Migraine and Stroke Risk: Understanding the Connection
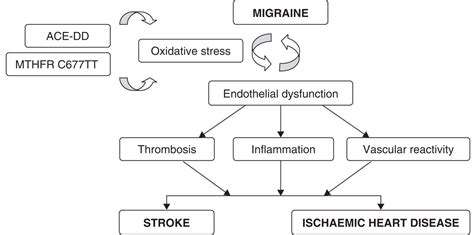
Potential Mechanisms Linking Migraine and Stroke
Neurotransmitter Imbalances
When exploring the connection between migraines and other health factors, one cannot overlook the critical role of neurotransmitter disruptions. Individuals suffering from migraines frequently exhibit irregularities in key neurotransmitters such as serotonin, norepinephrine, and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP). These chemical messengers are vital for maintaining proper pain perception and vascular function. When these systems become dysregulated, they can activate pain pathways, resulting in the characteristic pulsating headaches and accompanying symptoms. Emerging evidence indicates that environmental triggers like stress, sleep disturbances, and certain dietary components may initiate these neurotransmitter abnormalities.
Deeper exploration of how neurotransmitters interact with migraine triggers could revolutionize treatment approaches, leading to more precise and effective interventions.
Vascular Dysfunction
The study of vascular changes remains a cornerstone in migraine research. Migraine episodes often involve vasodilation - the expansion of cerebral blood vessels - which researchers believe plays a central role in generating pain and associated symptoms. This vascular expansion increases pressure on surrounding neural tissues, intensifying headache pain while potentially releasing inflammatory mediators that perpetuate the pain cycle. While the exact biological mechanisms remain under investigation, clarifying these vascular processes is essential for developing novel therapeutic strategies.
Genetic Predisposition
Mounting scientific evidence underscores the hereditary nature of migraine susceptibility. Researchers have pinpointed multiple genetic variants that appear to elevate migraine risk. This genetic connection explains why individuals with migraine-afflicted family members face higher odds of developing the condition themselves. However, the genetic landscape remains complex, with many pathways still requiring elucidation, leaving ample room for future scientific inquiry.
Unraveling these genetic factors could enable earlier detection and more customized treatment plans tailored to individual patients.
Inflammation
Inflammatory processes play a pivotal role in migraine pathophysiology. Clinical studies consistently demonstrate elevated inflammatory markers during migraine attacks. While researchers continue investigating the precise mechanisms, current understanding suggests inflammation activates pain pathways within the central nervous system. Potential inflammatory triggers under investigation include environmental exposures and dietary components that may initiate or exacerbate migraine episodes.
Developing interventions that target inflammatory pathways may yield innovative preventive and therapeutic options for migraine sufferers.
Sensory Processing Issues
Emerging evidence indicates that migraine patients may process sensory information differently than the general population. This heightened sensitivity to environmental stimuli - including light, sound, and odors - can both trigger and intensify migraine attacks. These observations suggest important connections between sensory processing abnormalities and migraine pain generation. Additional research is needed to fully characterize these sensory processing differences and their contribution to migraine development.
Role of the Trigeminal Nerve
The trigeminal nerve system occupies center stage in migraine pathophysiology. As the primary conduit for facial and cranial pain signals, this neural pathway plays an indispensable role in migraine experiences. Scientific investigations confirm that trigeminal nerve activation and sensitization represent fundamental components of migraine headache generation. Clarifying the precise mechanisms of trigeminal involvement may lead to breakthrough treatments specifically targeting this neural pathway.
Continued investigation of trigeminal nerve function could spur development of innovative therapies that precisely modulate this critical pain pathway.
Risk Factors and Protective Measures
Genetic Predisposition
Familial patterns clearly influence both migraine and stroke susceptibility. Those with affected relatives demonstrate increased vulnerability to both conditions. Hereditary factors appear to modify blood vessel functionality, pain processing systems, and neurological responses to environmental stimuli. Recognizing these genetic influences enables more proactive risk assessment and early intervention strategies.
Ongoing genomic research continues to identify specific genetic markers associated with migraine and stroke risk. These investigations may eventually enable personalized risk profiling and tailored prevention protocols.
Lifestyle Factors
Various lifestyle choices significantly impact migraine and stroke risk profiles. Chronic sleep deprivation, inadequate fluid intake, and irregular meal patterns can predispose individuals to both conditions. Sedentary behavior, unmanaged stress, and poor nutritional habits may exacerbate migraine frequency while simultaneously elevating stroke risk. Addressing these modifiable factors represents a crucial component of comprehensive neurological health maintenance.
Adopting healthy lifestyle practices - including regular physical activity, sufficient sleep, and balanced nutrition - can substantially mitigate these risks. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness meditation or yoga may help regulate potential triggers. Routine medical evaluations remain essential for monitoring underlying health issues and facilitating timely interventions.
Dietary Influences
Nutritional factors demonstrate significant influence over migraine and stroke risk profiles. Diets heavy in processed foods, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats correlate with increased incidence of both conditions. Conversely, dietary patterns emphasizing whole plant foods and omega-3 fatty acids may confer protective benefits. Understanding how specific nutrients influence cerebrovascular health and neurological function is paramount for effective risk reduction.
Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Health
Optimal blood pressure management represents a critical strategy for reducing both migraine and stroke risk. Hypertension dramatically elevates stroke probability while potentially worsening migraine frequency and intensity. Implementing lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, pharmacological interventions to control blood pressure provides essential protection against both conditions. Regular cardiovascular assessments enable early detection and intervention to prevent long-term complications.
Smoking and Substance Use
Tobacco use substantially increases stroke risk by damaging vascular integrity and promoting thrombus formation. Nicotine and other tobacco constituents may also precipitate migraine attacks in susceptible individuals. Similarly, excessive alcohol consumption can aggravate both conditions, leading to more frequent and severe episodes. Smoking cessation and alcohol moderation constitute vital components of comprehensive risk reduction strategies.
Environmental Factors
Various environmental exposures can influence migraine occurrence and severity. Airborne pollutants and meteorological fluctuations may trigger or exacerbate migraine episodes. Even minor head trauma can elevate both migraine and stroke risk, particularly among predisposed individuals. Minimizing exposure to environmental triggers and implementing head protection measures can significantly reduce neurological disorder risk.
Current Research and Future Directions

Current Trends in Direct Research
Contemporary research methodologies increasingly emphasize direct investigation approaches across multiple disciplines, reflecting growing recognition of empirical evidence's value in understanding complex biological phenomena. This paradigm shift acknowledges theoretical models' limitations while prioritizing data-driven insights. Modern investigators employ diverse methodological approaches including ethnographic studies, participant observation, and controlled experimental designs to generate comprehensive datasets. This trend is particularly prominent in behavioral sciences where human phenomena require direct researcher engagement.
Advanced data collection technologies are enabling more sophisticated direct research protocols. Digital recording systems and analytical software facilitate detailed observation documentation and interpretation. These technological advancements not only streamline research processes but also expand investigative scope and depth.
Emerging Technologies in Direct Research
Technological innovations are transforming direct research methodologies. Wearable biosensors now enable continuous physiological monitoring, capturing real-time data on biological responses, movement patterns, and environmental exposures. These technological breakthroughs allow unprecedented examination of complex biological processes, overcoming traditional research limitations.
Mobile technologies and digital platforms provide new opportunities for large-scale data collection. Researchers can analyze communication patterns, behavioral trends, and social interactions across diverse populations through these channels. Access to such extensive datasets promises to revolutionize our understanding of biological and social phenomena.
Ethical Considerations in Direct Research
Direct research involving human participants necessitates rigorous ethical safeguards. Investigator must prioritize participant welfare and privacy protection. Maintaining informed consent procedures and ensuring data confidentiality represent fundamental ethical requirements. Researchers must also address potential bias sources that could compromise study validity.
Power differentials between researchers and participants require careful consideration, particularly when studying vulnerable populations. Establishing clear ethical guidelines and oversight mechanisms ensures responsible research conduct.
Data Analysis Techniques in Direct Research
Advanced analytical methods are essential for maximizing direct research potential. Sophisticated statistical approaches, including machine learning algorithms, help identify patterns and relationships within complex datasets. These analytical capabilities enable researchers to extract meaningful insights from multifaceted biological data.
Qualitative analysis methods remain equally important for interpreting rich, nuanced data. Thematic analysis and discourse examination techniques help researchers comprehend dataset complexities, ensuring comprehensive understanding of studied phenomena.
Dissemination of Direct Research Findings
Effective knowledge translation is crucial for maximizing research impact. Direct research findings often carry significant implications for clinical practice and public health policy. Researchers must communicate findings clearly to diverse audiences including healthcare providers, policymakers, and the general public. Presenting complex scientific concepts in accessible formats enhances research utilization and societal benefit.
Future Directions for Direct Research
The future of direct research appears exceptionally promising. Methodological integration, technological innovation, and strengthened ethical frameworks will shape the field's evolution. Investigating applications of emerging technologies like virtual and augmented reality may open new avenues for understanding human biology and behavior.
Developing more sophisticated analytical techniques will be essential for interpreting the growing volume of research data. These advancements will facilitate more nuanced understanding of complex biological systems and more effective clinical interventions.
The Impact of Direct Research on Society
Direct research holds tremendous potential for societal benefit. Insights gained from rigorous investigation can inform effective interventions in healthcare, education, and social policy domains. Research findings may help address pressing societal challenges while promoting human wellbeing and social equity.
Ultimately, high-quality direct research contributes to building healthier, more sustainable communities through evidence-based decision making.