workouts, balanced meals, and sufficient rest, is instrumental in minimizing the likelihood of these headaches.
Scheduled pauses and ergonomic improvements in work and home environments can also help prevent tension headaches by encouraging proper posture and easing strain on neck and head muscles. These preventive tactics can markedly enhance life quality for those dealing with tension headaches.
Dental Issues and Their Connection to Left Temple Pain
Possible Dental Issues
Pain in the left temple might occasionally stem from dental concerns, especially those involving the upper left teeth. Various problems, from wisdom teeth complications to tooth decay, can cause pain that spreads to the temple area. Swelling in nearby tooth tissues, or even a sinus infection connected to dental issues, might also play a role. It's important to recognize that dental pain doesn't always stay confined to the tooth; it can appear in other head and facial regions, complicating diagnosis.
For instance, discomfort in the upper left back teeth might sometimes be perceived as a persistent ache or sharp pain in the temple on that side. This happens because nerves and blood vessels in this area interconnect and react to inflammation or pressure.
Sinus Infections and their Connection
Sinus infections, commonly paired with headaches, might sometimes be confused with dental problems. Swelling in the maxillary sinuses, positioned above the upper teeth, can occasionally produce pain that reaches the temple. This is particularly likely if the infection is intense or affects the specific zone near the upper left teeth. Accurate diagnosis demands careful examination to distinguish between dental and sinus-related pain.
Long-term sinusitis, marked by ongoing inflammation and infection, can result in a constant, pulsating ache in the temple, often alongside symptoms like blocked nose, fever, and facial pressure.
Jaw Joint (TMJ) Disorders
Disorders of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) can lead to notable left temple pain. Issues with this joint, such as arthritis, misalignment, or muscle tightness, can generate tension and discomfort that extends to surrounding areas, including the temple. The jaw joint is closely linked to the nerves and muscles of the head and face, making it a possible origin of referred pain.
TMJ disorder signs might include jaw clicking or popping, trouble chewing, and facial pain that spreads to the temple and ear. Determining TMJ as the cause requires specific assessment by a dental or medical specialist.
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is a nerve condition causing sudden, severe, stabbing facial pain. While mainly affecting the face, the pain can sometimes spread to the temple, especially around the upper left jaw area. This condition often relates to irritation or inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, which is key for facial sensation.
Trigeminal neuralgia pain is typically intense and disabling. Immediate medical care is crucial if you suspect this condition.
Other Potential Causes
Various other factors, including migraines, cluster headaches, and even stress, can result in left temple pain. Migraines, for instance, might involve throbbing pain on one side of the head, occasionally reaching the temple. Stress can also lead to muscle tension and headaches affecting the temple region.
A detailed medical history and physical exam are necessary to identify the pain's source and exclude more serious conditions.
When to Seek Professional Help
Persistent or intense left temple pain that doesn't respond to standard pain relievers requires professional evaluation. If the pain comes with other symptoms like fever, swelling, or numbness, prompt medical attention is essential. A dentist or neurologist can accurately diagnose the pain's origin and suggest suitable treatment.
Neglecting ongoing pain can lead to complications. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the underlying issue effectively and preventing additional discomfort or potential health problems.