Muscle Tension: A Common Culprit of Sharp Pain in the Left Side of the Head
The Connection Between Muscle Tension and Headaches
Understanding the Mechanisms of Muscle Tension
Research suggests that muscle tension is a complex phenomenon influenced by various physiological and psychological factors, including muscle fatigue, joint mobility, and stress levels. The muscles in the neck, face, and scalp are particularly prone to tension, as they play a crucial role in maintaining postural alignment and regulating blood flow to the brain. When these muscles become overactive or knotted, they can refer pain to distant areas, including the left side of the head, leading to headaches.
Clinical studies have identified several key factors that contribute to muscle tension, including poor posture, inadequate sleeping habits, and chronic stress. For instance, slouching or leaning forward can put strain on the muscles of the neck and shoulders, leading to muscle imbalance and pain in the left side of the head. Similarly, disrupted sleep patterns and chronic stress can lead to muscle fatigue, inflammation, and pain.
Furthermore, the brain's pain processing pathways play a significant role in muscle tension headaches. When the brain perceives pain as a threat, it triggers a cascade of chemical signals that amplify pain perception. This can create a self-reinforcing cycle of pain and muscle tension, making it challenging to break free from the cycle.
Neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to adapt and reorganize itself in response to new experiences, also plays a critical role in muscle tension headaches. Research suggests that repeated exposure to pain and stress can rewire the brain's pain processing pathways, leading to increased sensitivity and pain perception. This can contribute to the development of chronic headaches and muscle tension.
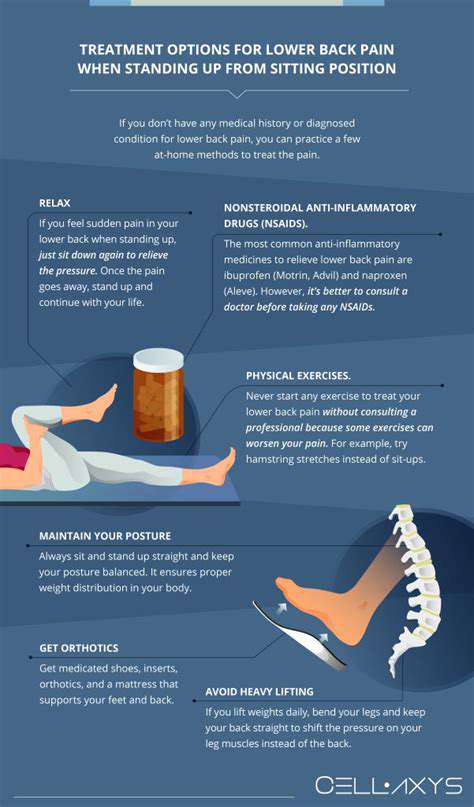
Fortunately, there are several strategies that can help alleviate muscle tension headaches, including stretching exercises, relaxation techniques, and stress management. By understanding the underlying mechanisms of muscle tension and incorporating these strategies into daily life, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic headaches and improve their overall well-being.
Identifying the Triggers of Muscle Tension
The triggers of muscle tension can vary widely from person to person, but some common culprits include poor posture, inadequate sleeping habits, and chronic stress. For instance, slouching or leaning forward can put strain on the muscles of the neck and shoulders, leading to muscle imbalance and pain in the left side of the head. Similarly, disrupted sleep patterns and chronic stress can lead to muscle fatigue, inflammation, and pain.
Additionally, certain medications and substances can contribute to muscle tension headaches. For example, withdrawal from caffeine or other stimulants can lead to muscle fatigue, headaches, and irritability. Similarly, certain antibiotics and other medications can cause muscle tension and headaches as a side effect.
Other potential triggers of muscle tension include dietary factors, such as a diet high in sugar and salt, and environmental factors, such as loud noise and poor air quality. By identifying and addressing these triggers, individuals can reduce their risk of developing muscle tension headaches and improve their overall well-being.
It's also worth noting that certain medical conditions, such as migraines and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, can contribute to muscle tension headaches. In these cases, seeking medical attention and working with a healthcare professional can help alleviate symptoms and prevent future episodes.
In addition to these triggers, certain lifestyle factors can contribute to muscle tension headaches. For example, a sedentary lifestyle and lack of physical activity can lead to muscle fatigue and weakness, making it more difficult to manage muscle tension.
Managing Muscle Tension with Stretching ExercisesManaging Muscle Tension with Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises are an effective way to manage muscle tension and alleviate headaches. By targeting specific muscle groups, such as the neck, shoulders, and scalp, individuals can reduce muscle tension and improve blood flow to the brain. Regular stretching can also help reduce muscle fatigue and inflammation, making it easier to manage muscle tension headaches.
One of the most effective stretching exercises for alleviating muscle tension is the "chin tuck." This exercise involves tucking the chin in towards the chest, squeezing the shoulder blades together, and holding for 10 seconds. This targets the muscles of the neck and shoulders, which are common contributors to muscle tension headaches.
Another effective stretching exercise is the "neck stretch." This involves gently tilting the head to the right, bringing the ear towards the shoulder, and holding for 10 seconds. This targets the muscles of the neck and can help alleviate tension in the left side of the head.
Additionally, incorporating relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation, can help manage muscle tension headaches. By teaching the brain to relax and release tension, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic headaches and improve their overall well-being.
Regular physical activity, such as yoga or Pilates, can also help manage muscle tension headaches. These exercises target specific muscle groups and improve flexibility, balance, and coordination, making it easier to manage muscle tension and alleviate headaches.
Furthermore, incorporating heat or cold therapy, such as a warm bath or cold compress, can help alleviate muscle tension and relieve headaches. By targeting specific areas of tension, individuals can reduce muscle spasms and improve circulation, making it easier to manage muscle tension headaches.
Addressing Underlying Causes of Muscle Tension
Addressing underlying causes of muscle tension is a critical step in managing headaches. By identifying and addressing the root causes of muscle tension, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic headaches and improve their overall well-being.
One of the most common underlying causes of muscle tension is poor posture. Slouching or leaning forward can put strain on the muscles of the neck and shoulders, leading to muscle imbalance and pain in the left side of the head. By practicing good posture and incorporating exercises to improve posture, individuals can reduce muscle tension and alleviate headaches.
Additionally, addressing stress levels can help manage muscle tension headaches. Chronic stress can lead to muscle fatigue, inflammation, and pain, making it challenging to manage muscle tension. By incorporating stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic headaches and improve their overall well-being.
Other underlying causes of muscle tension include inadequate sleeping habits, dietary factors, and environmental factors. By addressing these underlying causes, individuals can reduce their risk of developing muscle tension headaches and improve their overall well-being.
Furthermore, incorporating relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation and visualization, can help manage muscle tension headaches. By teaching the brain to relax and release tension, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic headaches and improve their overall well-being.
Seeking medical attention and working with a healthcare professional can also help address underlying causes of muscle tension headaches. By identifying and addressing underlying medical conditions, such as migraines or TMJ disorders, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic headaches and improve their overall well-being.
Preventing Muscle Tension Headaches
Preventing muscle tension headaches requires a multifaceted approach that addresses lifestyle factors, stress levels, and underlying medical conditions. By incorporating strategies to reduce muscle tension, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic headaches and improve their overall well-being.
One of the most effective ways to prevent muscle tension headaches is to practice good posture. By maintaining good posture and incorporating exercises to improve posture, individuals can reduce muscle tension and alleviate headaches.
Additionally, incorporating relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and progressive muscle relaxation, can help prevent muscle tension headaches. By teaching the brain to relax and release tension, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic headaches and improve their overall well-being.
Regular physical activity, such as yoga or Pilates, can also help prevent muscle tension headaches. These exercises target specific muscle groups and improve flexibility, balance, and coordination, making it easier to manage muscle tension and alleviate headaches.
Furthermore, incorporating stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or visualization, can help prevent muscle tension headaches. By reducing stress levels and promoting relaxation, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic headaches and improve their overall well-being.
Finally, seeking medical attention and working with a healthcare professional can help prevent muscle tension headaches. By identifying and addressing underlying medical conditions, such as migraines or TMJ disorders, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic headaches and improve their overall well-being.
Seeking Medical Attention for Muscle Tension Headaches
While muscle tension headaches can often be managed with self-care techniques, there are times when seeking medical attention is necessary. If muscle tension headaches are severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever or confusion, individuals should seek medical attention.
A healthcare professional can help diagnose the underlying cause of muscle tension headaches and develop a treatment plan to alleviate symptoms. This may include medication, physical therapy, or other interventions to address underlying medical conditions.
Additionally, a healthcare professional can help individuals develop a self-care plan to manage muscle tension headaches. This may include incorporating exercises to improve posture, relaxation techniques, and stress-reducing strategies to reduce muscle tension and alleviate headaches.
It's also worth noting that some medical conditions, such as migraines and TMJ disorders, can contribute to muscle tension headaches. In these cases, seeking medical attention and working with a healthcare professional can help alleviate symptoms and prevent future episodes.
Finally, incorporating preventive measures, such as regular physical activity and stress-reducing techniques, can help reduce the risk of developing muscle tension headaches and improve overall well-being.
Common Causes of Muscle Tension
Physical Stressors
Physical stressors refer to the various activities or situations that put undue strain on the body, leading to muscle tension. These can include prolonged periods of sitting, improper posture, or repetitive motions associated with specific tasks. For instance, workers who engage in desk jobs often experience tight shoulders and neck muscles, primarily due to their sedentary nature and lack of ergonomic setups. Over time, this accumulating stress contributes to discomfort and can provoke sharp pain in the left side of the head.
Another crucial physical stressor is intense exercise without adequate warm-up. Individuals who engage in high-impact workouts may place excessive stress on their muscles, resulting in tightness or cramps. It's essential for anyone who exercises regularly to incorporate proper stretching and cooldown routines to mitigate these effects. Failure to do so can lead to tension not just in the targeted muscle groups but also in surrounding areas, leading to cascading pain effects, including headaches.
Even daily activities such as lifting heavy objects incorrectly can lead to strain. The way we carry groceries, move furniture, or perform household chores significantly impacts muscle health. Improper lifting techniques can overexert muscles in the back and neck areas, giving rise to tension that may radiate to the head, further complicating one’s well-being. Understanding and correcting these habits is critical to preventing ongoing discomfort.
Emotional and Psychological Factors
Emotional stress is a prominent contributor to muscle tension, often manifesting in physical symptoms. Anxiety, stress, and depression can lead the body to adopt tense postures, effectively locking muscles in their contracted state. When the brain perceives threats, whether real or imagined, it activates the body's fight-or-flight response, which can cause the muscles to become tight, particularly in the shoulders and neck. This muscle tension frequently correlates with headaches, especially when the tension remains unresolved.
Chronic stress can form a vicious cycle, as persistent muscle tension can further exacerbate feelings of anxiety and stress, leading to more tension in a never-ending loop. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or therapy can help break this cycle by addressing the underlying stressors and promoting muscle relaxation through mental calmness. Learning to manage emotional stressors is crucial for maintaining not just mental wellness but physical health.
Additionally, psychological factors such as perfectionism and work-related pressures can contribute significantly to muscle tension. Those who habitually push themselves beyond reasonable limits may find their bodies responding with tight muscles and discomfort. Recognizing these patterns and learning to adopt healthier approaches to stress management can lead to improved overall health and reduction in related headache symptoms.
Poor Sleep Quality
Sleep plays a crucial role in muscle recovery and general well-being. Poor sleep quality can significantly contribute to muscle tension. When individuals experience disturbed or inadequate sleep due to stress or discomfort, their muscles do not have adequate time to repair, leading to tightness and soreness. Sleep deprivation can cause the body's muscles to remain tense, leading to discomfort that may extend to the head and neck areas.
Furthermore, sleeping in awkward positions or on unsuitable mattresses can exacerbate muscle tension, resulting in misalignment and stiffness. A lack of quality sleep not only limits the body’s ability to recuperate but also directly influences one's emotional and psychological state, creating an interconnected web of factors that can induce tension headaches.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions may also play a significant role in causing muscle tension. Disorders like fibromyalgia, which is characterized by widespread pain, can lead to persistent muscle tightness. Individuals with such conditions often experience muscle pain that may feel intense and is directly linked to an increased tension in various body areas, including the neck and shoulders.
Another example is temporomandibular joint (TMJ) dysfunction, which affects the joint connecting the jawbone to the skull. People suffering from TMJ issues may unwittingly clench their jaw, leading to tightness in the surrounding muscles, resulting in tension that can radiate to the head and cause severe discomfort, often localized on one side.
Symptoms of Muscle Tension Headaches

Understanding Muscle Tension Headaches
Muscle tension headaches are often characterized by a dull, aching pain that can feel like a tight band around the head. These headaches typically result from muscle strains in the neck and scalp. Identifying the signs and symptoms of muscle tension headaches is crucial for effective management.
People suffering from muscle tension headaches might experience discomfort in various areas of the head, particularly the temples, forehead, and back of the neck. They can also feel tenderness in the scalp, shoulders, and even the jaw. Chronic or frequent headaches can not only be debilitating but can also disrupt daily activities and lead to stress.
The severity of muscle tension headaches can vary; some individuals may experience mild discomfort while others endure intense pain. It’s important to note that these headaches can occur as a result of stress, poor posture, or prolonged periods spent at a desk without breaks. Understanding these factors can help in preventing the onset of these headaches.
Common Triggers of Muscle Tension Headaches
Various factors can trigger muscle tension headaches. Poor posture, particularly at work or while using electronic devices, can lead to strain on the neck and scalp muscles. Ensuring proper ergonomics and taking regular breaks can significantly reduce the risk of developing these headaches.
Emotional stress is another significant trigger. Fluctuations in stress levels can lead to muscle tightness and strain, particularly in the neck and shoulder areas. Recognizing stressors and learning coping strategies are essential steps to alleviate tension headaches.
Additionally, inadequate sleep or changes in sleeping patterns can contribute to the development of muscle tension headaches. Getting sufficient rest and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can play a vital role in headache prevention and overall well-being.
Symptoms Associated with Muscle Tension Headaches
Symptoms of muscle tension headaches can vary widely among individuals, but common signs include pressure or tightness in the forehead, temples, or the back of the head. These headaches are usually not accompanied by nausea or vomiting, which can help distinguish them from migraines. Recognizing these symptoms early is vital for effective treatment.
Other common symptoms may include difficulty concentrating, fatigue, and irritability. These symptoms can impact daily life, making it difficult for individuals to perform tasks at work or engage socially. It's important to address these headaches proactively to improve quality of life.
Some individuals may also report increased sensitivity to light or sound during a muscle tension headache. Although this sensitivity is less common compared to other headache types, it can still signal the presence of significant discomfort and contribute to overall distress.
Managing Muscle Tension Headaches
There are several effective management techniques for muscle tension headaches, starting with lifestyle changes. Regular physical activity is essential, as exercise helps reduce muscle tension, improve posture, and relieve stress. Incorporating stretching or yoga into a regular routine can be particularly beneficial.
Priority should also be given to stress management techniques. Stress reduction practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or mindfulness can contribute significantly to preventing the occurrence of tension headaches. Finding what works best for each individual may involve some trial and error.
Additionally, other methods like physical therapy to help alleviate muscle strain or the use of pain relief medication can be effective. Consultation with healthcare professionals can provide tailored advice on specific treatment options and strategies for effective symptom relief.
When to Seek Professional Help
While muscle tension headaches are often manageable with lifestyle modifications, there are instances when professional help should be sought. If headaches become more frequent or severe, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation. Persistent headaches may signal underlying issues that require medical intervention.
Moreover, if headaches are accompanied by unusual symptoms such as vision changes, confusion, or severe nausea, immediate medical attention is warranted, as these symptoms could indicate a more serious condition. Early detection can lead to more effective treatment options.
Establishing an open line of communication with healthcare providers is crucial. Regular check-ins can ensure that any changes to symptoms are addressed promptly, leading to a more proactive approach to managing muscle tension headaches effectively.
Managing Muscle Tension
Understanding Muscle Tension and Its Impact on Head Pain
Muscle tension is a common condition that results from a variety of factors including stress, poor posture, and physical overexertion. This tension can lead to discomfort not just in the muscles themselves but can also manifest as pain in different areas of the body, particularly the head. When the muscles in the neck and shoulders become tight, they can create a domino effect that influences the muscles in the head, leading to sharp pain, especially on the left side.
The relationship between muscle tension and head pain can often be misunderstood. Many individuals might believe that the pain stems solely from an issue within the head itself, such as a migraine or cluster headache. However, it’s essential to consider the role of muscle tension as a contributing factor to this discomfort. Understanding this connection allows for a more comprehensive approach to pain management and treatment.
Stress is a leading contributor to muscle tension and often exacerbates conditions affecting overall wellness. In high-stress situations, the body enters a fight-or-flight response, tightening muscles for readiness. Unfortunately, this chronic muscle tightness can accumulate over time, resulting in persistent discomfort or pain, particularly in the head and neck area. Addressing and managing stress can play a pivotal role in alleviating this tension.
Because muscle tension can be deceptive, seeking professional guidance can be invaluable. A healthcare provider or specialist trained in musculoskeletal health can help patients identify specific muscle groups that may be contributing to their head pain. This targeted understanding can facilitate more effective treatments that address the root cause rather than just alleviating symptoms.
Effective Strategies for Managing Muscle Tension
To combat muscle tension, it is crucial to implement effective management strategies. Regular physical activity, including stretching and strengthening exercises, is beneficial for maintaining muscle flexibility and preventing tightness. Activities like yoga and Pilates not only enhance flexibility but also promote relaxation, reducing overall tension levels in the body.
In addition to physical exercise, incorporating mindful practices such as meditation or deep-breathing exercises can significantly reduce both muscle tension and stress. These techniques promote a state of relaxation that helps to unwind the tight muscles, particularly those around the neck and shoulders, which are often culprits of head pain. Finding a routine that integrates these practices can yield long-term benefits.
Finally, another critical strategy involves ergonomics—ensuring that your work and living environments support proper posture and comfort. Adjusting desk height, using supportive chairs, and setting up screen positions can help reduce strain on the neck and shoulders, minimizing the risk of developing muscle tension. Making these small adjustments can have a lasting positive effect on muscle health and overall comfort.
Seeking Professional Help for Persistent Muscle Tension
When muscle tension becomes persistent, it is crucial to consider seeking professional help. Physical therapists can design individualized exercise programs specifically tailored to address muscle tension and associated pain. By assessing posture, mobility, and strength prior to developing a treatment plan, these professionals can target specific areas of discomfort effectively.
In addition to physical therapy, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential, especially if the tension seems unmanageable or has lasted an extended period. Medical professionals can conduct thorough evaluations to rule out any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the pain. Furthermore, they might prescribe medications to help alleviate the painful symptoms associated with muscle tension.
Another option to explore is chiropractic care, where practitioners focus on spinal manipulation and adjustments. These treatments can lead to improved alignment and mobility, significantly contributing to alleviating muscle tension. Regular chiropractic adjustments can help maintain a well-aligned body and prevent tension from returning in the future.
Finally, it's vital for individuals suffering from chronic muscle tension-related pain to build a supportive care network. Engaging in group therapy or support groups can offer emotional relief and connection with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences and coping strategies can help not only with managing muscle tension but also in making lasting lifestyle changes conducive to overall health.
When to Seek Medical Advice

Recognizing Symptoms That Indicate Medical Attention
When dealing with muscle tension, it's crucial to identify symptoms that may suggest a more serious underlying issue. Consistent or severe pain in the left side of the head could be indicative of conditions beyond mere tension headaches. Patients often experience related symptoms like dizziness, blurry vision, or even numbness, which can signal the need for immediate medical consultation.
Another sign to look out for is the duration of the pain. If the sharp pain persists over a longer period, this could necessitate medical advice. Pain that lasts several days without any relief may be a warning sign that should not be ignored. Chronic conditions sometimes masquerade as simple muscle tension, making discernment vital for proper treatment.
Additionally, pay attention to any accompanying symptoms, such as weakness on one side of the body. This could be a potential indicator of a serious condition like a stroke or neurological disorder. In such cases, immediate medical help is paramount. Ignoring such symptoms may lead to significant long-term consequences.
A sudden increase in the intensity of pain is also a reason to seek medical attention. Sharp pain that escalates rapidly could represent a more serious medical condition, necessitating a thorough evaluation. It's important not to dismiss this escalating discomfort as mere muscle strain.
Finally, if you've recently suffered from an injury or trauma, particularly to the head or neck, persistent pain should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider. Injuries can lead to complications that might not be immediately apparent, but can have lasting effects if untreated.
When to Visit a Healthcare Professional
Understanding when to visit a healthcare professional can be daunting, especially with muscle tension presenting in various forms. Generally, if the pain is debilitating and limits your ability to perform daily activities, seeking medical help is advisable. Immediate evaluation is essential for addressing discomfort that hinders your quality of life. A healthcare practitioner can offer insights and treatment options to facilitate recovery.
It's also wise to consult a doctor if you notice any significant changes in your headache patterns. For example, if headaches occur more frequently than before, this change could indicate a need for further investigation. Consistency in seeking help can lead to a timely diagnosis and more effective management of your condition.
If over-the-counter medications are not providing relief or if you find yourself relying on them excessively, it's time for a professional assessment. This dependency can hinder a proper understanding of underlying issues, complicating your treatment plan and prolonging discomfort.
Moreover, if your symptoms are impacting your mental health—causing anxiety, stress, or depression—it’s critical to seek help. Mental health and physical health are closely interlinked, and addressing your symptoms may provide relief on both fronts.
Finally, never hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider if the stress or tension associated with your headaches becomes overwhelming. Healthcare professionals are equipped to offer both physical treatment and supportive therapy to manage stress and enhance well-being.