Migraine Management
Pain Relief
HTML
Styling
Dietary Changes
Migraine Prevention
HTML Element
CSS Styling
Combinando Terapias Agudas e Preventivas de Enxaqueca
Alívio Rápido para Ataques Imediatos
Terapias Preventivas de Enxaqueca: Estratégias de Longo Prazo para Redução de Frequência
Modificações Dietéticas para Prevenção da Enxaqueca
Adotar uma dieta amigável à enxaqueca pode reduzir significativamente a frequência e a gravidade dos ataques
Integrando Abordagens Agudas e Preventivas para Resultados Ótimos
Compreendendo a Sinergia de Medidas Agudas e Preventivas
A integração de abordagens agudas e preventivas é crucial para alcançar resultados de saúde ótimos. Esta estratégia holística reconhece que abordar questões imediatas (problemas agudos de saúde)...
Read more about Combinando Terapias Agudas e Preventivas de Enxaqueca
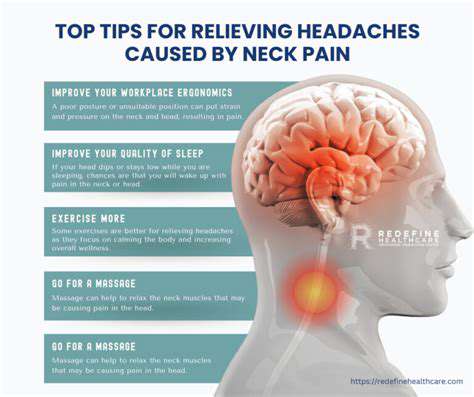
Causas, Impacto e Estratégias de AlívioA dor de cabeça e pescoço é um problema prevalente que afeta muitas pessoas, impactando significativamente a vida diária e a produtividade. Este guia abrangente explora várias causas, desde má postura e tensão muscular até estresse e condições médicas subjacentes. Discute a importância de buscar aconselhamento médico profissional quando a dor persiste, bem como remédios caseiros eficazes e mudanças de estilo de vida que podem aliviar os sintomas. Os principais tópicos incluem: - Impacto na Vida Diária: A dor de cabeça e pescoço pode dificultar atividades rotineiras e criar efeitos em cadeia na saúde mental. - Causas Comuns: Aprenda sobre fatores como tensão muscular, estresse e lesões que contribuem para a dor. - Consulta Médica: Entenda quando buscar ajuda profissional e os benefícios dos tratamentos personalizados. - Remédios Caseiros: Explore estratégias eficazes, como ajustes ergonômicos, exercícios e práticas de atenção plena. - Terapias Alternativas: Descubra como a acupuntura, a terapia de massagem e o quiropraxia podem complementar tratamentos tradicionais. Para aqueles que sofrem de dor de cabeça e pescoço, entender esses elementos é crucial para um manejo eficaz da dor e bem-estar geral. Priorizar uma abordagem holística pode levar a melhorias significativas na qualidade de vida.
Oct 15, 2024
Entendendo a Tensão e a Distensão MuscularExplore as causas da tensão e da distensão muscular, incluindo as respostas fisiológicas ao estresse, esforço excessivo e má postura. Este guia abrangente discute medidas preventivas, como hidratação adequada, técnicas eficazes de alongamento e os benefícios da terapia de calor e frio. Aprenda sobre estratégias de alívio imediato, como massagem e práticas de atenção plena, bem como estratégias de gerenciamento a longo prazo para a saúde muscular. Reconheça os sintomas precocemente e implemente técnicas de autocuidado para abordar o desconforto e melhorar a recuperação. Seja você um atleta, entusiasta do fitness ou uma pessoa sedentária, entender a tensão muscular pode levar a uma melhor saúde e prevenção de lesões.
Jan 13, 2025
Dor de cabeça ao caminhar: Causas e opções de alívio
May 01, 2025
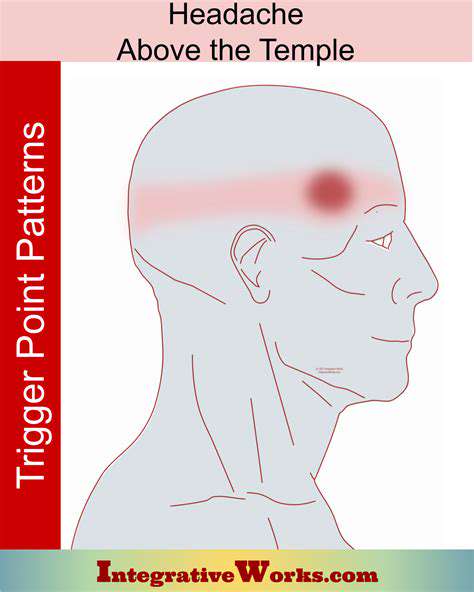
Meu Templo Esquerdo Dói: Entendendo os Sintomas e Remédios
May 01, 2025
Refeições puladas e oscilações de açúcar no sangue como gatilhos de enxaqueca
May 03, 2025
Técnicas de Redução de Estresse para Prevenir Cefaleias
May 05, 2025
Problemas Dentários e Cefaleias: Explorando a Conexão
May 06, 2025
Mudanças no Tempo: Preparando-se para Mudanças na Pressão Barométrica
May 07, 2025
O papel das flutuações hormonais como gatilhos de enxaqueca
May 08, 2025
De Vítima a Vencedor: Uma Mentalidade de Migraine Empoderada
Jun 28, 2025
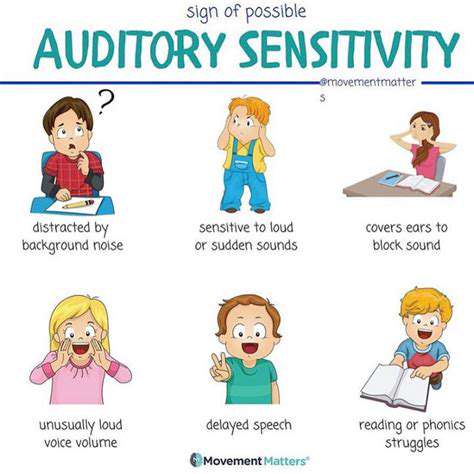
Desencadenantes Ambientais: Sensibilidade à Luz, Som e Olfato
Jul 01, 2025
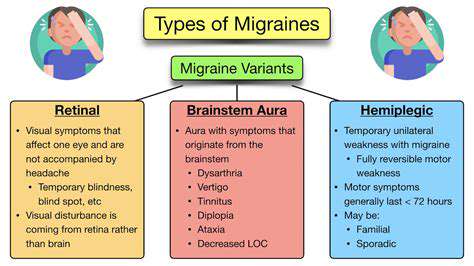
Enxaqueca vs. Cefaleia: Compreendendo as Principais Diferenças
Jul 02, 2025