Every Time I Cough My Head Hurts: Possible Reasons
The Connection Between Coughing and Head Pain
The Physiology of Coughing
Coughing is a reflex action that forces air out of the lungs, which can trigger a number of physiological responses in the body. The sudden contraction of the diaphragm and abdominal muscles during a cough can cause tension in the head and neck region, leading to localized pain. This is especially true if the coughing is frequent or vigorous, as it can strain the muscles in that area.
When you cough, the increase in intrathoracic pressure can also affect blood flow, potentially resulting in temporary headaches. The connection between coughing and headaches is particularly significant in individuals who have underlying conditions that affect their respiratory or nervous systems.
Moreover, if the coughing is associated with other symptoms like congestion or post-nasal drip, it may exacerbate sinus pressure and trigger sinus headaches. Thus, understanding the interplay between these actions is essential for addressing both coughing and head pain effectively.
Potential Underlying Conditions
Chronic coughs may stem from various medical conditions such as allergies, asthma, or even respiratory infections. Each of these conditions can produce inflammation that not only leads to coughing but can also cause headaches due to increased pressure and muscle strain in the head.
The presence of migraines or tension-type headaches in conjunction with coughing could indicate a more complex interplay of factors involving the nervous system. A healthcare professional can help determine if there is a significant correlation between your coughing and headache symptoms, allowing for more targeted treatments.
Additionally, conditions like hypertension or sinusitis might contribute to both persistent coughing and head pain. It is crucial to keep track of your symptoms and consult with a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation to rule out serious underlying issues.
Common Causes of Cough-Related Head Pain

Understanding the Connection Between Coughing and Head Pain
Coughing, although a common reflex, can lead to a variety of physical reactions in the body. One such reaction is pain in the head, which some individuals may experience after persistent coughing. This pain can be attributed to the intense muscle contractions that occur during a cough. When these muscles around the head and neck tense up, it can result in headaches or even migraines for some people.
Moreover, the pressure created in the chest and throat during coughing may also lead to a temporary increase in intracranial pressure, which could contribute to discomfort. It's important to recognize that not all headaches following a cough are the same; they can vary in intensity and duration.
Additionally, for people with pre-existing conditions such as sinusitis or asthma, coughing can exacerbate head pain due to inflammation and irritation. Understanding the underlying mechanisms can help in managing and alleviating these painful episodes.
Being aware of these connections can aid individuals in discussing their symptoms with healthcare providers, ensuring they receive proper care for both their cough and associated head pain.
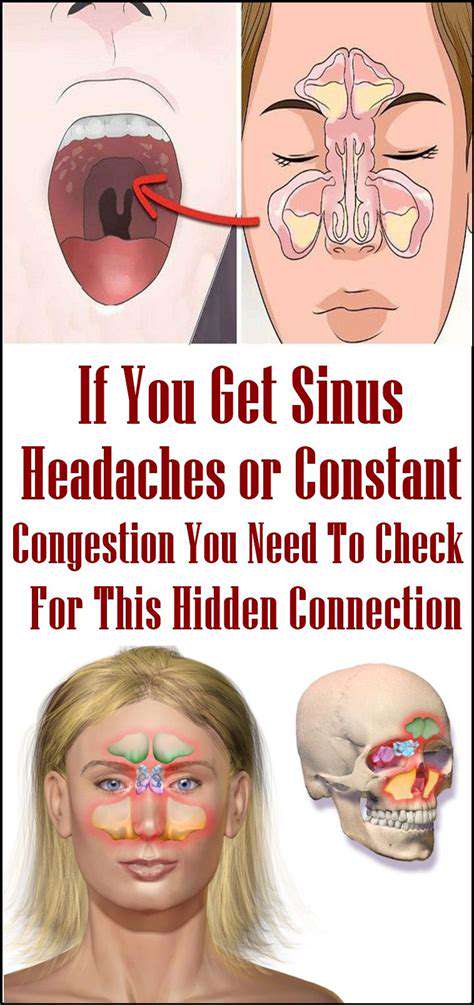
Sinus Issues and Cough-Related Headaches
Sinusitis is a common condition where the sinuses become inflamed, often leading to congestion and a cough. When inflammation occurs, it can cause pressure in the head, leading to pain that may worsen with coughing. This pressure can also result in throbbing headaches or facial pain. Thus, a persistent cough may be a symptom of a sinus issue rather than an isolated problem.
Individuals suffering from allergies or upper respiratory infections may experience similar symptoms owing to mucus build-up. As mucus accumulates, it increases pressure in the sinuses, which can make coughing even more painful.
Treatment typically focuses on addressing the underlying sinus issue, utilizing decongestants or antihistamines to relieve symptoms. Adequate hydration and steam inhalation can also assist in clearing congestion and reducing head pain.
Awareness of sinus health and its impact on coughing can empower individuals to take preventive measures, such as managing allergies and recognizing early signs of sinusitis.
Muscle Strain from Persistent Coughing
Persistent coughing can lead to muscle strain in the neck, back, and abdominal regions. Each cough requires a sudden contraction of multiple muscle groups, which can lead to soreness and pain over time. These strains can be particularly pronounced in individuals with chronic cough conditions. This muscle discomfort can radiate to the head, contributing to overall head pain.
People with chronic cough conditions, such as chronic bronchitis or COPD, are especially vulnerable to these strains. In such cases, it’s crucial to address not just the cough itself, but also the resultant muscle tension that can cause further distress and discomfort.
Incorporating stretching exercises or gentle movements may help relieve muscle tension associated with persistent coughing. Physical therapy may also be a beneficial option for those experiencing ongoing pain due to coughing.
Recognizing the signs of muscle strain can facilitate timely interventions and improve overall quality of life for individuals who cough frequently.
Coughing and Migraines: A Complex Relationship
For some individuals, coughing can trigger migraines or severe headaches. This can be particularly troubling for those who already suffer from migraines as the act of coughing changes intracranial pressure and may provoke an episode. Understanding this trigger is vital for individuals looking to manage their migraine conditions effectively.
Research indicates that the forceful contraction of abdominal and thoracic muscles during a cough may lead to vascular changes in the brain, which can initiate a migraine response. For migraine sufferers, it’s essential to recognize when coughing may be an associated trigger.
Managing cough and addressing its underlying causes can ultimately help mitigate the frequency and severity of migraine headaches for these individuals. Preventive migraine medications may also be considered alongside treatments for cough.
Open discussions with healthcare professionals about both migraines and any potential coughing issues can lead to more comprehensive care tailored to individual needs.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While occasional head pain from coughing can be common and manageable, there are times when it is necessary to seek medical attention. If head pain persists or is accompanied by other severe symptoms such as fever, vision changes, or neurological deficits, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. Such symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires immediate evaluation.
Furthermore, if coughing lasts for an extended period or worsens, it may signal an underlying respiratory condition that needs to be addressed. Often, chronic coughs require a thorough medical assessment to determine their cause and appropriate treatment.
Keeping a symptom diary, noting the frequency, intensity, and any other accompanying symptoms can help healthcare providers make more accurate diagnoses. This proactive approach can significantly impact treatment effectiveness and overall health outcomes.
Continuous communication with healthcare professionals can lead to a clearer understanding of one's health concerns, especially those involving intertwined symptoms like cough and head pain.
When to Seek Medical Attention

Understanding the Symptoms
When experiencing a headache with each cough, it's crucial to assess the characteristic nature of the headache. Determine whether the pain is sharp, dull, or throbbing. This can help in identifying the underlying causes. Additionally, timing can also be relevant; notice if the headache occurs immediately or lingers after the cough.
Document any other symptoms that accompany this headache. For instance, fever, nausea, or sensitivity to light can suggest a more serious condition. It's important to keep a detailed record of your symptoms for reporting to your healthcare provider.
Understanding if this is a new symptom or a recurring issue can provide insights into potential triggers. Recurring symptoms could indicate chronic conditions that need evaluation. In contrast, sudden onset headaches could signal an acute issue requiring immediate attention.
Consider the frequency and intensity of your cough as well. A cough associated with a respiratory infection may lead to strain on the head and neck, resulting in discomfort. If the cough is severe, this could exacerbate headache pain.
Also, paying attention to any recent activities or changes in your environment is essential. Stress, dehydration, or exposure to allergens can significantly affect both coughing and headache symptoms.
Common Causes of Headache with Coughing
Several conditions can lead to headaches exacerbated by coughing. Sinusitis is a common cause where inflammation in the sinuses leads to increased pressure and pain, especially when coughing. This condition often presents with nasal congestion and facial pain.
Another potential cause is tension headaches, which can be triggered by the physical strain of coughing. The muscles in the neck and scalp tighten, leading to referred pain in the head. Understanding your posture while coughing can also contribute to the intensity of this headache.
Coughing fits associated with a respiratory infection can lead to exertion headaches. This happens due to strain during the cough, activating pain pathways in the brain. In these cases, treating the underlying infection often helps reduce headaches.
Allergies and irritants can lead to post-nasal drip, also contributing to headache development. The constant irritation can result in inflammation that may trigger headaches when coughing. Keeping environments allergen-free can reduce both cough and headache occurrences.
Certain serious conditions, although rare, can also cause a headache with coughing. These include conditions like intracranial hypertension or even tumors. If symptoms are persistent or worsening, seeking immediate medical evaluation is advised.
When to Seek Help
Knowing when to seek medical attention is critical for your health. If headaches persist despite treatment or are accompanied by other severe symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider. This is especially true for symptoms like vision changes or significant nausea.
It is advisable to seek help if your headaches occur suddenly and are of severe intensity, often described as a "thunderclap" headache. Such headaches can indicate serious underlying issues that need urgent care.
Headaches along with neurological symptoms such as weakness, or difficulty speaking should not be ignored. These symptoms may suggest a stroke or other acute neurological conditions requiring prompt intervention.
Additionally, if over-the-counter medications do not alleviate headaches or coughing discomfort, professional assessment should be sought. Persistent coughing may need diagnostic tests to determine the underlying issue.
Lastly, if lifestyle modifications, such as hydration and rest, do not lead to symptom improvement, it's time to consult a healthcare professional. Early evaluation can prevent potential complications and lead to more effective treatment plans.
Managing Cough and Associated Head Pain
Understanding the Connection Between Coughing and Head Pain
Coughing is a common reflex action that helps clear the airways of irritants, mucus, or foreign substances. However, it can sometimes lead to discomfort or pain in the head. Understanding why these two symptoms are connected can help you manage them better.
When you cough, your body experiences a sudden increase in pressure in the chest and head. This can cause strain in various areas, particularly in the sinus cavities, leading to headaches. The intensity and duration of the cough play a significant role in the severity of the head pain experienced.
In addition, persistent coughing, often seen in conditions such as bronchitis or allergies, can lead to tension-type headaches. This occurs as the muscles around the neck and scalp tighten in response to the discomfort caused by frequent coughing.
Moreover, the nature of the cough itself—whether it is dry or productive—can influence head pain. A dry cough may cause irritation in the throat and lead to increased tension, while a productive cough, which brings up mucus, might be associated with sinus pressure and congestion, both of which can contribute to headaches.
Recognizing the specific type of cough you have can help in identifying the underlying issues causing your headaches. Keeping a record of your symptoms can be instrumental in discussions with healthcare professionals.
Common Conditions Leading to Cough and Head Pain
There are several medical conditions where coughing and head pain are commonly reported together. Identifying these conditions can aid in seeking appropriate treatment measures.
One of the most prevalent causes is sinusitis, an inflammation of the sinus cavities that can lead to coughing due to post-nasal drip. This condition often results in significant pressure and pain around the forehead and eyes.
Another condition is bronchitis, which causes persistent coughing and can result in referred pain to the head from muscle strain or irritation. Viral infections often accompany bronchitis, exacerbating symptoms and causing further discomfort.
Allergic reactions can also be a culprit. Allergens may trigger coughing and inflammation in the nasal passages, leading to sinus headaches due to mucus buildup. Identifying allergens and reducing exposure may alleviate both symptoms.
Lastly, conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can lead to coughing that irritates the throat, causing headaches as a secondary symptom. Addressing these underlying conditions can help manage both the cough and the head pain more effectively.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of cough and head pain can be managed at home, there are specific circumstances in which you should seek medical attention. If your symptoms persist for more than a week, it may be time to consult a healthcare provider.
Severe headaches that accompany symptoms like fever, neck stiffness, or confusion warrant an immediate visit to a doctor, as these could indicate serious underlying conditions such as meningitis or a brain injury.
Additionally, if the cough persists and is accompanied by blood or unusual color in mucus, it could indicate a more serious respiratory issue that needs prompt evaluation.
If over-the-counter medications do not relieve your symptoms after a few days, professional assessment may be necessary. Healthcare providers can offer treatments that are more effective for specific conditions.
It's essential to trust your instincts about your health. If something feels off or if the symptoms worsen, don't hesitate to seek medical guidance.
Home Remedies to Alleviate Coughing and Head Pain
For many individuals, home remedies can provide significant relief from coughing and associated head pain. Staying well-hydrated is paramount, as fluids can help thin mucus and soothe throat irritation.
Steam inhalation is another effective remedy, as it can open nasal passages and relieve sinus pressure, reducing headaches associated with congestion. You might try taking a hot shower or using a humidifier.
Over-the-counter medications, such as cough suppressants or decongestants, can also be beneficial. These medications work by alleviating the cough reflex or reducing sinus pressure, which may subsequently ease headache symptoms.
Natural remedies, such as honey or ginger tea, have also been reported to soothe coughs and provide anti-inflammatory benefits, potentially helping to reduce head pain as well.
Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or mindfulness meditation, can alleviate muscle tension in the neck and head, offering further relief from pain induced by coughing.
Preventive Measures for Coughing and Head Pain
Taking steps to prevent cough and head pain can drastically improve your quality of life. One effective strategy is to avoid known allergens and irritants. Keeping your living space clean and free from dust can significantly reduce allergic reactions.
Maintaining a strong immune system through a healthy diet can also help. Consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains boosts your immunity and may decrease the likelihood of respiratory infections that lead to coughing.
Regular exercise has multiple benefits as well, improving respiratory health and enhancing overall well-being. Engaging in physical activity can help clear the airways and reduce stress, which has been linked to tension headaches.
Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals, can further reduce your chances of getting colds or the flu, which are common triggers for persistent coughing.
Finally, staying up to date on vaccinations, such as the flu shot and pneumonia vaccine, helps protect against infections that can cause coughing and associated complications.