Pain on the Left Side: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Common Causes of Left-Sided Pain
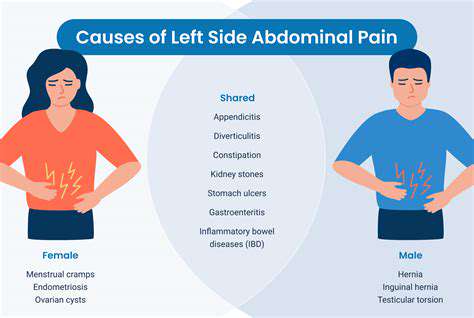
Musculoskeletal Issues
Pain on the left side can often be attributed to musculoskeletal issues, which include strains, sprains, and injuries to the muscles or ligaments. These injuries can occur from activities such as lifting heavy objects or engaging in intense physical exercise. It is not uncommon for individuals to experience discomfort in the left side of the back, potentially resulting from poor posture or overuse of muscles.
In many cases, musculoskeletal pain may be treated effectively with rest and physical therapy. Stretching and strengthening exercises can also help alleviate pain and improve mobility. Ice and heat therapy are often recommended to reduce inflammation and promote healing. If pain persists, consulting a healthcare professional may be necessary for a thorough examination and appropriate treatment plan.
Postural imbalances and repetitive movements may contribute to chronic musculoskeletal pain. It is essential to be mindful of body mechanics during daily activities to minimize strain on the left side. Ergonomic adjustments in the workplace can also play a critical role in preventing discomfort.
Individuals with preexisting musculoskeletal conditions should monitor pain levels closely. Seeking assistance from a physical therapist can provide tailored exercises and advice for managing pain effectively.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Gastrointestinal issues can manifest as pain on the left side, most commonly due to conditions like diverticulitis or colitis. These conditions involve inflammation or infection of the digestive tract and can cause discomfort, cramping, and other digestive symptoms. Individuals may experience changes in bowel habits or abdominal swelling alongside pain in the left abdomen.
It is important to address any gastrointestinal symptoms promptly to prevent complications. In some cases, dietary adjustments can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall digestive health. Additionally, staying hydrated and incorporating fiber-rich foods into the diet are often recommended.
Severe or persistent pain that does not improve with dietary changes may require medical attention. Diagnostic imaging, such as ultrasounds or CT scans, can help identify underlying gastrointestinal conditions. Appropriate treatments may include medication or, in some cases, surgical interventions.
Awareness of the body's signals is crucial, especially when dealing with digestive-related pain. Individuals should seek medical advice if they experience severe pain, fever, or signs of dehydration.
Cardiovascular Concerns
Pain on the left side can sometimes indicate cardiac-related issues, especially if accompanied by other symptoms like shortness of breath or dizziness. Conditions such as angina or even heart attacks may present with left-sided pain, typically radiating from the chest to the arm or shoulder. It is important to recognize these signs and seek immediate medical attention.
Risk factors for cardiovascular problems include age, family history, smoking, and high blood pressure. Individuals with these risk factors should monitor their health closely and engage in preventive measures, such as maintaining a heart-healthy diet and regular exercise. Routine check-ups and discussions with healthcare providers are essential in managing cardiovascular risk.
Understanding the difference between muscular pain and pain that could indicate a heart problem is critical. While not all left-sided pain is related to the heart, being proactive about one’s health can help in early detection and treatment of potential issues.
If experiencing any warning signs related to cardiovascular health, it is crucial to act quickly. Early intervention can lead to better health outcomes and improved quality of life.
Recognizing Symptoms and When to Seek Help
Common Symptoms Associated with Left-Sided Pain
Pain on the left side of the body can manifest in various forms, including sharp, dull, or throbbing sensations. The nature of the pain may provide clues about its underlying cause. For instance, sharp pain could suggest issues with the lungs or heart, while a dull ache might indicate muscular strain or gastrointestinal problems.
Accompanying symptoms can further help in identifying the condition. Common symptoms might include shortness of breath, nausea, or dizziness. These symptoms are critical for establishing whether the pain could be related to a serious condition, such as a heart attack or lung disease.
Additionally, symptoms like swelling, redness, or warmth in the affected area may indicate inflammation or injury. Patients should consider contextual factors such as recent physical activity, trauma, or existing health conditions when assessing their symptoms.
It's important to note that referred pain can complicate diagnosis. For example, pain originating from internal organs, like the spleen or pancreas, may be felt on the left side but stem from issues elsewhere in the body.
Maintaining a symptom diary can help track changes over time and assist healthcare professionals in making an accurate diagnosis. Documenting the onset, duration, and intensity of pain can lead to more effective treatment plans.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Determining when to seek medical help for left-sided pain can be challenging but is crucial for ensuring proper care. If the pain is severe or sudden, it is recommended to seek immediate attention, as it may indicate a life-threatening condition, such as a heart attack.
Other red flags include persistent pain that does not improve with rest or over-the-counter medications. If pain is accompanied by symptoms like chest pain, sweating, or difficulty breathing, it warrants urgent evaluation.
Additionally, if the pain is coupled with gastrointestinal symptoms, such as vomiting or severe abdominal cramping, immediate medical consultation is advisable, as it could be indicative of conditions like pancreatitis or a ruptured spleen.
For chronic pain that gradually worsens over time, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider to rule out potential underlying conditions. Early intervention can prevent complications and lead to more effective treatment strategies.
Finally, if pain interferes with daily activities or quality of life, individuals should not hesitate to seek professional help. Pain management options are available and can significantly improve overall well-being.
Treatment Options for Left-Sided Pain
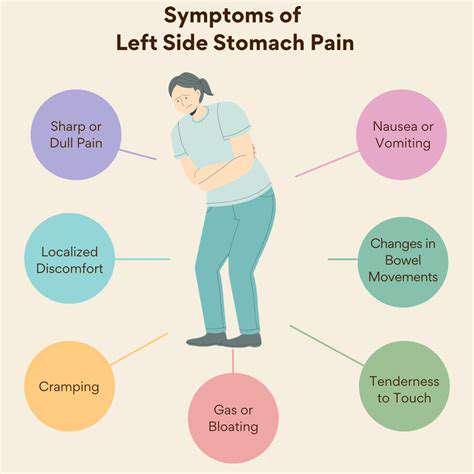
Treatment Overview
Treatment for left-sided pain depends largely on the underlying cause of the discomfort. Addressing the root cause is essential for effective management of symptoms. For instance, if the pain is caused by muscle strain, over-the-counter pain relievers, rest, and physical therapy may be recommended. Conversely, if the pain arises from a more serious condition, such as a heart issue, immediate medical intervention is crucial.
Medical professionals often assess the location, intensity, and nature of the pain to determine the best course of treatment. This comprehensive evaluation helps tailor the treatment plan to the individual patient's needs. After diagnosis, both conservative and aggressive treatments may be employed based on severity.
In some cases, lifestyle modifications play an important role in treatment. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques can contribute significantly to overall pain relief and improve quality of life.
Medications and Physical Therapies
Medications are a common avenue for treating left-sided pain, particularly for conditions like inflammation or chronic discomfort. NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) are often prescribed to alleviate symptoms. In cases of severe pain, stronger prescription medications may be necessary.
Physical therapy can also be a vital component of treatment. A physical therapist can design a customized program that includes exercises and manual therapy techniques aimed at reducing pain and enhancing mobility. Engaging in regular physical therapy can result in significant long-term benefits for those suffering from left-sided pain.
In addition to traditional medications and therapies, alternative treatments such as acupuncture or chiropractic care may provide relief for some individuals. These approaches focus on holistic healing and can work in conjunction with conventional methods for comprehensive care.
Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
Diet plays a crucial role in managing certain types of left-sided pain, especially when related to gastrointestinal issues or inflammation. Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can reduce inflammation in the body. Maintaining a healthy gut can alleviate many symptoms associated with digestive disorders.
Staying hydrated is equally important, as proper hydration supports overall bodily functions and can help manage pain. Avoiding trigger foods, such as those high in sugar or fat, may also make a significant difference for individuals with specific conditions.
Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines can further enhance pain management. Gentle exercises like yoga or swimming can improve flexibility and strength, which may alleviate some causes of left-sided pain.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of left-sided pain may resolve with home remedies or self-care, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical evaluation. For example, persistent or severe pain accompanied by shortness of breath, chest pain, or radiating discomfort may indicate a serious condition, such as a heart attack.
Other alarming signs that should prompt a doctor visit include neurological symptoms like weakness or numbness, high fever, and unexplained weight loss. Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment and can prevent further complications.
It is always best to err on the side of caution. Keeping a detailed record of one's symptoms can help healthcare providers make informed decisions regarding diagnosis and treatment, ensuring the patient's health and safety.