HTML
CSS
Physiology
Circulatory System
Styling
Risk Management
Project Management
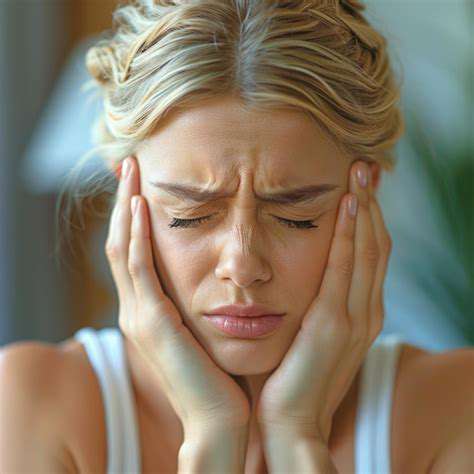
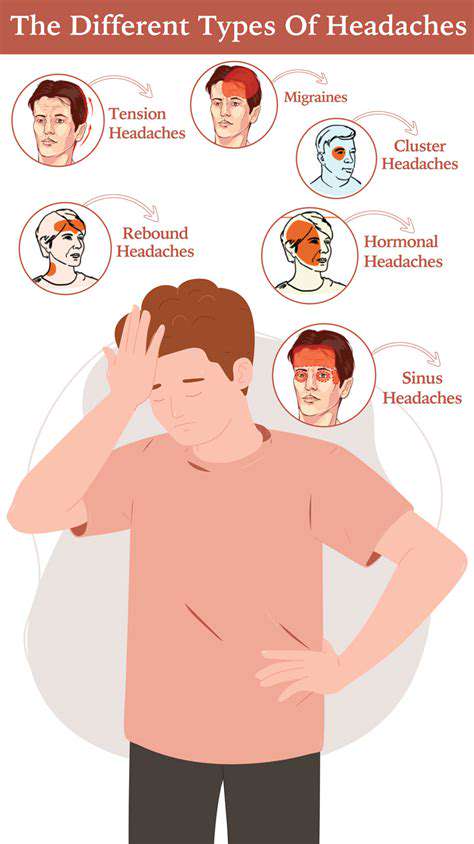
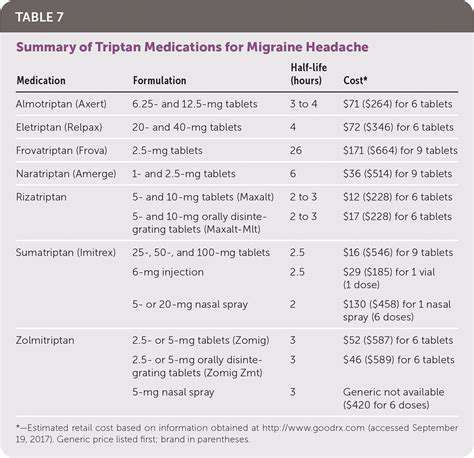
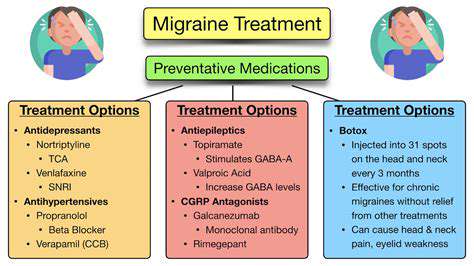
酒精與偏頭痛:了解誘發作用
微妙的平衡

了解血管動力學
血管擴張的重要性
血管擴張代表血管,尤其是從主要動脈延伸出的較小動脈,生理上的擴張。這個生物學上的
規範機制
複雜的控制系統
自主神經系統透過複雜的訊號通路,仔細協調血管擴張和血管收縮之間的錯綜複雜的相互作用。這個神經網路確保根據人體波動的需求精確分配血液流量。
臨床意義
健康後果
血管調節的紊亂可能導致各種醫療狀況。血管舒張受損可能導致高血壓和循環不足,而過度血管舒張則可能導致低血壓,潛在導致暈厥或頭暈
全面風險評估
風險識別
有效的風險管理基礎在於徹底識別所有可能不利於組織目標的潛在弱點和威脅。潛在的脆弱性和威脅。這包括...
實施與監督
計畫執行
應將文件完善的風險回應計畫清楚地傳達給所有利害關係人,確保他們了解各自的責任。這些計畫必須包含處理各種風險情境的詳細程序,從輕微事件到重大緊急狀況