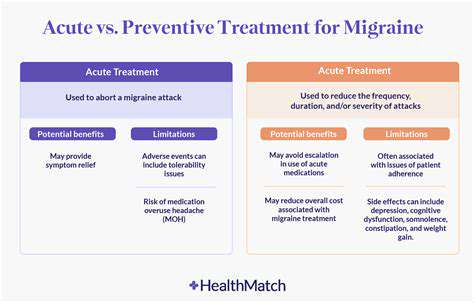
The Use of Peripheral Nerve Stimulators for Headaches
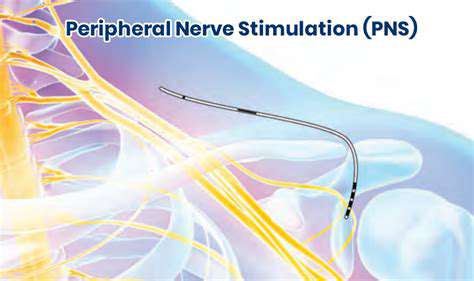

Safety Considerations and Potential Side Effects
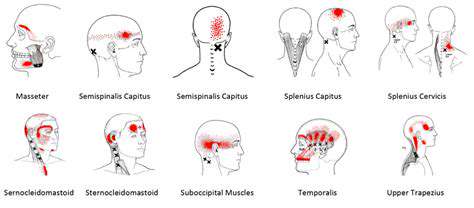
Electrode Placement and Skin Integrity
Proper electrode placement is crucial for ensuring effective peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS) while minimizing the risk of skin irritation and damage. Electrodes should be positioned according to the specific nerve being targeted and should be checked for secure contact throughout the stimulation procedure. Failure to maintain proper electrode contact can lead to inconsistent stimulation, inadequate treatment outcomes, and potentially painful skin reactions. Careful consideration should be given to the skin's condition to avoid potential complications from irritation or infection, particularly in individuals with pre-existing skin conditions or sensitivities.
Maintaining skin integrity is paramount during PNS. Using appropriate electrode gels or conductive pastes can facilitate electrical transmission while protecting the skin from excessive pressure and friction. Regular monitoring of the skin beneath the electrodes is essential. Any signs of redness, blistering, or irritation should be addressed immediately, potentially by adjusting electrode placement, reducing stimulation parameters, or discontinuing the treatment altogether. This proactive approach helps prevent more serious skin complications.
Stimulation Parameters and Duration
Precise control over stimulation parameters, such as intensity, frequency, and pulse width, is critical. Excessive stimulation intensity can lead to discomfort, pain, or even nerve damage. Starting with a low stimulation level and gradually increasing it as tolerated is a crucial safety precaution. Patients should be educated on how to recognize and report any discomfort. This approach allows for personalized adjustments to optimize the treatment effect while minimizing adverse reactions.
The duration of stimulation sessions should be carefully considered and tailored to individual needs and tolerance. Prolonged stimulation sessions might lead to muscle fatigue or discomfort. Regular breaks during treatment can help mitigate these potential side effects. Monitoring the patient's response during the entire stimulation session is essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of the treatment.
Potential for Muscle Contractions and Spasms
Peripheral nerve stimulation can elicit muscle contractions, which is often a desired effect for therapeutic purposes. However, excessive or uncontrolled muscle contractions can lead to muscle spasms or cramping. Careful monitoring of muscle activity is necessary, and adjusting stimulation parameters may be required to ensure that the contractions remain within a comfortable range. This includes understanding the potential for prolonged muscle fatigue and implementing appropriate rest periods.
Adverse Effects on Surrounding Tissues
While generally safe, peripheral nerve stimulation can potentially affect surrounding tissues. Careful consideration must be given to the proximity of blood vessels, nerves, and other sensitive structures. Excessive stimulation may cause temporary or even permanent damage to these surrounding tissues. The stimulation parameters must be adjusted to minimize the risk of any such damage, and regular monitoring of the patient's condition is crucial. Clinical judgment and meticulous attention to detail are paramount to ensuring the safety of the patient.
Patient Education and Informed Consent
Thorough patient education is essential to ensure informed consent and to manage expectations regarding potential side effects. Patients should be clearly informed about the potential risks and benefits of PNS, including the possibility of discomfort, muscle contractions, or skin reactions. Open communication between the patient and the healthcare provider is vital to address any concerns and ensure that the patient understands the procedure and its implications. This includes providing clear instructions on how to report any adverse effects promptly.