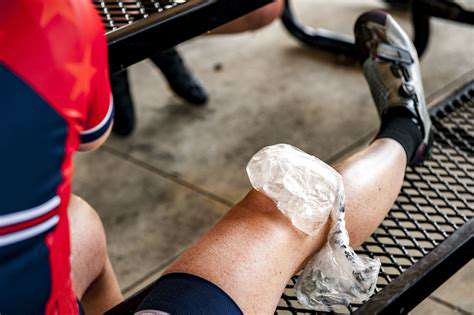
Common Causes of Muscle Strain and Effective Prevention Tips
Identifying the Common Causes of Muscle Strain
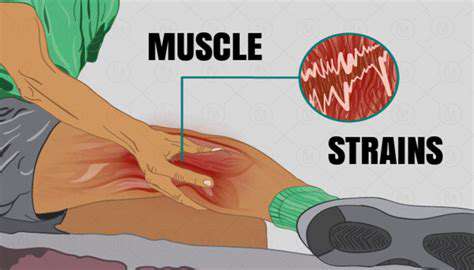
Overexertion and Improper Technique
One of the most common causes of muscle strain is overexertion, which occurs when a person pushes their muscles beyond their normal limits. This often happens during intense physical activity without adequate conditioning. Athletes and weekend warriors alike may experience this issue, leading to discomfort and injury.
Additionally, improper technique during exercises or sports can contribute significantly to muscle strain. When movements are performed incorrectly, not only does the risk of injury increase, but the effectiveness of the workout is also diminished. Proper form and technique are crucial for preventing strains and ensuring overall physical safety.
Lack of Warm-Up and Flexibility
Failing to warm up adequately before physical activity is another common factor that leads to muscle strain. A proper warm-up increases blood flow to the muscles and prepares them for the stress of exercise. Skipping this crucial step can leave muscles cold and vulnerable to injury.
Moreover, a lack of flexibility can predispose individuals to muscle strains. Stretching helps to maintain and improve muscle elasticity, which is essential for injury prevention. Incorporating regular flexibility training can significantly reduce the risk of strains during vigorous activities.
Muscle Fatigue and Dehydration
Muscle fatigue is a significant contributor to strains, as fatigued muscles are less capable of supporting physical activity. When the muscles are tired, coordination and strength decline, increasing the likelihood of injury. It's vital to listen to your body and rest when signs of fatigue arise.
Additionally, dehydration plays a critical role in muscle performance. When the body is dehydrated, muscle function decreases, leading to cramps and strains. Staying well-hydrated is essential for optimal muscle performance and injury prevention.
Inadequate Recovery and Overtraining
Inadequate recovery time between workouts can also lead to muscle strain, as the body does not have enough time to repair and strengthen itself. Overtraining can cause muscles to become increasingly susceptible to injury. Implementing rest days and allowing proper recovery can significantly mitigate this risk.
Furthermore, understanding individual limits is essential in preventing muscle strain. Not all athletes can perform at the same level continuously, and recognizing when your body needs a break is crucial. Tailoring training programs to individual capabilities can help prevent overtraining and subsequent injuries.
Effective Prevention Techniques

Overuse and Repetitive Motion
Muscle strain can occur when you engage in repetitive activities that involve heavy lifting, bending, or stretching. This can be due to various factors such as improper lifting techniques, inadequate warm-up or cool-down exercises, or simply doing too much of the same activity over and over.
It is essential to take regular breaks and give your muscles time to rest and recover between activities.
Additionally, incorporating exercises that improve flexibility and strength, such as stretching and strengthening exercises, can help reduce the risk of muscle strain.
Proper warm-up and cool-down routines can also help prevent muscle strain by increasing blood flow and reducing muscle stiffness.
Wearing proper fitting shoes and using proper equipment can also help reduce the risk of muscle strain, especially in high-risk activities such as running or weightlifting.
Poor Posture and Body Mechanics
Muscle strain can also be caused by poor posture or body mechanics, which can put unnecessary stress on your muscles.
Maintaining good posture and using proper body mechanics can help distribute the load more evenly and reduce the risk of muscle strain.
Proper lifting techniques, such as bending at the knees and lifting with your legs rather than your back, can also help prevent muscle strain.
Strengthening the core muscles, such as the abdominals and back muscles, can also help improve posture and reduce the risk of muscle strain.
Frequent changes in position or activities can also help reduce muscle fatigue and prevent strain.
Sudden or Traumatic Injuries
Sudden or traumatic injuries, such as falls or car accidents, can cause muscle strain by putting excessive stress on the muscles.
Seeking medical attention immediately after a traumatic injury is crucial to prevent further damage and promote proper healing.
Applying ice packs or cold compresses to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Stretching and exercising the affected area can help maintain flexibility and promote healing.
Wearing a cast or splint can also help protect the affected area and promote healing.
Medical Conditions and Medications
Muscle strain can also be caused by underlying medical conditions, such as fibromyalgia or rheumatoid arthritis.
Managing these conditions through medication or other treatments can help reduce the risk of muscle strain.
Medications such as pain relievers or muscle relaxants can also help alleviate muscle strain symptoms.
Staying hydrated and getting enough sleep can also help reduce muscle fatigue and prevent strain.
A healthy diet rich in essential nutrients can also help promote muscle health and reduce the risk of strain.
Aging and Muscle Loss
Muscle strain can become more common with age due to natural muscle loss.
Regular exercise, especially resistance training, can help maintain muscle mass and reduce the risk of strain.
Proper nutrition and hydration can also help support muscle health and reduce the risk of strain.
Adequate rest and recovery time is also essential to allow muscles to repair and rebuild themselves.
Addressing underlying medical conditions, such as osteoporosis or hypothyroidism, can also help reduce the risk of muscle strain.