Rebound Headaches: The Danger of Medication Overuse
The Hidden Risks of Overusing Pain Medications
When Relief Becomes a Problem
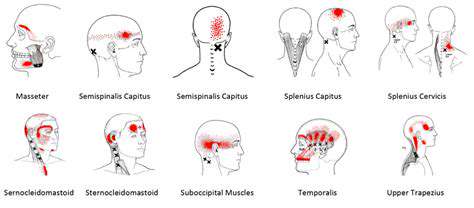
Many people don't realize that their headache medications might actually be making their pain worse. This paradoxical situation occurs when the body becomes dependent on pain relievers, creating a vicious cycle where more medication leads to more headaches. The medical term for this phenomenon is medication overuse headache (MOH), and it affects millions of people worldwide.
Our bodies are remarkably adaptable. When exposed to frequent doses of pain medication, they begin to compensate by becoming more sensitive to pain signals. This adaptation means that when the medication wears off, the pain returns stronger than before. It's like your nervous system is constantly playing catch-up, always trying to compensate for the artificial pain relief.
How Dependency Develops
The process of developing medication dependence is subtle and often goes unnoticed. Initially, the medication works exactly as intended - providing relief from pain. But over time, the body adjusts its natural pain regulation systems to account for the regular presence of the drug. This adjustment can lead to:
- Increased pain sensitivity between doses
- Withdrawal symptoms when medication is delayed
- Reduced effectiveness of the medication over time
What begins as occasional use for legitimate pain can gradually transform into a daily necessity. The line between treatment and dependence can blur without the patient even realizing it.
The Body's Natural Healing Process
Our bodies have sophisticated systems for managing pain and promoting healing. When we interfere with these natural processes through frequent medication use, we might actually be slowing down our recovery. Research suggests that:
- Chronic pain medication use can disrupt neurotransmitter balance
- Sleep patterns often become disturbed
- The immune system may function less efficiently
Perhaps most concerning is how these medications can mask important warning signs. Pain serves an important biological function - it tells us when something is wrong. By constantly suppressing pain signals, we might be ignoring underlying issues that need attention.
Recognizing Medication Overuse Headaches
Key Indicators to Watch For
Medication overuse headaches have several telltale signs that patients and doctors can identify. These headaches typically:
- Occur daily or nearly daily
- Start soon after waking up
- Temporarily improve with medication but return later
As research shows, these headaches often develop after months or years of regular pain medication use. The threshold is surprisingly low - just 10-15 days per month of medication use can trigger the cycle.
Breaking the Cycle
Overcoming medication overuse headaches requires a carefully managed approach. The most effective strategies include:
- Gradual reduction of pain medication under medical supervision
- Implementation of alternative pain management techniques
- Addressing any underlying headache disorders
This process requires patience, as symptoms often worsen before they improve. Most patients experience significant improvement within 2-6 weeks of stopping the overused medication.
Prevention Strategies
The best approach is to prevent medication overuse headaches before they start. Effective prevention includes:
- Limiting acute medication use to 2-3 days per week
- Exploring non-medication treatment options
- Maintaining a headache diary to track patterns
Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider can help catch potential overuse early. Early intervention makes the recovery process much easier.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you suspect you might be experiencing medication overuse headaches, professional guidance is essential. Warning signs that warrant medical attention include:
- Headaches that persist despite medication
- Needing higher doses for the same relief
- Withdrawal symptoms when skipping doses
A qualified healthcare provider can develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses both the medication overuse and any underlying headache disorder. With proper management, most patients can break the cycle and return to healthier pain management strategies.