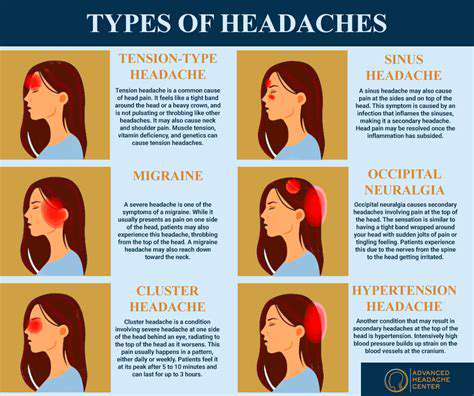
Headache Management While Breastfeeding
Identifying Headache Triggers During Lactation

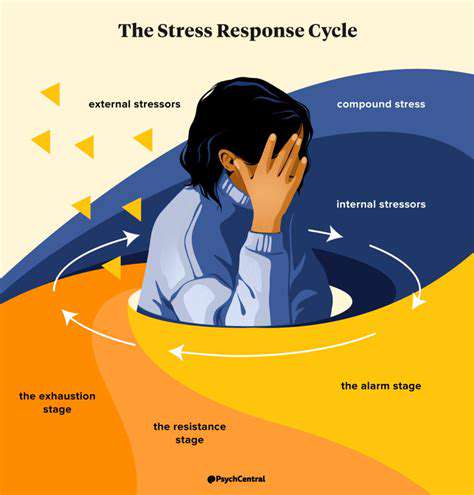
Understanding the Role of Stress
Stress is a significant factor in many types of headaches, often acting as a trigger or exacerbating existing pain. Chronic stress, whether from work, personal relationships, or financial pressures, can lead to muscle tension and constriction in the head and neck, ultimately contributing to headache pain. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or mindfulness practices can be crucial in mitigating headache episodes.
Identifying specific stressors and developing coping mechanisms is essential for preventing stress-related headaches. This proactive approach often involves lifestyle adjustments and the adoption of healthy habits to better manage daily pressures.
Dietary Factors and Headache Pain
Certain foods and beverages can act as triggers for headaches, often due to their effect on blood vessels in the head. Foods high in tyramine, such as aged cheeses, cured meats, and some alcoholic beverages, can cause a rapid increase in blood pressure, potentially resulting in headache pain. Similarly, caffeine withdrawal can also lead to headaches, highlighting the importance of maintaining a consistent caffeine intake.
Avoiding known triggers and paying attention to your body's response to different foods is crucial for identifying dietary patterns that might be contributing to your headaches.
Environmental Influences on Headaches
Environmental factors, such as changes in weather patterns, barometric pressure fluctuations, and exposure to strong smells or allergens, can all contribute to headache pain. These influences can affect the blood vessels and nerves in the head, leading to the onset or worsening of various headache types.
Changes in altitude, particularly rapid ascents or descents, can also induce headaches, as the body adjusts to the differing atmospheric pressures. Recognizing and avoiding these environmental triggers can help in preventing future episodes.
Sleep Disruptions and Headaches
Inadequate or inconsistent sleep patterns can significantly impact headache frequency and intensity. Lack of sleep can lead to increased muscle tension, stress hormones, and dehydration, all of which can contribute to the onset of tension headaches. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule and ensuring adequate rest are crucial for preventing sleep-related headaches.
A consistent sleep routine, including a relaxing bedtime ritual and a sleep-conducive environment, can help regulate the body's natural sleep-wake cycle, reducing the risk of headaches associated with sleep disturbances.
Dehydration and Headaches
Dehydration is a frequently overlooked factor that can trigger or worsen headaches. When the body is not properly hydrated, blood volume can decrease, leading to changes in blood pressure and constriction in blood vessels within the head. This can manifest as headache pain. Consuming enough fluids throughout the day is essential for maintaining optimal hydration and preventing headaches associated with dehydration.
Staying adequately hydrated, especially during physical activity or in hot weather, is a preventative measure to reduce the risk of dehydration-related headaches. Monitoring urine color can be a helpful indicator of hydration levels.

Medication Options for Breastfeeding Mothers with Headaches
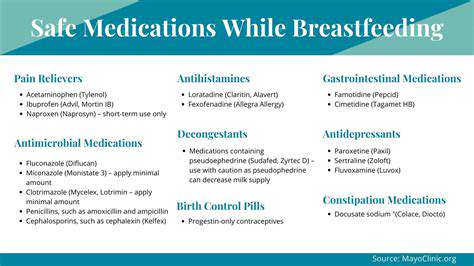
Pharmacological Considerations for Breastfeeding Mothers
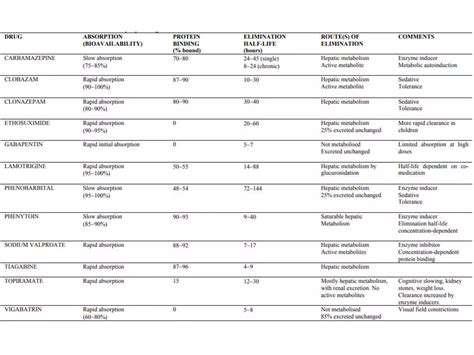
Breastfeeding mothers often face unique challenges when considering medication use, as certain drugs can be transferred to the infant through breast milk. It's crucial to carefully weigh the potential benefits of the medication against the potential risks to the nursing infant. A thorough discussion with a healthcare provider is essential to determine the safest and most effective course of action.
The choice of medication should be based on factors such as the severity of the mother's condition, the potential benefits of the medication, and the potential risks to the nursing infant. This includes considering the drug's half-life, its potential for accumulation in breast milk, and the infant's age and overall health.
Common Medications and Breastfeeding
Many common medications, including over-the-counter pain relievers, antibiotics, and antidepressants, can be safely used by breastfeeding mothers with appropriate precautions. However, some medications should be avoided or used with extreme caution due to their potential to harm the nursing infant.
Consulting a healthcare professional is essential in determining the suitability of any medication for breastfeeding mothers. They can provide personalized advice based on the specific medication and the individual circumstances.
Antibiotics and Breastfeeding
Several antibiotics are generally considered safe for breastfeeding mothers. However, it's essential to choose the appropriate antibiotic to minimize potential side effects for both the mother and the infant. The selection of the antibiotic should consider factors such as the specific infection, the severity of the infection, and the potential for adverse reactions.
Some antibiotics can have minimal effects on the infant if given in the correct dosage and time frame. Mothers should always discuss the risks and benefits of antibiotic use with their healthcare provider.
Pain Relief and Breastfeeding
Many pain relievers, including acetaminophen and ibuprofen, are generally considered safe for breastfeeding mothers in appropriate doses. However, it is essential to follow the recommended dosage and duration of use, as excessive use or prolonged use of certain pain relievers could have unintended consequences. Following the prescribed dosage and duration of use is crucial to minimize potential risks to the nursing infant.
Antidepressants and Breastfeeding
Some antidepressants are compatible with breastfeeding, while others may require careful consideration. The choice of antidepressant should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional who can assess the potential risks and benefits for both the mother and the infant. The doctor will consider factors such as the specific antidepressant, the mother's condition, and the infant's age and health.
It is essential to monitor the infant for any potential side effects following the administration of the medication to the mother. A healthcare professional should be consulted if any unusual or concerning symptoms arise.
Herbal Remedies and Breastfeeding
Many herbal remedies are available, but their safety and effectiveness during breastfeeding are not always well-established. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before using any herbal remedies while breastfeeding. Some herbal remedies might have potential adverse effects on the infant, and their use should be carefully evaluated.
The potential interactions and effects of herbal supplements on breast milk are often unknown or understudied. A healthcare professional can provide guidance on the appropriate use of herbal remedies and potential risks.
Monitoring for Side Effects
Breastfeeding mothers should closely monitor their infants for any adverse reactions or unusual behaviors after taking medication. Prompt reporting of any potential side effects to the healthcare provider is crucial. This allows for prompt intervention and adjustments to the medication regimen if necessary.
Mothers should understand that some medications may take a while to leave the system, and therefore, it is essential to continue monitoring the infant for any long-term effects. This allows the healthcare provider to adjust the medication as needed.