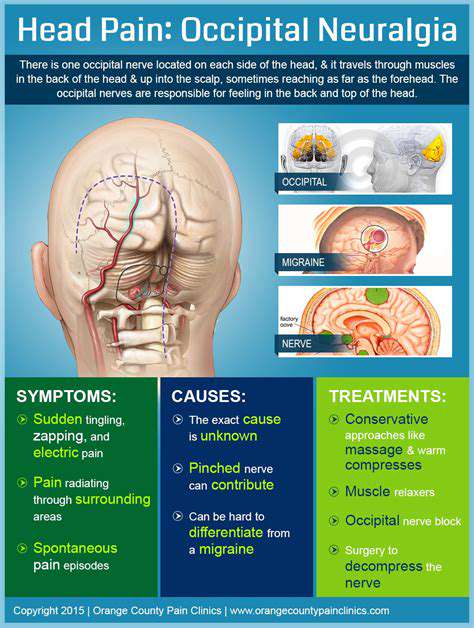
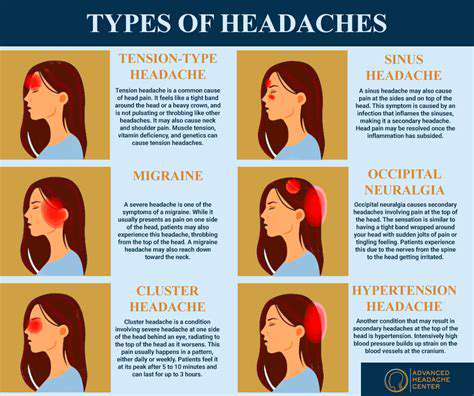
On the other hand, secondary headaches are symptoms of another medical condition. For instance, sinus infections, high blood pressure, or even an injury can trigger this type of headache. Understanding the distinction between these two types is crucial as it influences how they are treated.
Common Causes of Headaches
Identifying the causes of headaches is essential for effective treatment. Stress, dehydration, and poor posture are among the most common triggers for tension headaches. This type of headache often feels like a tight band around your head.
In contrast, migraines can be triggered by a variety of factors, including hormonal changes, certain foods, and environmental changes. According to research, about 12% of the population suffers from migraines, highlighting the need for effective management strategies.
Symptoms of Tension Headaches vs. Migraines
Tension headaches often present as a dull, aching pain that can be accompanied by tightness in the shoulders or neck. The discomfort usually remains moderate and doesn’t impair daily activities. On the contrary, migraines can cause debilitating pain, often accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to light and sound.
Individuals often report a pulsating quality to their migraine pain, which can last for hours or even days. Recognizing these symptoms is vital for timely and appropriate treatment, which varies considerably between these two Types of Headaches.
Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Diagnosing headaches typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and sometimes imaging tests. For tension headaches, over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen are often sufficient. In contrast, treatment for migraines may require prescription medications, including triptans or preventive therapies like beta-blockers.
It's also recommended to keep a headache diary for both types to identify triggers, which can be immensely beneficial for both patients and healthcare providers in managing the condition effectively.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
Making certain lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of headaches. Regular exercise, adequate hydration, and a balanced diet should be key components of your routine. Adequate sleep is also crucial; disruptions in sleep patterns can drastically affect headache occurrence.
Additionally, stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation can help minimize tension headaches. It's often a combination of these changes that yields the best results in preventing both tension headaches and migraines.
When to Seek Professional Help
It's essential to seek medical attention if headaches become more frequent or if their intensity increases. Sudden, severe headaches may indicate a serious condition like an aneurysm or a stroke. Family history or other symptoms accompanying headaches can also warrant a doctor's visit.
Consulting a healthcare professional can provide clarity on the appropriate treatments and necessary lifestyle adjustments. Timely intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from recurrent headaches or migraines.
Defining Migraines

Understanding the Types of Migraines
Migraines are not a one-size-fits-all condition; they come in various forms, each with unique features. The most common type is the migraine without aura, which affects approximately 75% of migraine sufferers. In contrast, migraines with aura, characterized by visual disturbances such as flashing lights or zigzag patterns, affect around 25% of individuals suffering from this condition.
Another notable type is the Chronic migraine, where a person experiences 15 or more headache days per month, with at least 8 of those being migraines. This can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making effective management crucial.
Symptoms: What to Look For
Diagnosing a migraine involves recognizing a variety of symptoms. The primary indicators include severe, throbbing pain, often localized to one side of the head, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light and sound. These symptoms can disrupt daily activities and may last anywhere from a few hours up to three days.
Additionally, many individuals report prodromal symptoms, which can occur a day or two before a migraine strikes, such as mood changes, food cravings, or fatigue, aiding in the early identification of an upcoming attack.
Triggers: Common Causes of Migraines
- Stress and anxiety
- Hormonal changes, especially in women
- Dietary factors, such as caffeine or aged cheeses
- Environmental factors, including strong smells or bright lights
Identifying triggers is vital in managing migraines effectively. Many patients find that stress can be a significant trigger, often leading to a migraine episode after a hectic week at work. Hormonal fluctuations, particularly those related to menstruation, can also exacerbate the frequency of migraines in women.
Managing dietary intake is equally important, as certain foods like aged cheeses, processed meats, and even chocolates may precipitate attacks for some people. Keeping a detailed food diary can help in tracking specific triggers and patterns.
Treatment Options Available
Management of migraines typically involves a dual approach: acute treatment and preventive strategies. Acute treatments aim to alleviate pain during an attack, usually involving over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or prescription medications like triptans. Understanding which medication to use is essential as these drugs act on different mechanisms of migraine physiology.
For chronic sufferers, preventive treatments, including beta-blockers, antidepressants, or newer biologic medications, are often recommended to reduce the frequency and severity of attacks. Speaking with a healthcare provider to tailor a treatment plan is crucial.
Lifestyle Changes for Prevention
Adopting lifestyle changes can significantly reduce migraine frequency. Regular sleep patterns, a balanced diet, and consistent exercise can promote overall wellness and mitigate stress. Managing hydration levels is equally important, as dehydration can trigger headaches for many individuals.
Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can help improve stress resilience, potentially reducing the incidence of migraines over time.
When to See a Doctor
If migraines are frequent or debilitating, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. They will provide a comprehensive evaluation, which may include a medical history review and possibly imaging studies to rule out other conditions. Any changes in headache patterns, including increasing frequency or severity, should be discussed promptly.
Seeking professional help not only aids in accurate diagnosis but also opens the door to receiving effective, tailored treatments. This is especially vital for individuals who experience sudden changes in their migraine pattern or associated neurological symptoms.
The Importance of a Support System
A strong support system plays a crucial role in managing migraines. Family and friends can help create a more understanding environment, providing assistance during difficult migraine days. Education about the condition can empower loved ones, enabling them to support an individual more effectively.
Support groups, both in-person and online, offer valuable platforms for sharing experiences, tips, and coping strategies. Engaging with others who understand these challenges can alleviate feelings of isolation, promoting better management of this often debilitating condition.
Diagnostic Approaches
Types of Headaches: A Comprehensive Overview
Headaches can be classified into several categories, with Tension-type headaches and migraines being the most prevalent. Tension-type headaches are often characterized by a dull, persistent ache across the forehead or at the back of the head, resulting from muscle tension or stress. In contrast, migraines are typically more severe, often accompanied by additional symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light and sound.
Other types include cluster headaches, which occur in cyclical patterns, causing intense pain on one side of the head. Sinus headaches are linked to inflammation of the sinuses, often presenting with nasal congestion. Understanding these nuances helps in effective diagnosis and treatment.
Clinical Evaluation and Symptom Assessment
The Clinical evaluation of headaches primarily involves a thorough patient history and symptom assessment. It's crucial for healthcare providers to gather detailed information about the frequency, duration, and intensity of the headaches, as well as any previous medical history and family history of similar conditions. This data can often paint a clear picture and guide the healthcare professional in making an accurate diagnosis.
Additionally, tools like the Headache Impact Test (HIT-6) can be utilized to understand how headaches affect daily life and overall well-being. This structured assessment allows the clinician to quantify the impact, helping tailor an effective treatment plan.
Role of Diagnostic Imaging in Headache Evaluation
In certain cases, diagnostic imaging may be necessary to rule out more severe underlying conditions. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computed Tomography (CT) scans can help identify abnormalities such as tumors, lesions, or structural issues within the brain. These imaging techniques provide essential information that can alter treatment pathways significantly.
However, it’s essential to balance the benefits of such imaging with potential risks, including radiation exposure with CT scans. In most routine headache cases, imaging is not needed unless specific red flags are present, such as sudden changes in headache pattern or additional neurological signs.
Diagnostic Criteria Established by the International Classification of Headache Disorders
The International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD) provides established criteria for diagnosing different types of headaches, enhancing the consistency of diagnosis among clinicians. For migraines, the criteria include the presence of at least five attacks meeting specific features such as unilateral location, pulsating quality, and exacerbation by physical activity, along with nausea or photophobia.
Using these internationally recognized criteria ensures that patients receive appropriate treatment for their specific headache type, minimizing the chances of misdiagnosis. Compliance with these standards is vital within clinical practice, offering a systematic approach to headache management.
Patient Education and Self-Management Strategies
Educating patients about their condition plays a critical role in the management of headaches and migraines. Providing literature on triggers, lifestyle modifications, and effective coping strategies can empower patients to take charge of their health. Common triggers include stress, specific foods, and irregular sleep patterns, making it essential for individuals to identify and manage these factors proactively.
Self-management techniques, like regular exercise and mindfulness practices, can significantly alleviate symptoms for some individuals. Many healthcare providers advocate for a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapies, leading to improved outcomes.
Consulting Specialists for Comprehensive Care
In some cases, referring patients to specialists such as neurologists or headache clinics may be warranted, especially for those with chronic migraines resistant to standard treatments. Specialists can offer advanced therapeutic options like Botox injections, neurostimulation, or custom-tailored medication regimens designed for chronic headache management.
A multidisciplinary approach involving dietitians and psychologists can also enhance treatment efficacy. By considering various aspects of a patient's life, specialists can help address underlying issues that contribute to headache frequency and severity.
Effective Treatments and Management

Understanding Headache Treatments
- Oral medications such as NSAIDs are commonly effective for mild headaches.
- For some individuals, preventive treatments may be necessary, including prescription medications.
- Alternative therapies, including acupuncture, can also provide relief.
For many, over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen are the first line of defense against headaches. These drugs can be effective in numbing the pain and reducing inflammation. They are generally safe when used as directed, but it's essential to monitor the dosage to prevent side effects.
Interestingly, chronic headache sufferers might find relief through preventive medications, such as beta-blockers or antidepressants. These treatments not only reduce the frequency of headaches but also help manage their intensity, demonstrating a multifaceted approach to care.
Managing Migraines Effectively
- Migraine-specific treatments like triptans provide targeted relief.
- Botox injections have emerged as a promising preventive strategy for chronic sufferers.
- Maintaining a migraine diary can help identify triggers.
When it comes to migraines, identifying the right treatment is crucial. Many individuals benefit from medications known as triptans, which work by constricting blood vessels and blocking pain pathways. Such medications can significantly reduce migraine duration and intensity, allowing patients to regain control of their lives.
In addition to pharmacological options, Lifestyle changes can serve as effective management strategies. Regular exercise, adequate hydration, and sleep hygiene aren't just buzzwords—they form part of a practical toolkit. Many patients report a notable difference when they adopt these simple, yet impactful, measures.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing Severe Symptoms
It’s crucial to distinguish between a typical headache and one requiring immediate medical attention. Symptoms that are severe or unusual can indicate more serious conditions, such as meningitis or brain tumors. If you experience a headache that suddenly becomes the worst pain you have ever felt, or headaches accompanied by confusion, seizures, or loss of consciousness, you should seek emergency care. Research suggests that these symptoms can signal elevated intracranial pressure or other critical health issues.
Additionally, Headaches Following a head injury should never be overlooked. The CDC reports that these types of headaches can indicate traumatic brain injury, which could lead to significant complications. In these cases, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider immediately to prevent any long-term damage and to receive the necessary evaluation and treatment without delay.
When to Be Concerned About Recurrence
If you find yourself experiencing headaches more frequently than usual, it may be time to assess the pattern. Research shows that chronic headaches can impact life significantly, often requiring a comprehensive treatment plan. If you notice a shift in frequency, intensity, or duration of your headaches, tracking these changes in a diary can be helpful. Documenting when the headaches occur, their severity, and any accompanying symptoms can provide valuable information to your healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.
Moreover, it's important to be attentive to how headaches disrupt daily activities. If you find that headaches are affecting your work performance or social interactions, it implies a level of seriousness that should not be ignored. Many people benefit from a proactive approach, seeking professional help even if symptoms seem manageable. A specialist may offer preventive strategies or medications that could reduce the incidence and severity of migraines or headaches.