Magnesium for Migraines: Does Supplementation Help?
Magnesium Deficiency and Migraine: Is There a Connection?
Understanding Magnesium's Role in the Body
Magnesium is a crucial mineral that plays a vital role in numerous bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function, blood sugar regulation, and blood pressure control. It's involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions within the body, making it essential for maintaining overall health. A deficiency in this vital mineral can have a wide range of effects, potentially impacting various systems and contributing to various health issues.
Magnesium is often referred to as a relaxant mineral due to its involvement in muscle relaxation. This role extends beyond skeletal muscles, affecting smooth muscles throughout the body, including those in the blood vessels. Maintaining adequate magnesium levels is therefore important for proper blood vessel function and preventing spasms or constrictions that could contribute to migraine triggers.
Migraine Symptoms and Triggers
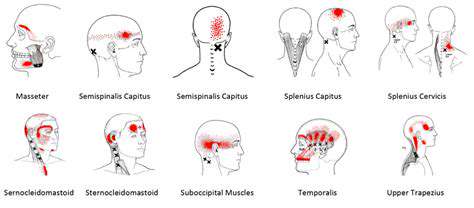
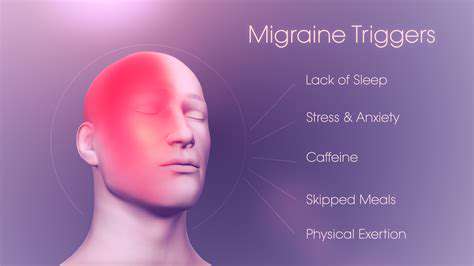
Migraine headaches are characterized by severe throbbing pain, often on one side of the head, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. Various factors can trigger a migraine, including stress, lack of sleep, certain foods and drinks, hormonal fluctuations, and environmental changes. Understanding these triggers is crucial for preventative measures and management.
While the exact mechanisms behind migraine development are complex and not fully understood, research suggests that imbalances in neurotransmitters, including serotonin and norepinephrine, may play a role. Magnesium, with its involvement in neurotransmitter regulation, could potentially influence these imbalances and thus potentially mitigate the risk of migraine attacks.
Magnesium and its Potential Role in Migraine Prevention
Several studies have explored the potential link between magnesium deficiency and migraine. While more research is needed to definitively establish a cause-and-effect relationship, some studies suggest that supplementing with magnesium may reduce the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks in individuals who are deficient.
The potential benefits of magnesium supplementation in migraine prevention stem from its role in regulating neurotransmitter function, relaxing blood vessels, and potentially reducing inflammation. These mechanisms could contribute to a reduction in migraine triggers and the overall severity of attacks.
Magnesium Deficiency and Migraine: Exploring the Connection
A significant number of individuals who experience migraines might have suboptimal magnesium levels. This deficiency could potentially contribute to the occurrence of migraine attacks, though more research is needed to fully understand this correlation.
Identifying a potential link between magnesium deficiency and migraine could lead to innovative preventative strategies. Addressing potential magnesium deficiencies through dietary adjustments or supplementation might offer a pathway to reducing migraine frequency and intensity.
Dietary Sources of Magnesium
Magnesium is found in a variety of foods, making it possible to obtain adequate amounts through a balanced diet. Leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains are excellent sources of magnesium. Ensuring a diet rich in these foods can contribute to maintaining optimal magnesium levels and potentially reducing the risk of migraines.
However, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes or starting magnesium supplementation, especially if you have existing health conditions. A personalized approach is key to understanding and addressing individual needs.
Magnesium Supplements and Safety Considerations
Magnesium supplements are available in various forms and dosages. If you suspect a magnesium deficiency or are considering supplementation for migraine prevention, it's essential to discuss this with your doctor. They can assess your specific needs and recommend appropriate dosages, taking into account any existing health conditions or medications.
While magnesium is generally safe, taking excessive amounts can lead to side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. Following your doctor's recommendations and monitoring your body's response to magnesium supplementation is crucial for maintaining safety and efficacy.
businesses operating in today's global marketplace face a complex web of regulations, spanning international trade agreements, environmental standards, and labor laws. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is crucial for maintaining compliance and avoiding costly penalties. Successfully navigating these intricacies requires specialized knowledge and dedicated resources. This often necessitates hiring legal counsel or employing compliance officers to ensure that operations are not only profitable but also legally sound.
Effectiveness and Considerations: Is it Right for You?
Effectiveness in Migraine Relief
Magnesium plays a crucial role in numerous bodily functions, including muscle and nerve function. Studies suggest that magnesium deficiency may be linked to migraine triggers and severity. Supplementing with magnesium, particularly magnesium glycinate, has shown promise in reducing migraine frequency and intensity for some individuals. However, it's important to remember that individual responses to magnesium supplementation can vary greatly.
While some people experience significant improvements, others may find only minimal relief. The effectiveness of magnesium for migraines isn't a guaranteed cure, but rather a potential supportive treatment that can be explored alongside other strategies.
Understanding the Potential Mechanisms
The precise mechanisms through which magnesium alleviates migraine symptoms are still being investigated. One theory suggests that magnesium deficiency can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, contributing to the inflammatory processes that often accompany migraines. Magnesium may help to stabilize these neurotransmitter systems, potentially reducing the likelihood and severity of migraine attacks.
Furthermore, magnesium has been linked to vasodilation and vasoconstriction, suggesting a possible impact on the blood vessels in the head. This mechanism is thought to play a role in the pain associated with migraine attacks, and magnesium supplementation might help to regulate this process.
Dosage and Considerations for Supplements
The optimal dosage of magnesium for migraine relief varies based on individual needs and factors like age, health conditions, and existing medications. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any magnesium supplement regimen. They can assess your individual circumstances and recommend an appropriate dosage.
It's important to remember that magnesium supplements can interact with other medications, particularly blood thinners and diuretics. A doctor can help determine if magnesium supplementation is safe for your specific situation.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
While generally considered safe, magnesium supplements can sometimes cause side effects like diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. These side effects are usually mild and temporary, but it's essential to be aware of them. If you experience any severe or persistent side effects, discontinue use and contact your doctor immediately.
As previously mentioned, magnesium supplements can interact with certain medications. Therefore, thorough discussion with your doctor about potential interactions is crucial.
Lifestyle Factors and Dietary Considerations
Magnesium is found in a variety of foods, including leafy greens, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Incorporating magnesium-rich foods into your diet can be a beneficial strategy for maintaining adequate magnesium levels. However, for individuals with specific dietary restrictions or challenges in meeting their magnesium needs through diet alone, supplementation might be necessary.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Considering the multifaceted nature of migraines, it's valuable to explore a range of alternative and complementary therapies alongside magnesium supplementation. Techniques like stress reduction practices, mindfulness exercises, and biofeedback therapy can address underlying factors that contribute to migraine triggers. These therapies may complement magnesium's potential benefits, leading to a more comprehensive approach to managing migraine episodes.
It's also important to remember that migraine management is often a personalized journey. What works for one person may not work for another. Combining magnesium with other strategies might be the most effective approach for long-term migraine relief.