HTML
CSS
Pain Management
Musculoskeletal Disorders
Myofascial Pain
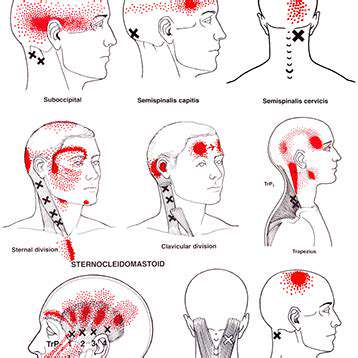
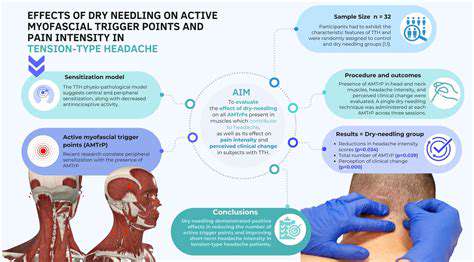
Dry Needling
探索干针治疗肌筋膜疼痛和头痛
Read more about 探索干针治疗肌筋膜疼痛和头痛
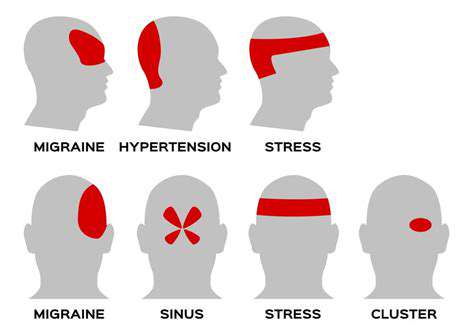
理解丛集性头痛:病因、症状与治疗选择 元描述:探索丛集性头痛的复杂性,从其病因和症状到有效的治疗选择。了解如何通过专家见解和应对策略来管理这种严重的头痛状况。内容摘要:丛集性头痛是一种剧烈、令人虚弱的头痛,呈周期性发作,常常表现为一侧头部的剧烈疼痛。理解其独特的症状,包括鼻塞和流泪,对于有效管理至关重要。这些头痛受到遗传因素、昼夜节律和环境因素的影响,可能会显著影响日常生活。治疗通常涉及氧气治疗和曲坦用于立即缓解,以及预防药物。生活方式的改变和对个人诱因的认知可以增强管理策略,而替代疗法和支持小组则提供额外的支持。了解如何应对丛集性头痛的挑战,通过知情策略和专业指导改善生活质量。
Oct 11, 2024
原因、影响及缓解策略头颈疼痛是一个普遍问题,影响着许多人,并显著影响他们的日常生活和工作效率。本综合指南探讨了各种原因,包括不良姿势、肌肉紧张、压力和潜在的健康状况。它讨论了在疼痛持续时寻求专业医疗建议的重要性,以及有效的家庭疗法和生活方式改变,可以缓解症状。关键主题包括:- 对日常生活的影响:头颈疼痛可能妨碍日常活动,并对心理健康产生连锁影响。- 常见原因:了解诸如肌肉紧张、压力和受伤等导致疼痛的因素。- 医疗咨询:了解何时寻求专业帮助及量身定制治疗的好处。- 家庭疗法:探索如人体工学调整、锻炼和正念练习等有效策略。- 替代疗法:发现针灸、按摩疗法和脊椎按摩的传统治疗如何相辅相成。对于那些遭受头颈疼痛的人来说,理解这些因素对于有效的疼痛管理和整体健康至关重要。优先考虑整体方法可以显著改善生活质量。
Oct 15, 2024
了解咳嗽时肌肉拉伤的原因、症状和缓解策略Meta描述:发现咳嗽引起的肌肉拉伤的原因、常见症状和有效的缓解策略。学习如何预防和管理肌肉拉伤,以改善呼吸健康。---咳嗽时肌肉拉伤的原因是什么?咳嗽是清理气道的自然反射,但可能导致肌肉拉伤,特别是在胸部和腹部。本文探讨了咳嗽时肌肉拉伤的机制、常见的加重因素以及整体肌肉健康的重要作用。咳嗽引起的肌肉拉伤的症状了解如何识别局部疼痛、紧绷感和肿胀等症状。理解这些迹象对于管理不适和预防慢性问题至关重要。预防措施和缓解策略探索预防咳嗽引起的肌肉拉伤的实用技巧,包括维持呼吸健康、保持水分和正确的呼吸技巧。发现有效的缓解方法,如冷热疗法、轻柔拉伸,以及何时寻求医疗建议。增强您的健康通过了解咳嗽与肌肉拉伤之间的关系,采取积极措施管理您的健康。与医疗专业人员咨询,并参与锻炼以增强您的肌肉抵抗力,从而改善健康。有关预防和管理咳嗽引起的肌肉拉伤的更多见解,请访问我们的完整指南!
Dec 31, 2024