HTML
CSS
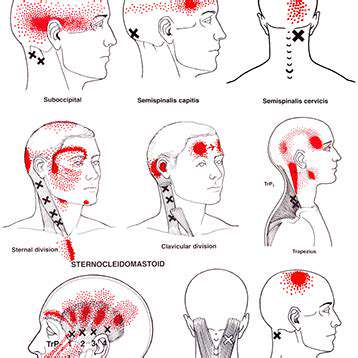
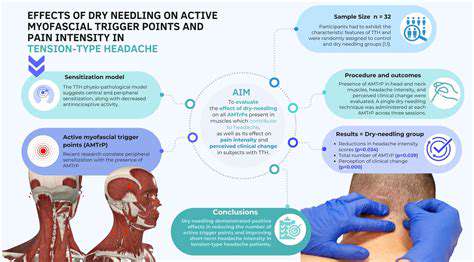
Pain Management
Musculoskeletal Disorders
Myofascial Pain
Dry Needling
探索乾針治療肌筋膜疼痛和頭痛
Read more about 探索乾針治療肌筋膜疼痛和頭痛
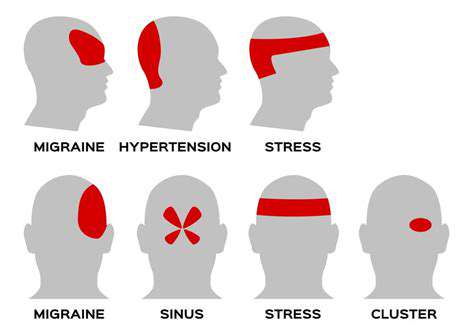
理解叢集性頭痛:病因、症狀與治療選擇 元描述:探索叢集性頭痛的複雜性,從其病因和症狀到有效的治療選擇。了解如何通過專家見解和應對策略來管理這種嚴重的頭痛狀況。內容摘要:叢集性頭痛是一種劇烈、令人虛弱的頭痛,呈周期性發作,常常表現為一側頭部的劇烈疼痛。理解其獨特的症狀,包括鼻塞和流淚,對於有效管理至關重要。這些頭痛受到遺傳因素、晝夜節律和環境因素的影響,可能會顯著影響日常生活。治療通常涉及氧氣治療和曲坦用於立即緩解,以及預防藥物。生活方式的改變和對個人誘因的認知可以增強管理策略,而替代療法和支持小組則提供額外的支持。了解如何應對叢集性頭痛的挑戰,通過知情策略和專業指導改善生活質量。
Oct 11, 2024
原因、影響及緩解策略頭頸痛是一個普遍問題,影響許多人,並顯著影響他們的日常生活和生產力。本綜合指南探討了各種原因,包括不良姿勢、肌肉緊張、壓力和潛在的健康狀況。它討論了在疼痛持續時尋求專業醫療建議的重要性,以及有效的家庭療法和生活方式改變,可緩解症狀。關鍵主題包括:- 對日常生活的影響:頭頸痛可能妨礙日常活動,並對心理健康產生連鎖影響。- 常見原因:了解如肌肉緊張、壓力和受傷等導致疼痛的因素。- 醫療諮詢:了解何時尋求專業幫助及量身定制治療的好處。- 家庭療法:探索如人體工學調整、運動和正念練習等有效策略。- 替代療法:發現針灸、按摩療法和脊椎按摩如何與傳統治療相輔相成。對於那些遭受頭頸痛的人來說,理解這些元素對於有效的疼痛管理和整體健康至關重要。優先考慮整體方法可以顯著改善生活品質。
Oct 15, 2024
了解咳嗽時肌肉拉傷的原因、症狀與緩解策略Meta描述:發現咳嗽引起的肌肉拉傷的原因、常見症狀和有效的緩解策略。學習如何預防和管理肌肉拉傷,以改善呼吸健康。---咳嗽時肌肉拉傷的原因是什麼?咳嗽是清理氣道的自然反射,但可能導致肌肉拉傷,特別是在胸部和腹部。本文探討了咳嗽時肌肉拉傷的機制、常見的加重因素以及整體肌肉健康的重要角色。咳嗽引起的肌肉拉傷的症狀學會識別像是局部疼痛、緊繃感和腫脹等症狀。理解這些跡象對於管理不適和預防慢性問題至關重要。預防措施和緩解策略探索預防咳嗽引起的肌肉拉傷的實用技巧,包括維持呼吸健康、補充水分和正確的呼吸技巧。發現有效的緩解方法,如熱冷療法、輕柔拉伸,以及何時尋求醫療建議。增強您的健康透過了解咳嗽與肌肉拉傷之間的關係,採取積極措施管理您的健康。與醫療專業人員諮詢,並參加鍛煉以增強您的肌肉抵抗力,從而改善健康。關於預防和管理咳嗽引起的肌肉拉傷的更多見解,請訪問我們的完整指南!
Dec 31, 2024