Pain in Left Side of Temple: Causes and Solutions
Introduction
Understanding Temple Pain: An Overview
Pain in the temple area can manifest in various forms, including sharp, dull, or throbbing sensations. The temporal region of the head houses important structures, which, when affected, can lead to discomfort and significant distress. Understanding the anatomy of the temple area can provide insights into the diverse causes of pain that may arise.
The temple region is mainly governed by the temporal artery, veins, muscles, and nerves, any of which can contribute to sensation changes. When these structures are irritated or inflamed, the result can be localized or referred pain that may extend to adjacent areas, including the forehead, cheeks, and jaw.
Recognizing the symptoms associated with temple pain is essential for determining the underlying cause. Common accompanying symptoms may include headaches, sensitivity to light, or even nausea, which can enhance the complexity of diagnosis and treatment.
Common Causes of Left-Sided Temple Pain
There are several potential causes of pain in the left side of the temple, ranging from tension headaches to more serious conditions. Tension headaches are among the most common culprits, often arising from stress or muscular tightness in the neck and shoulders.
Migraines are another frequent cause of unilateral temple pain. These intense headaches are usually accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound, creating a debilitating experience for those afflicted.
Additionally, conditions such as temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders can lead to Left-Sided Temple Pain due to the close proximity of the jaw and temporal structures. This pain often intensifies with jaw movement and can be associated with jaw clicking or grinding noises.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing when to seek medical help is crucial for left-sided temple pain. If the pain is sudden, severe, or accompanied by neurological symptoms such as confusion, weakness, or difficulty speaking, immediate medical attention is advised as these may be signs of a serious condition like a stroke.
Additionally, if the pain persists despite over-the-counter medications or if it affects daily activities, it is important to consult a healthcare provider. Persistent pain could indicate an underlying condition requiring professional assessment.
Regular check-ups can also help maintain overall health, particularly for individuals with known migraines or chronic headaches. Communicating symptom patterns and triggers to a healthcare provider can facilitate more effective management strategies.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In many cases, effective home remedies can alleviate left-side temple pain, especially if it stems from tension or stress. Keeping hydrated and practicing good posture can reduce muscle strain, which may contribute to headache development.
Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress levels, potentially diminishing the frequency and severity of temple pain. Utilizing heat or cold packs on the temple area may also provide soothing relief.
Regular exercise and adequate sleep play pivotal roles in managing pain, as a well-balanced lifestyle can help mitigate triggers. Keeping a headache diary may assist in identifying patterns and triggers, further aiding in the establishment of preventive measures.
Medical Treatments and Therapies
For more severe or chronic pain, medical treatments may be necessary. Healthcare providers may prescribe medications, including analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or muscle relaxants, depending on the diagnosis. Some patients may benefit from migraine-specific treatments, such as triptans.
Physical therapy can also be an effective option for those experiencing TMJ-related pain. Techniques may include exercises that strengthen jaw muscles and improve mobility, helping to alleviate pain and prevent recurrence.
Alternative therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, or biofeedback may offer additional relief for those who prefer holistic approaches. Exploring a combination of treatments can often yield the best results in managing and reducing pain in the left side of the temple.
Common Causes of Left-Sided Temple Pain
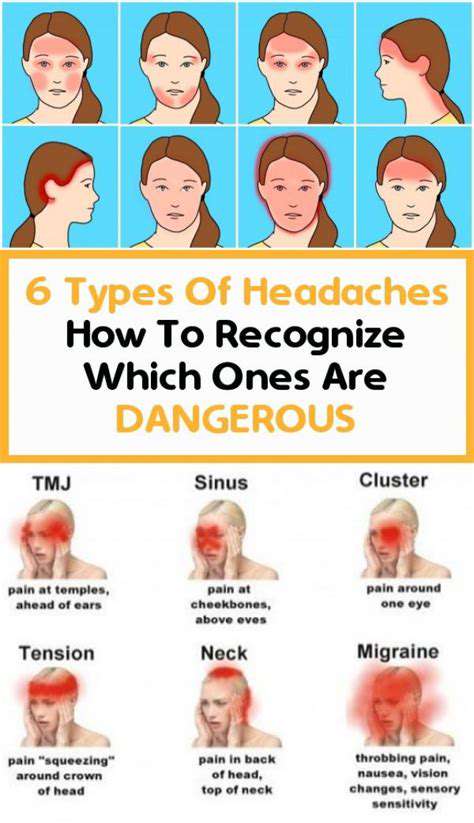
Muscle Tension and Stress
Pain in the left side of the temple is often attributed to muscle tension, which can arise from stress, poor posture, or extended periods of physical activity. Many people fail to recognize the Impact of Stress on their muscles, leading to discomfort and pain. Prolonged tension in the jaw, neck, and scalp can contribute to headaches that manifest in this specific area. Regular relaxation techniques, like yoga or meditation, can help alleviate this tension and reduce overall stress levels.
Additionally, realizing the signs of muscle strain can be crucial. Symptoms may include tightness or soreness around the temple and a general feeling of fatigue. Developing a routine to unwind at the end of the day can significantly lower stress-induced pain. Simple practices like deep breathing exercises or gradual stretching can be effective solutions.
Another effective approach is ergonomic adjustments in your workspace. Evaluating your computer setup and ensuring you're sitting in a comfortable position can minimize muscle strain. Ensuring that your body is aligned properly can greatly reduce the risk of tension headaches. Moreover, incorporating regular breaks during long tasks can also prevent neck and shoulder tension.
Ultimately, acknowledging and managing stress through various techniques can significantly relieve temple pain. If symptoms persist despite implementing these changes, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation.
Migraine and Cluster Headaches
Migraine headaches primarily affect one side of the head and can cause intense throbbing pain around the temple region. The left side is often the most affected, with symptoms that can include nausea and heightened sensitivity to light. This severe type of headache can be debilitating and might require medical attention for management. Many individuals who experience recurrent migraines are advised to maintain a headache diary to identify triggers.
Cluster headaches, on the other hand, are characterized by sudden, sharp pain that can occur frequently within a relatively short time period. They can also be focused on one side of the head, often around the eye or temple, and may be accompanied by symptoms like tearing eyes or nasal congestion. Living with cluster headaches can be challenging due to their abrupt onset and severity.
Treatment options for both types of headaches can vary widely. Preventative medications may be prescribed for those who experience chronic migraines or clusters. Moreover, lifestyle changes like regular sleep patterns, hydration, and a balanced diet can help in reducing the frequency and severity of these headaches.
In some cases, alternative therapies such as acupuncture or biofeedback may also provide relief. Consulting with a healthcare provider to tailor a treatment plan based on the individual's needs is essential for managing these conditions effectively.
Sinus Issues and Infections
Identifying sinus problems early on can be critical to preventing more serious complications. Patients are often advised to monitor changes in their sinus health with seasonal allergies or frequent colds.
Effective treatments for sinus-related pain include over-the-counter decongestants and nasal sprays, which can provide relief from pressure and inflammation. Staying hydrated and using saline sprays can also assist in alleviating symptoms. In more severe cases, a healthcare professional may prescribe antibiotics to treat the underlying infection.
Additionally, maintaining good air quality in living spaces can help minimize sinus issues. Using a humidifier can keep air moist and alleviate irritation in nasal passages. Regular cleaning of areas prone to mold or dust can also contribute to better respiratory health.
Ultimately, tracking any recurring sinus symptoms can also assist in recognizing when professional intervention is necessary. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can provide tailored advice and treatment options for managing sinus problems.
Neurological Conditions
Certain neurological conditions, such as trigeminal neuralgia or multiple sclerosis, can lead to pain in the left side of the temple. Trigeminal neuralgia is characterized by sudden, severe facial pain that can feel like an electric shock, often triggered by routine activities like eating or speaking. For those affected, this type of pain can severely impact daily life. Understanding the nature of these conditions is integral to managing symptoms effectively.
Multiple sclerosis can also present with various painful sensations, including temple pain. This neurological disorder affects the central nervous system, leading to various symptoms that may include fatigue, vision problems, and cognitive changes. Each patient's experience can differ significantly, emphasizing the need for individualized treatment plans.
Diagnosis of these conditions usually involves a thorough neurological examination and may include imaging tests such as MRIs. Treatment options often involve medications aimed at managing pain levels and minimizing relapses. Consultation with a neurologist can provide targeted recommendations for managing symptoms effectively.
Furthermore, lifestyle modifications can complement medical treatment strategies. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy diet, and managing stress can positively affect overall neurological health. Collaborating with healthcare providers to establish a comprehensive care plan is vital for those with these potentially chronic conditions.
Symptoms Associated with Left Temple Pain
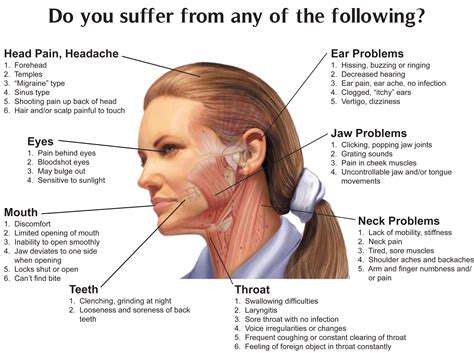
Common Symptoms
Pain in the left side of the temple can manifest in several ways. It may present as a dull ache, throbbing sensation, or sharp stabbing pain. Often, individuals might experience additional symptoms such as Sensitivity to light or sound. This pain can sometimes lead to concentration difficulties and irritability. In some cases, the intensity of the pain may fluctuate throughout the day.
Dizziness is another symptom that can accompany temple pain. When the pain is severe, it might even result in temporary vision disturbances. Individuals might notice that the pain intensifies with certain movements or postures. Keeping a pain diary can be beneficial in tracking these symptoms over time. Understanding the pattern of symptoms is crucial for diagnosing underlying conditions.
In addition to physical pain, emotional symptoms can also occur. Anxiety and stress often exacerbate pain conditions, including those affecting the temple region. Some people report feelings of depression when dealing with chronic pain. The interconnection between physical and emotional health means that addressing one can help alleviate the other. Recognizing these symptoms allows for a more comprehensive approach to treatment.
Potential Underlying Conditions
Left Temple pain can be indicative of several underlying medical conditions. Tension headaches are among the most common culprits. These headaches often arise from muscle tension in the head and neck area. In some cases, they can be triggered by stress, lack of sleep, or poor posture. Understanding these triggers is essential for effective management.
Migraines can also present with pain localized to the temple area. Migraine sufferers may experience visual disturbances and nausea. Identifying the specific type of migraine is important for selecting appropriate treatments. Some people have food or environmental triggers that can lead to these attacks. Therefore, keeping track of what precedes an attack is beneficial for prevention.
Other serious conditions, such as temporal arteritis, may cause left temple pain as well. This inflammation of the arteries can lead to complications if left untreated. Symptoms like jaw pain or difficulty chewing may accompany this condition. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent permanent damage. It’s crucial for anyone experiencing these symptoms to consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Management and Treatment Options
Addressing left temple pain requires a multi-faceted approach. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen are common first-line treatments. Lifestyle modifications, including stress reduction techniques, can also play a significant role. Practices such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises help manage stress levels. Alongside these measures, hydration is essential, as dehydration can worsen headache symptoms.
For recurrent or severe cases, consulting a healthcare provider is advisable. They may recommend prescription medications specifically designed for migraines or tension headaches. Physical therapy can also help alleviate muscle tension contributing to temple pain. Providers may suggest headache management programs or cognitive behavioral therapy for chronic sufferers. Tracking pain patterns can assist healthcare professionals in tailoring effective treatments.
Complementary therapies like acupuncture or chiropractic care might benefit some individuals as well. Alternative treatments can provide relief and help address underlying issues. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers can foster a collaborative approach. Additionally, keeping a symptom diary can help individuals better understand their pain triggers and patterns. Ultimately, integrating various solutions can lead to more effective management of left temple pain.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Understanding the Signs
Experiencing pain in the left side of the temple can manifest in various ways. Recognizing the type and intensity of the pain is crucial for determining its cause. Some individuals may experience a throbbing sensation, while others may feel a sharp or dull ache.
It’s important to take note of any accompanying symptoms, such as nausea or visual disturbances. These details can provide valuable insights to healthcare professionals. If the pain is persistent or worsens over time, it may indicate a more serious issue.
Monitoring the duration and frequency of the headaches can also aid in identifying triggers. This can help in managing pain effectively and improving overall well-being.
Potential Causes of Pain
Various factors can contribute to pain on the left side of the temple. Tension headaches, migraines, or even sinus issues are common culprits. Each of these conditions has distinct characteristics and treatment approaches.
Other possible causes include cluster headaches, which often present as severe, one-sided pain. This type of headache can be particularly debilitating and requires prompt attention. In some cases, more serious conditions such as neurological disorders may be indicated.
Understanding the root cause of the pain is essential for effective management. Therefore, consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
When to Seek Help
It is essential to know when to seek medical attention for left temple pain. If the pain is sudden and severe, this may signify a more serious condition such as a stroke or aneurysm. In such cases, immediate medical intervention is required.
If the headache is accompanied by other symptoms like confusion, difficulty speaking, or loss of coordination, it is vital to call for emergency help. Recognizing these warning signs can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.
Additionally, individuals who experience frequent headaches or a significant change in their headache pattern should consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can prevent potential complications.
Management and Treatment Options
There are various strategies to manage and treat pain in the left temple effectively. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate mild to moderate pain. For more severe cases, prescription medications may be necessary.
Non-pharmacological treatments such as relaxation techniques, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments can also provide relief. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and adequate hydration contribute positively to overall health and can help mitigate headaches.
Furthermore, alternative therapies like acupuncture and chiropractic care have shown promising results for some individuals. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help tailor a treatment plan that suits one's specific needs.
Management and Treatment Options
Understanding the Causes of Left Temple Pain
Pain in the left side of the temple can arise from various underlying conditions. A thorough understanding of these causes is vital for effective treatment. Common causes include tension headaches, migraines, and cluster headaches, all of which can cause localized pain. Tension headaches often stem from stress and muscle strain, while migraines may accompany nausea and sensitivity to light.
In addition to headaches, other medical conditions can contribute to temple pain. For example, temporal arteritis is an inflammation of blood vessels and can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Dental issues, such as a tooth abscess or jaw disorders like temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMJ), can also radiate pain to the temple area.
Infections, like sinusitis or ear infections, may lead to referred pain in the temple. It's crucial to observe accompanying symptoms, such as fever or congestion, which may provide clues to the underlying cause. Lastly, lifestyle factors such as dehydration, poor posture, or excessive screen time can also result in temple discomfort.
Understanding these causes is the first step in effectively addressing temple pain. Keeping a symptom diary may help in identifying triggers and patterns, aiding healthcare professionals in diagnosing the issue accurately.
Identifying Symptoms Associated with Temple Pain
Knowing the symptoms that accompany pain in the left temple can help in diagnosing the cause effectively. Common symptoms include throbbing or pulsating pain that may be mild to severe. Patients might also experience sensitivity to light, noise, or smells, particularly in the case of migraines.
Other symptoms can include visual disturbances, such as seeing flashes of light or blind spots, which often accompany migraine attacks. Nausea and vomiting are also frequently reported by those suffering from more severe headache conditions.
In some cases, tenderness around the temple area may be noted, especially if inflammation is present, such as in temporal arteritis. Symptoms of jaw pain or tightness may indicate a TMJ disorder, while sinus pressure can manifest as a dull ache near the temples.
Monitoring these symptoms can be crucial, as they can help guide treatment options and indicate whether medical intervention is necessary. It’s always recommended to consult a healthcare professional if severe symptoms arise or if pain persists.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
Many individuals find relief from left temple pain through simple home remedies and lifestyle changes. One effective approach is to manage stress through mindfulness techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Regular practice of these techniques can help reduce muscle tension and prevent headaches.
Staying hydrated is another essential lifestyle change. Dehydration is a common trigger for headaches, so ensuring adequate fluid intake can help mitigate this risk. Herbal teas, particularly those containing peppermint or ginger, may also soothe tension and reduce headache severity.
Adjusting screen time and ensuring proper ergonomics during work can alleviate strain on the muscles in the neck and head. Taking regular breaks and adopting a good posture while sitting can significantly impact headache frequency.
Developing a sleep schedule that promotes sufficient rest can also be beneficial. Poor sleep can lead to increased tension and headaches, so prioritizing sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a cool and dark bedroom, can aid in reducing incidences of temple pain.
Medications and Over-the-Counter Treatments
When home remedies are insufficient, various medications can effectively manage pain in the left temple. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, can provide relief from mild to moderate headaches.
For individuals with more severe headaches, prescription medications may be necessary. Triptans are commonly prescribed for migraines and can alleviate symptoms significantly when taken early in an attack. Additionally, anti-nausea medications may be recommended if nausea accompanies the headache.
Preventative medications may also be an option for individuals suffering from frequent migraines. Beta-blockers, certain antidepressants, and anticonvulsants have shown effectiveness in reducing the frequency and severity of migraine attacks.
It’s crucial to follow a healthcare provider’s guidelines when using medications to ensure safety and effectiveness. A healthcare professional can help tailor medication regimens based on the individual’s specific symptoms and medical history.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many cases of temple pain can be managed at home, certain situations necessitate professional medical attention. Persistent or severe pain that does not respond to over-the-counter remedies should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. Additionally, if temple pain is accompanied by neurological symptoms, such as weakness, confusion, or difficulty speaking, it’s crucial to seek emergency care.
Other red flags include sudden onset of severe pain, pain following a head injury, or changes in vision. These symptoms may indicate more serious conditions such as a concussion, hemorrhage, or other neurological issues.
Furthermore, individuals over the age of 50 experiencing new, unexplained headaches should also consult a healthcare provider, as this can sometimes signal conditions like temporal arteritis, which requires immediate treatment to prevent complications.
Establishing a good line of communication with a healthcare provider can lead to early diagnosis and intervention, minimizing the impact of left temple pain on daily life. Regular check-ups, particularly for individuals with a history of headaches or related conditions, can ensure ongoing management and care.