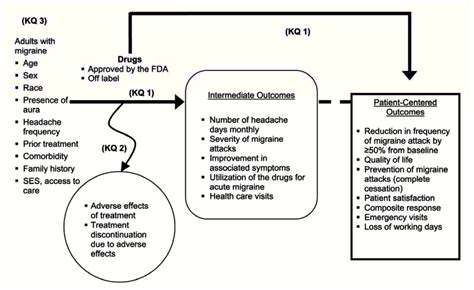
Akupunktur bei Migräne: Evidenz und Wirksamkeit
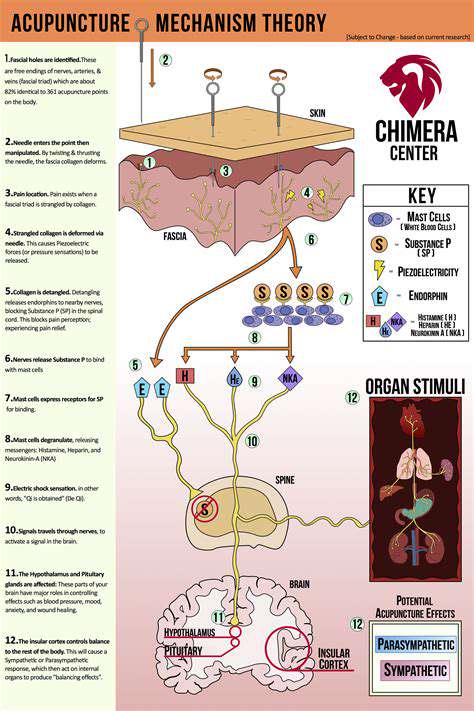
Wirkungsmechanismus: Erste Interaktionen
Während die genauen Mechanismen der Akupunktur weiterhin erforscht werden, haben Forscher mehrere plausible Erklärungen für ihre therapeutischen Wirkungen vorgeschlagen. Der Prozess beginnt, wenn dünne Nadeln in festgelegte Punkte eindringen
Neuronale Bahnen und Reflexe
Die Insertion von Akupunkturnadeln stimuliert spezialisierte Nervenfasern, die als A-Delta- und C-Fasern bezeichnet werden. Diese sensorischen Nerven leiten Signale über Rückenmarkbahnen zu verschiedenen Hirnregionen, einschließlich des Thalamus und des limbischen Systems. Diese neuronale Aktivierung scheint Reflexreaktionen einzuleiten.
Neurochemische Freisetzung und Modulation
Die Akupunktur-Stimulation löst die Freisetzung mehrerer endogener Substanzen aus, darunter Opioidpeptide, die als körpereigene Schmerzmittel wirken. Gleichzeitig beeinflusst sie die Produktion von stimmungsregulierenden Neurotransmittern wie Serotonin und Dopamin. Diese neurochemische M Klinische Beobachtungen deuten darauf hin, dass Akupunktur die Funktion der Hypothalamus-Hypophysen-Nebennierenrinden-Achse normalisieren kann, was möglicherweise ihre stressreduzierenden Effekte erklärt. Die Therapie scheint die Cortisolsekretion zu beeinflussen und möglicherweise andere Hormone zu regulieren, die an Stoffwechsel, Reproduktion und Immunfunktion beteiligt sind. Akupunktur zeigt messbare Auswirkungen auf die Mikrozirkulation, wobei Studien zeigen, dass der lokale Blutfluss an den Nadelstelle erhöht ist. Diese vaskuläre Reaktion kann die Gewebereparatur unterstützen und gleichzeitig Entzündungsmediatoren wie Zytokine beeinflussen. Die scheinbare Fähigkeit der Therapie, Neue Erkenntnisse deuten darauf hin, dass Akupunktur die Immunüberwachung über mehrere Wege verbessern kann, darunter die Stimulation der natürlichen Killerzellenaktivität und die Regulierung der Immunglobulinwerte. Diese immunmodulierenden Effekte deuten auf mögliche Anwendungen bei der Behandlung von Autoimmunerkrankungen hin und Verankert in der traditionellen chinesischen Medizin, basiert die Akupunktur auf dem Prinzip, dass Gesundheit vom ausgewogenen Energiefluss durch Meridianbahnen abhängt. Moderne Interpretationen legen nahe, dass diese Meridiane möglicherweise den Faszienebenen oder Nervenbahnen entsprechen. Die westliche Medizin verwendet evidenzbasierte Protokolle, die durch rigorose klinische Tests entwickelt wurden, und nutzt pharmakologische Interventionen, chirurgische Verfahren und fortschrittliche diagnostische Technologien. Während sie sehr effektiv bei akuten Erkrankungen und Traumata ist, können einige chronische Gesundheitsprobleme davon profitieren Die vielversprechendsten Gesundheitsmodelle kombinieren den ganzheitlichen Ansatz der Akupunktur mit der technologischen Präzision der konventionellen Medizin. Diese integrative Strategie ermöglicht personalisierte Behandlungspläne, die sowohl die Linderung von Symptomen als auch die Behandlung der Wurzelursachen ansprechen.
Auswirkungen auf das endokrine System
Regulation des Blutflusses und der Entzündung
Die Rolle des Immunsystems
Akupunktur verstehen
Konventionelle Behandlungsmethoden im Gesundheitswesen
Komplementäre Ansätze: Integration von Akupunktur und konventionellen Behandlungen