Forehead Hurt: Understanding Symptoms and Treatments
1. Tension Headaches
What Are Tension Headaches?
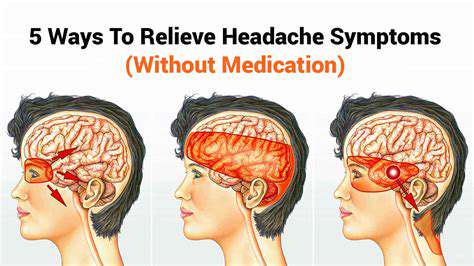
Tension headaches are the most common type of primary headache. They are characterized by a dull, aching pain and a sensation of tightness around the forehead. Many people experience these headaches as a result of stress, anxiety, or muscle tension in the neck and shoulders. Understanding the nature of tension headaches can help in managing them effectively. Unlike migraines, they do not usually come with nausea or sensitivity to light.
They can last for a few hours or several days, depending on the individual and the underlying causes of the headache. Recurring episodes can interfere with normal activities and impact overall quality of life. Therefore, identifying triggers is crucial for those who suffer from frequent tension headaches.
Some common culprits behind tension headaches include posture problems, not enough sleep, and prolonged screen time. Addressing these factors through lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce their frequency. Recognizing and modifying lifestyle habits is key to preventing future bouts of tension headaches.
Tension headaches can be classified into episodic or chronic forms, which help in determining the most effective treatment strategies. Episodic tension headaches occur less than 15 days per month, while chronic tension headaches occur more frequently.
Searching for remedies or treatment options is essential for alleviating the discomfort associated with tension headaches. Many individuals turn to over-the-counter medications, lifestyle changes, and stress management techniques to find relief.
Symptoms of Tension Headaches
The primary symptom of tension headaches is a dull, aching pain that is often described as a tight band around the head. This feeling can be accompanied by tenderness in the neck, shoulder, and scalp muscles. People suffering from tension headaches may experience a constant pressure sensation rather than sharp pains.
In addition to the aching, some individuals may notice that their concentration levels decline when they have a tension headache. This can make it challenging to complete daily tasks effectively. Identifying these symptoms early can lead to prompt management and prevention.
Another symptom includes a mild sensitivity to light and sound, though it is usually less severe than in migraines. Many patients also report that they feel irritable when experiencing these headaches. It’s important to acknowledge these symptoms to create appropriate treatment plans.
Some may even experience tightness in the jaw or temples, often linked to physical stressors such as grinding teeth. Keeping track of these symptoms can help establish patterns that lead to more effective interventions.
For individuals who experience frequent tension headaches, maintaining a headache diary can be an effective tool. It helps in pinpointing triggers and developing coping strategies tailored to their unique situations.
Causes of Tension Headaches
The exact cause of tension headaches is not entirely understood, but they are often connected to various lifestyle factors. Stress is a major contributor, as emotional and mental strains can trigger muscle tension, leading to headaches. This can stem from work, family issues, or other personal challenges.
Poor posture while sitting or standing, especially during extended periods of work, can also result in tension headaches. Slouching or leaning forward can stress the neck and shoulder muscles. Maintaining good posture is vital for minimizing the risk of tension headaches.
Additionally, inadequate hydration and improper nutrition can play a role in triggering tension headaches. Skipping meals or consuming excessive caffeine can lead to dehydration and headaches. Ensuring a balanced diet and staying hydrated can significantly reduce headache occurrences.
Sleep disturbances, including insomnia or irregular sleep schedules, are frequently reported by individuals suffering from tension headaches. Proper sleep hygiene can stabilize sleep patterns and lessen headache frequency. It’s important to develop consistent sleep routines to promote better rest.
Over time, certain repetitive motions or an unchanging work environment can contribute to chronic muscle tension, leading to persistent headaches. Identifying and modifying these repetitive stressors can be essential in preventing ongoing tension headaches.
Treatment Options
Treatment for tension headaches typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medication. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen are often effective in managing pain. It’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider for personalized treatment plans, especially for recurring headaches.
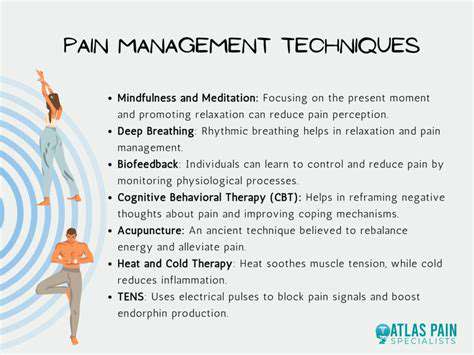
Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga can also help reduce stress and muscle tension. Incorporating these techniques into a daily routine can assist in lessening headache frequency. Regular relaxation practices are an important component of managing tension headaches.
Physical therapy may be beneficial for those dealing with chronic tension headaches, as it can address muscle tightness and strengthen affected areas. Additionally, massage therapy can relieve muscle tension and promote relaxation. Many individuals find these treatments effective for headache relief.
In some cases, preventive medications may be prescribed by a healthcare professional for those who experience chronic tension headaches. These may include antidepressants or anticonvulsant medications that help stabilize nerve activity and reduce headache frequency.
Lastly, lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, adequate hydration, and maintaining a balanced diet significantly contribute to the overall management of tension headaches. Developing healthy habits supports not only headache prevention but also overall physical and mental well-being.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While tension headaches are common and often manageable, there are instances when medical advice is necessary. If the headaches become significantly more intense or frequent than usual, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. Unexplained changes in headache patterns warrant investigation.
Additionally, if headaches are accompanied by other symptoms such as visual disturbances, severe nausea, or neurological changes, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial. These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition. Understanding when to seek help can lead to timely interventions and better outcomes.
Individuals should also reach out for support if their headaches interfere with daily activities or quality of life. Healthcare providers can assist in developing an effective management plan that aligns with the individual's needs.
In case of severe, sudden-onset headaches or headaches following a head injury, emergency medical attention is required. These situations could signify conditions such as migraines, stroke, or aneurysms.
Establishing an open line of communication with a healthcare provider can demystify headache disorders. This proactive approach can lead to tailored treatment options and better long-term management of tension headaches.
2. Sinusitis
What is Sinusitis?
Sinusitis, commonly referred to as a sinus infection, occurs when the tissues lining the sinuses become inflamed and swollen. This condition can be triggered by infections, allergies, or irritants in the environment. When the sinuses are unable to drain properly, mucus builds up, leading to increased pressure and pain.
There are two main types of sinusitis: acute and chronic. Acute sinusitis typically lasts for a short duration, usually up to four weeks, while chronic sinusitis can persist for months or even years. Understanding the type of sinusitis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment.
Common symptoms of sinusitis include facial pain and pressure, particularly around the cheeks, eyes, and forehead. Other symptoms may include nasal congestion, thick nasal discharge, reduced sense of smell, and sometimes fever. Identifying these symptoms can help in seeking timely medical attention.
Sinusitis can result from various factors, including allergies, colds, and other respiratory infections. Identifying the underlying cause is vital in formulating an effective treatment strategy to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
If left untreated, sinusitis can lead to complications such as the spread of infection to nearby structures, including the eyes or brain. Therefore, timely diagnosis and treatment are essential to avoid further health issues.
Treatment Options for Sinusitis
The treatment for sinusitis largely depends on its cause, severity, and duration. For acute sinusitis, the initial approach often includes rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications to relieve pain and congestion. Decongestants may also help reduce sinus pressure and improve breathing.
In cases where a bacterial infection is suspected, a healthcare professional may prescribe antibiotics. It is important to complete the entire course of antibiotics even if symptoms improve, to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
Chronic sinusitis often requires a more comprehensive approach. Nasal corticosteroids can reduce inflammation, and saline sprays or rinses may help to keep the nasal passages moist and clear. Allergy management is also key for patients who suffer from sinusitis triggered by allergens.
In severe cases or when conservative treatments have failed, surgical options, such as endoscopic sinus surgery, might be considered to improve drainage and alleviate symptoms. This procedure can help clear blocked sinuses and improve the quality of life for patients suffering from chronic sinusitis.
It’s essential for individuals experiencing symptoms of sinusitis to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. Each case may require a unique approach to achieve the best outcome and relieve discomfort effectively.
3. Migraine Attacks
What Are Migraine Attacks?
Migraine Attacks are a type of headache that often presents with intense, throbbing pain on one side of the head. They can be debilitating and may last from a few hours to several days, making it challenging to perform daily activities. Many people experience additional symptoms beyond headache pain, such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
Migraines can vary widely in frequency and intensity, with some individuals experiencing them occasionally while others may have chronic migraines. These attacks can be triggered by a variety of factors, including hormonal changes, stress, certain foods, and environmental changes. Understanding one's own triggers can be a significant step in managing migraine conditions.
Understanding the nature of migraine attacks is important, as they differ from regular headaches in terms of severity and accompanying symptoms. For many, recognizing the signs of an impending migraine can help in seeking treatment early, potentially reducing the duration and intensity of the attack.
Treatment Options for Migraine Attacks
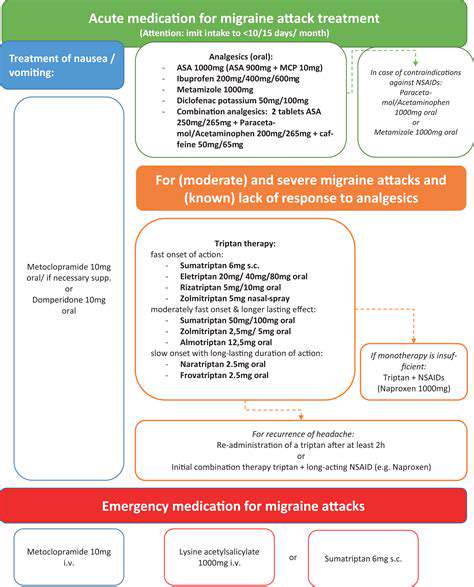
Treatment for migraines generally falls into two categories: acute treatments and preventive measures. Acute treatments are designed to relieve symptoms during a migraine attack. These can include over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, as well as specific prescription medications like triptans that target the cause of migraine pain.
Preventive treatments aim to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines and can include daily medications such as beta-blockers, antidepressants, or anti-seizure drugs. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, limiting caffeine and alcohol, and managing stress through relaxation techniques, can also be influential in minimizing migraine occurrences.
In addition to traditional pharmacological treatments, alternative therapies such as acupuncture, biofeedback, and cognitive behavioral therapy are gaining popularity. These methods may help some individuals find relief, particularly when combined with conventional treatments. It's important for those suffering from migraines to work with healthcare providers to create a personalized treatment plan that meets their specific needs.