Stabbing Head Pain Left Side: Understanding Symptoms and Treatments
Catalog
- Various medical conditions cause stabbing head pains on the left side, including migraines and tension headaches.
- Environmental factors like noise, bright lights, and strong odors can trigger migraines or tension-type headaches.
- Lifestyle choices, stress, and anxiety can also contribute to stabbing head pain on the left side.
- Physical activity and overexertion can exacerbate stabbing pain in the head.
- Psychological triggers, such as high stress levels, anxiety, and depression, can also contribute to stabbing head pain.
- Diagnosing the cause of left-sided head pain requires a comprehensive approach and thorough medical history evaluation.
- Imaging tests may be necessary to rule out severe conditions, such as tumors or structural abnormalities.
- Treatment for left-sided head pain primarily hinges on the identified underlying cause, with medication, lifestyle modifications, and other therapies available.
- It is essential to seek medical attention if head pain occurs suddenly, reaches an extreme intensity, or is accompanied by alarming symptoms.
- Migraines, tension headaches, and cluster headaches are potential causes of stabbing head pain on the left side.
- Sinuseitis and other sinus issues can cause unilateral head pain.
- Stress, anxiety, and depression can trigger or exacerbate stabbing head pain.
- Treatment options include medication, lifestyle modifications, and other therapies.
- A comprehensive approach to managing left-sided head pain considers physical, emotional, and lifestyle factors.
Potential Causes of Stabbing Head Pain on the Left Side
Common Medical Conditions Linked to Left-Sided Head Pain
Many people experience Stabbing Head Pains on the left side due to various underlying medical conditions. Conditions like migraines and tension headaches commonly cause this type of pain, making them significant issues to address. Migraines are often characterized by intense throbbing or pulsing sensations, which can be debilitating and may be accompanied by nausea or sensitivity to light.
Tension headaches, on the other hand, typically feel like a tight band wrapping around the head and can be triggered by stress, anxiety, or poor posture. Understanding these conditions can lead to more effective management and treatment options that improve the quality of life for sufferers. Other conditions like cluster headaches and sinusitis can also manifest as stabbing pain on the left side of the head, each requiring different approaches for relief.
Cluster headaches, though less common, occur in cyclical patterns and often affect one side of the head. Patients may experience severe pain behind one eye, combined with red or watery eyes. Sinusitis can also contribute to unilateral head pain, as inflammation in the sinus cavities may cause pressure and discomfort that radiates to one side of the head. Recognizing these distinct conditions is vital for targeted treatment.
In summary, various medical issues can lead to stabbing head pain on the left side. Recognizing the symptoms associated with these conditions can assist individuals in addressing their pain effectively, enabling them to seek proper medical advice and possible treatment options. Understanding these potential causes empowers patients to take an active role in managing their health.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Pain
Environmental factors often play a crucial role in the onset of stabbing head pain, especially for those experiencing discomfort on the left side. Excessive noise, bright lights, and strong odors can trigger migraines or tension-type headaches, leading to localized pain. Individuals working in noisy environments or those with high levels of stress may find that their symptoms worsen under these conditions.
Lifestyle choices also significantly impact the frequency and severity of head pain. Poor sleep patterns, inadequate hydration, and an unbalanced diet can predispose individuals to headaches. Ensuring a stable routine that includes sufficient sleep, regular hydration, and nutritious meals can mitigate these risks. Furthermore, those who rely heavily on caffeine or consume excessive alcohol may notice increased head pain or headache episodes.
Physical activity is another essential aspect to consider. Regular exercise helps alleviate stress and tension but can also lead to pain if an individual overexerts themselves or does not stay properly hydrated. Engaging in physical activity while maintaining good hydration can foster overall well-being and reduce the incidence of headaches. However, overdoing it can lead to muscle tension, which may exacerbate stabbing pain in the head.
In essence, environmental and lifestyle factors can heavily influence the occurrence of left-sided head pain. By identifying and addressing these elements, individuals can not only reduce their symptoms but also contribute to a healthier lifestyle overall. A comprehensive approach to managing these factors can lead to significant improvements in overall health.
Psychological Triggers of Stabbing Pain on the Left Side
Psychological factors often serve as underlying triggers for stabbing head pain experienced on the left side. High stress levels, anxiety, and depression can contribute significantly to headache occurrences, highlighting the mind-body connection. Recognizing the emotional and psychological components of pain is essential; they can intensify the perception of pain or even lead to tension headaches.
Stress management techniques can be pivotal in alleviating symptoms. Individuals can benefit from incorporating practices such as meditation, mindfulness, or cognitive-behavioral therapy into their daily routines. These techniques may help individuals better cope with stress and reduce the severity and frequency of pain episodes. Developing healthy coping mechanisms can significantly impact overall head health.
The role of emotional well-being in headaches should not be overlooked. Negative emotional states can lead to muscle tension, especially in the neck and shoulders, which may contribute to stabbing pain in the head. Addressing underlying emotional issues through therapy or support groups can provide long-term relief for those suffering from chronic head pain. The integration of emotional health considerations into pain management plans can enhance therapeutic outcomes.
In summary, the psychological triggers of stabbing head pain on the left side should be taken into account. Implementing strategies to manage psychological factors can lead to a significant reduction in the incidence of pain, improving the overall quality of life for sufferers. Recognizing the connection between mental health and physical symptoms is a crucial step toward finding effective treatments.
Available Treatment Options for Stabbing Head Pain
When it comes to treating stabbing head pain on the left side, various options exist that cater to individual needs. Over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can provide quick relief for mild to moderate pain. For those suffering from more severe headaches, prescription medications like triptans may be necessary to alleviate symptoms effectively.
Aside from medication, non-pharmacological treatments often prove beneficial. Therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, and biofeedback can help many individuals manage their pain without relying solely on medications. These alternative approaches aim to address the underlying causes of headaches by promoting relaxation and restoring balance within the body.
Additionally, lifestyle modifications can play a role in effective pain management. Maintaining a headache diary to identify potential triggers can empower individuals to make informed choices related to diet, sleep, and stress management. Establishing a consistent routine and identifying specific triggers can significantly reduce headache frequency and severity. Making these changes can lead to greater overall well-being and less dependence on medication.
In conclusion, a variety of treatment options exist for managing stabbing head pain on the left side. Understanding the different approaches, from medication to lifestyle changes, can lead to comprehensive care tailored to individual needs. Consultation with healthcare professionals can help create an optimal treatment plan that incorporates both traditional and alternative therapies to address pain effectively.
Recognizing Symptoms Associated with Left-Sided Head Pain
Common Causes of Left-Sided Head Pain
Left-sided head pain can stem from various underlying conditions, each presenting its own challenges for diagnosis and treatment. Tension headaches are among the most prevalent causes, where stress and muscle tension trigger persistent discomfort affecting one side of the head. As these headaches build up, they may lead to sensations of tightness around the forehead or behind the eye, creating a notable impact on daily activities.
Another significant contributor to left-sided head pain is migraines. This neurological condition may not always manifest with the classic features but can often present as intense, throbbing pain localized to one side of the head. Accompanying symptoms such as nausea, light sensitivity, and aura can exacerbate the overall experience, making it vital for individuals to identify triggers that may lead to these painful episodes.
Cluster headaches also deserve attention as a severe cause of left-sided pain. Characterized by sudden and intense agony, cluster headaches typically occur in cyclical patterns, often affecting men more than women. The pain typically focuses around one eye, and individuals may experience additional symptoms such as nasal congestion or swelling, showing just how multifaceted these headaches can be.
Identifying Associated Symptoms
To properly address left-sided head pain, recognizing the associated symptoms is crucial. Common symptoms can include a throbbing sensation, nausea, dizziness, and highlights of sensitivity to light and sound. A throbbing pain often intensifies with physical activity or sudden movements, compelling individuals to seek for a dark, quiet environment to alleviate discomfort.
In some cases, left-sided head pain can be accompanied by neurological symptoms, such as visual disturbances or difficulties in speaking. These additional signs may indicate the need for immediate medical attention, as they could suggest more serious conditions such as a stroke. Monitoring these symptoms carefully can help differentiate between benign headaches and potentially life-threatening issues.
Emotional symptoms like anxiety and increased sensitivity to stress can often accompany episodes of head pain, especially in tension-type headaches. It's essential to address both the physical and emotional aspects of left-sided head pain to promote overall well-being and facilitate effective treatment options moving forward.
The Importance of a Thorough Diagnosis
Diagnosing the cause of left-sided head pain requires a comprehensive approach that can significantly influence treatment outcomes. Medical professionals often start with a detailed medical history and symptom evaluation to pinpoint specific characteristics of the pain. Such an assessment may involve directing questions towards the patient's lifestyle, potential triggers, and any previous incidences of headaches.
Imaging tests such as MRIs or CT scans may be necessary to rule out severe conditions, including tumors or structural abnormalities. These diagnostic tools can provide imagery that unveils underlying issues, guiding healthcare professionals in determining an accurate diagnosis. Timely diagnoses can lead to tailored treatment plans designed to combat specific headache types effectively.
Moreover, it is essential for patients to actively participate by keeping a headache diary, logging frequency, intensity, and associated symptoms. Such valuable information aids healthcare professionals in creating a holistic view of the patient’s condition, ultimately fostering informed decisions regarding appropriate therapies and management strategies.
Treatment Options for Left-Sided Head Pain
Treatment for left-sided head pain primarily hinges on the identified underlying cause. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can offer immediate relief for mild to moderate discomfort, making them first-line options for many individuals suffering from occasional tension headaches.
For chronic issues such as migraines or cluster headaches, healthcare providers may prescribe stronger medications, including triptans or preventive therapies like beta-blockers. These treatments focus on addressing the frequency and severity of headache attacks to enhance quality of life and reduce disruption caused by such episodes.
Beyond medication, lifestyle modifications are vital in managing head pain effectively. A well-balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management techniques such as yoga or meditation, and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can play essential roles in alleviating symptoms and reducing the recurrence of left-sided head pain.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Understanding when to seek medical attention for left-sided head pain is crucial in ensuring timely interventions. If head pain occurs suddenly, reaches an extreme intensity, or is accompanied by alarming symptoms such as confusion, vision changes, or neck stiffness, it is imperative to seek immediate care from a healthcare professional.
Additionally, if the frequency or intensity of headaches increases over time or if episodes significantly disrupt daily life, participating in a thorough evaluation is essential. Pre-existing conditions, such as hypertension or a history of migraines, may further necessitate a prompt medical consultation.
Finally, individuals experiencing new headache patterns or symptoms after age 50 should also obtain a professional assessment, as this could indicate a change in health status. Taking these proactive steps can significantly impact not only pain management but also overall health awareness and outcomes.
Effective Treatments for Stabbing Head Pain on the Left Side
Understanding the Causes of Stabbing Head Pain on the Left Side
Stabbing head pain on the left side can arise from various underlying conditions, each with its own set of symptoms. Migraines, for instance, are known to cause severe unilateral pain, often accompanied by nausea and light sensitivity. Understanding the specific triggers of these headaches can help in managing the pain more effectively.
Tension headaches, while more common, can also lead to sharp, stabbing sensations on one side of the head. These headaches may stem from muscle tightness due to stress or poor posture, making it essential to identify any lifestyle factors that could contribute to the pain.
Cluster headaches, although rare, are another potential cause for stabbing pain localized to the left side. These headaches occur in cyclical patterns and can be excruciatingly painful, often accompanied by watering eyes or nasal congestion. Recognizing them early can lead to quicker and more effective treatment.
Other serious conditions, such as a brain aneurysm or a stroke, may also present with stabbing pain. Understanding that sudden, severe headaches can indicate a medical emergency is crucial in seeking timely medical attention and preventing complications.
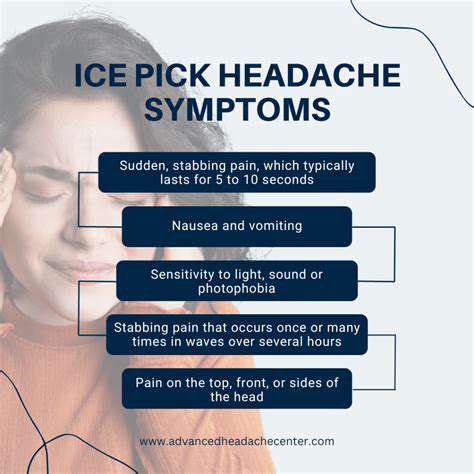
Common Symptoms Associated with Stabbing Head Pain
Alongside the primary stabbing pain, individuals may experience a range of other symptoms, which can help in diagnosing the underlying issue. For many,light sensitivity, or photophobia, accompanies intense headaches, making it challenging to function in bright environments. This can exacerbate the discomfort and increase stress levels.
Nausea and vomiting are also common companions of severe headaches, particularly those stemming from migraines. The experience of queasiness not only distracts from pain relief efforts but can also render dietary habits difficult, further affecting a person's well-being.
Aura symptoms, such as visual disturbances, are frequently reported by migraine sufferers. These events can include bright spots or zigzag lines flashing in one’s vision, often foretelling an imminent migraine attack. Recognizing these signs can be paramount for timely intervention.
In some cases, patients report neck stiffness or pain accompanying their head symptoms, suggesting an underlying issue such as tension-type headaches. This ride-along symptom can indicate muscle strain and necessitate a multifaceted approach to treatment aimed at both the head and neck.
Effective Treatment Options for Left-Sided Stabbing Pain
Pharmaceutical interventions can play a significant role in alleviating stabbing head pain. Over-the-counter analgesics, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, are often the first line of defense. For more severe cases, healthcare providers might prescribe triptans, which can specifically target migraine pain effectively.
Non-pharmaceutical approaches are equally essential in managing recurrent headaches. Lifestyle changes, including proper hydration, regular exercise, and balanced nutrition, can greatly contribute to symptom relief. Many individuals also find that establishing a consistent sleep routine helps stave off headache attacks.
Therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help address psychological factors contributing to pain severity. Stress reduction techniques, including mindfulness and relaxation exercises, can greatly improve overall quality of life and reduce the frequency of attacks.
Alternative treatments like acupuncture or chiropractic care may provide relief for some individuals battling left-side stabbing pain. While research on their effectiveness varies, many patients report satisfying results, emphasizing the importance of exploring all options in a personalized treatment plan.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Stabbing Head Pain
It is crucial to recognize when stabbing head pain becomes a reason for urgent medical evaluation. A sudden onset of severe pain, often described as a "thunderclap headache," warrants immediate attention. This could indicate a more severe issue requiring prompt intervention before complications arise.
If headaches are accompanied by neurological symptoms, such as vision changes, difficulty speaking, or weakness in limbs, these are red flags indicating a possible stroke or other serious condition. Seeking help immediately can be life-saving and minimize long-term damage.
Persistent or worsening headaches that do not respond to typical treatments should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. Continuous pain can signal an underlying condition that might require more intensive intervention, underlining the importance of proactive healthcare.
Finally, individuals should maintain a dialogue with their healthcare providers regarding any changes in headache patterns. Frequent occurrences or increasing severity can provide critical insight into necessary lifestyle adjustments, preventive measures, or the need for more aggressive treatment plans.