One Side of My Head Hurts: Common Causes and Treatments
Contents
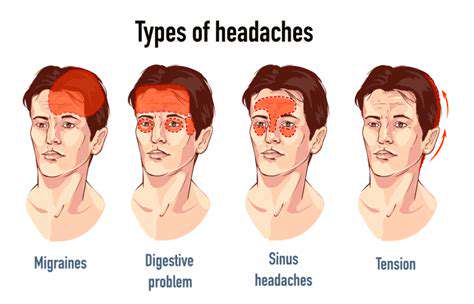
Tension-Type Headaches are common, triggered by stress and poor posture.
Migraine attacks cause severe pain, often with nausea and light sensitivity.
Cluster headaches feature intense pain around one eye, following a cyclical pattern.
Sinus headaches arise from inflammation, causing pain around the forehead and cheeks.
Identifying headache types is crucial for effective treatment and management.
Medication varies by headache type, with triptans often prescribed for migraines.
Lifestyle changes like hydration and stress reduction can help prevent headaches.
Consult healthcare professionals for tailored medication and treatment options.
Common Causes of One-Sided Headaches
1. Tension-Type Headaches
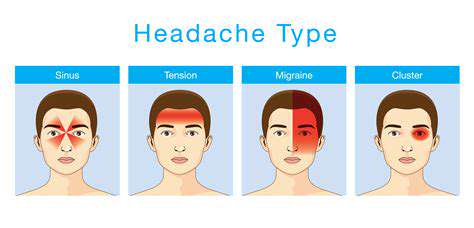
Tension-type headaches are among the most prevalent forms of headache, often characterized by a dull, aching sensation on one side of the head. These headaches can be triggered by various factors including stress, anxiety, and poor posture. Many individuals report that these headaches often increase in intensity throughout the day, sometimes becoming debilitating.
In many cases, the pain associated with tension-type headaches can radiate to the neck and shoulders, making it difficult to concentrate on tasks. Recognizing the signs early and managing stress effectively can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of these headaches. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and maintaining a balanced diet, can also play a crucial role in prevention.
To alleviate tension-type headaches, over-the-counter pain relief medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, are frequently recommended. Additionally, engaging in relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can help relax the muscles in the head and neck area, thereby reducing the likelihood of future headaches.
2. Migraine Attacks
Migraine headaches typically manifest as severe, pulsating pain on one side of the head, often accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to light and sound. These headaches can last from a few hours to several days, severely impacting one's quality of life. Migraines are thought to be caused by changes in brain chemistry, genetics, or environmental factors, making them a complex condition to treat.
Identifying and avoiding triggers is a critical strategy for managing migraines. Common triggers include certain foods, hormonal changes, lack of sleep, and environmental factors like bright lights or strong odors. Keeping a headache diary can help individuals pinpoint their specific triggers and develop strategies to manage them more effectively.
For treatment, many patients turn to prescription medications specifically designed to relieve migraine symptoms or prevent their occurrence. In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications, including regular sleeping patterns, hydration, and stress management techniques, can significantly reduce the frequency of migraine attacks.
3. Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches, while less common, are known for their intense and debilitating pain, often felt on one side of the head, usually around the eye. These headaches follow a cyclical pattern, occurring for weeks or months at a time, followed by remission periods. The pain of a cluster headache is so severe that it often leads individuals to pace or become restless during an attack.
The exact cause of cluster headaches remains unidentified, but they are believed to involve the hypothalamus, the part of the brain that regulates many biological processes. Symptoms may include redness or swelling around the affected eye and nasal congestion on the same side, which can provide clues for diagnosis.
Effective treatments for cluster headaches include fast-acting medications, such as oxygen therapy, and preventive therapy, which may involve medications like corticosteroids or lithium. Patients should consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment strategy tailored to their needs.
4. Sinus Headaches
Sinus headaches are usually felt on one side of the head, particularly around the forehead, cheeks, or eyes, and they occur when the sinus cavities become inflamed or congested. These headaches are often associated with sinus infections or allergies, leading to significant discomfort and pressure in the facial region. The throbbing pain can worsen when bending down or tilting the head, making everyday activities challenging.
Identifying the underlying cause of sinus headaches is essential for effective treatment. Congestion, often resulting from a cold or allergic reaction, can lead to inflammation of the sinus passages, which in turn causes headache pain. Treatment may involve decongestants, antihistamines, or pain relief medications to reduce inflammation and alleviate discomfort.
In addition to medication, natural remedies such as steam inhalation or warm compresses can provide symptom relief. Adjusting your environment to reduce allergens and ensuring proper hydration might also help alleviate sinus-related headaches over time.
Treatment Options for One-Sided Headaches
Understanding the Types of One-Sided Headaches
One-sided headaches can take various forms, each with its own set of underlying causes and symptom profiles. Migraines are one of the most infamous examples, often manifesting as intense throbbing pain on one side of the head. These episodes can last from a few hours to several days, often accompanied by symptoms like nausea, sensitivity to light, or auditory disturbances.
Tension-type headaches, on the other hand, may present with a more generalized pain but can also localize to one side. Often described as a dull, pressing sensation, these headaches can result from stress, anxiety, or muscle tension in the neck and shoulders. Understanding the different headache types is crucial for effective treatment.
Cluster headaches are another specific category that primarily affects one side, typically around the eye region. These headaches are known for their rapid onset and short duration, but they can occur multiple times throughout the day. Their excruciating nature necessitates a clear differentiation from other types for prompt management.
Identifying the type of one-sided headache is essential for selecting the appropriate treatment. Each headache type may require a different approach, underscoring the importance of accurate diagnosis by a healthcare professional as a vital component of effective treatment strategies.
Medication Options for One-Sided Headaches
Medication is a commonly employed treatment option for one-sided headaches, and it can vary based on the headache type. For migraines, triptans are often the first-line defense. These medications work by constricting blood vessels in the brain and reducing inflammation, providing significant relief during acute attacks when taken at the first sign of symptoms.
Over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, offer a more accessible option for many individuals suffering from tension-type headaches. Although these medications may not be as effective as targeted treatments for migraines, they can alleviate mild-to-moderate pain effectively.
For chronic and severe cases of one-sided headaches, preventive medications may be prescribed. These could include beta-blockers, antidepressants, or anticonvulsants. Preventive strategies are crucial for those who experience frequent or debilitating headaches, aiming to reduce the frequency and severity of episodes.
Consulting a healthcare professional is essential for anyone seeking medication options for headaches. Proper dosages, potential side effects, and interactions with other medications should always be considered and managed through professional guidance to avoid complications.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Beyond medication, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing one-sided headaches. Regularly practicing relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can help reduce overall stress levels, a common trigger for tension-type headaches. Such practices may promote better mental clarity and reduce the frequency of head pain.
Hydration is crucial as well; often, dehydration is an unrecognized cause of headaches. Individuals should aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, particularly during hot weather or after exercise. Maintaining proper hydration can be a simple yet effective preventive strategy.
Additionally, paying attention to sleep hygiene can mitigate the incidence of one-sided headaches. Establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleeping environment, and limiting screen time before bed can enhance sleep quality, which is vital for neurological health.
Diet also plays a key role, as certain foods may trigger headaches in sensitive individuals. Keeping a food diary can help identify potential triggers. By making dietary adjustments, along with other lifestyle modifications, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the occurrence of one-sided headaches.