Health
Stress Management
HTML
CSS
Sleep Hygiene
伴隨疾病之頭痛管理 (例如纖維肌痛、腸躁症)
頭痛與慢性疾病的複雜互動

Read more about 伴隨疾病之頭痛管理 (例如纖維肌痛、腸躁症)
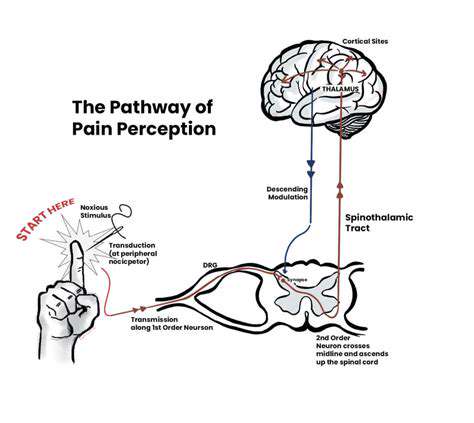
了解常見的嚴重症狀及其含義。本篇文章探討了識別常見嚴重症狀及其對整體健康潛在影響的重要性。從胸痛到無法解釋的體重減輕,以及如焦慮和抑鬱等心理健康問題,了解這些症狀對及時的醫療介入至關重要。文章強調了專業醫療評估和可以減輕嚴重症狀的生活方式改變的重要性。它還凸顯了針對特定警告信號尋求立即幫助的迫切性。通過教育讀者識別症狀並諮詢醫療提供者,該資源旨在使個人能夠優先考慮他們的健康和福祉,以獲得更好的結果。
Nov 07, 2024
理解壓力及其對健康的影響
探索我們全面指南中壓力的複雜性。了解壓力的不同類型——急性、偶發性和慢性——以及它們如何影響心理和身體健康。發現壓力的生物反應,長期壓力的心理影響,以及與生活方式選擇的聯繫。我們提供有效的壓力管理策略,包括正念練習、運動以及建立支持性的社交網絡。了解身體的生理反應和未管理壓力的長期後果。通過識別你的壓力誘因並採取積極的應對策略,你可以改善整體健康,過上更健康、更平衡的生活。
Nov 10, 2024
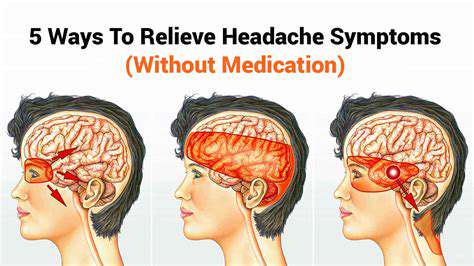
了解常見的頭痛類型及其治療,探索頭痛的類型——從緊張性頭痛和偏頭痛到叢集性頭痛和鼻竇性頭痛。了解這些病症如何隨著時間推進以及可能加重症狀的各種因素。此頁面提供有效管理策略的見解,包括減壓技巧和生活方式改變,以緩解頭痛疼痛。我們還討論了何時需要尋求專業幫助和為慢性頭痛患者制定個性化治療方案。了解如何控制自己的健康,提升生活品質,並找到頭痛的誘因及適當的干預措施。
Nov 17, 2024
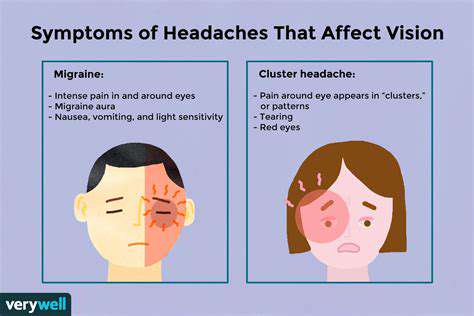
原因與緩解策略 了解眼睛與頭部疼痛的常見原因,包括眼睛疲勞、偏頭痛、鼻竇頭痛等。學習壓力如何影響這些情況,並發現有效的症狀識別方法。了解眼痛與頭痛之間的聯繫,例如緊張性頭痛和偏頭痛。本指南概述了可行的緩解策略,從像20-20-20規則的自然療法到包括處方藥物和專門介入的醫療治療。辨識何時尋求專業幫助對於維持整體健康至關重要。通過了解眼部健康和頭痛之間的複雜關係來增強您的福祉。繼續閱讀,以提升您的舒適感和健康狀況!
Jan 04, 2025
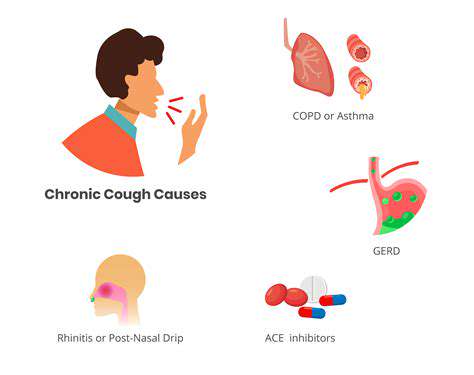
咳嗽引發頭痛的常見原因探索咳嗽引發的頭痛的常見原因,了解這些條件如何導致咳嗽時的疼痛。我們提供全面的指南。從鼻竇炎和偏頭痛到神經系統問題,了解這些疾病如何在咳嗽發作時導致不適。發現伴隨的症狀,如頭暈和鼻塞,以及何時尋求醫療幫助。我們還討論可能的治療方法,包括家庭療法、醫療干預和生活方式的改變,以有效管理因咳嗽引起的頭痛。透過了解這種常被忽視的症狀,增強自己的健康意識,採取積極措施改善健康。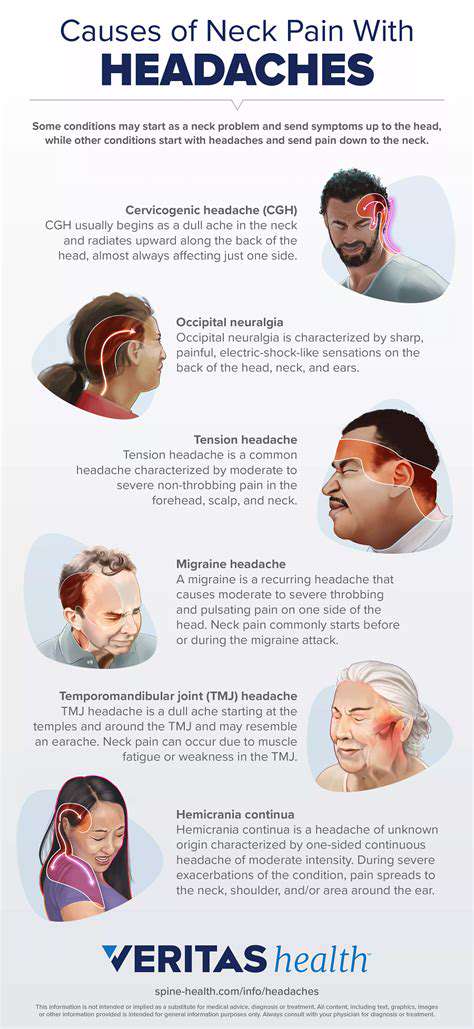
Mar 07, 2025