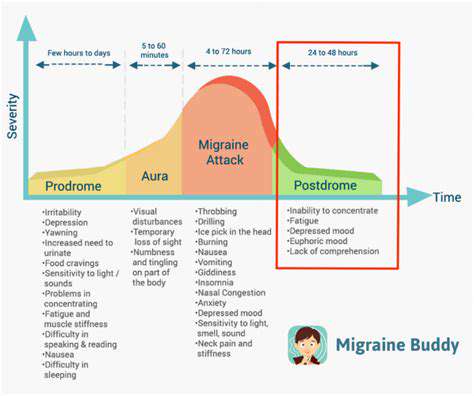
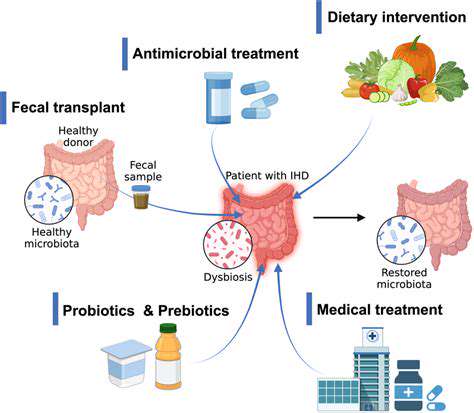
Elimination Diets to Identify Food Triggers for Migraines
Tracking Your Progress and Identifying Triggers
Understanding Your Baseline
Before embarking on any elimination diet, it's crucial to understand your current baseline. This involves tracking your symptoms, both physical and emotional, over a period of several weeks. Detailed journaling is essential, noting not just the presence or absence of symptoms but also their severity, duration, and any accompanying factors like stress levels, sleep patterns, or recent changes in your diet. This baseline data will provide a crucial point of reference for identifying any changes or patterns that emerge during the elimination phase.
Identifying Potential Triggers
One key aspect of tracking your progress is identifying potential triggers. Pay close attention to how your body reacts to different foods and beverages. Record not only the foods you consume but also the time of consumption, portion sizes, and any accompanying symptoms. This meticulous record-keeping will help you pinpoint specific foods or food groups that might be contributing to your discomfort or exacerbate your symptoms. This proactive approach to identifying triggers is fundamental to the success of any elimination diet.
Monitoring Symptoms During the Diet
Throughout the elimination diet, continuous monitoring of symptoms is vital. Note any changes, no matter how subtle, in your physical or emotional well-being. Do you experience increased fatigue? Are there fluctuations in your energy levels? Do any specific symptoms worsen or improve after consuming particular foods? The key is to meticulously document these observations, as they can provide invaluable insights into the potential causes of your issues. This meticulous data gathering will assist you in identifying the specific foods that might be problematic.
Analyzing Your Data and Recognizing Patterns
Regularly reviewing your recorded data is essential for identifying patterns and trends. Look for correlations between specific foods and symptoms. Are certain food groups consistently linked to particular reactions? Do particular meals or snack times seem to coincide with heightened discomfort? By analyzing this data, you can start to develop a clearer picture of your body's responses to different foods. This analysis is crucial to pinpoint the specific food groups or individual foods that might be causing your problems.
Adjusting the Diet and Evaluating Results
Based on your analysis, you can adjust your diet accordingly. If a particular food group seems to be a culprit, you can temporarily eliminate it from your diet. Track your symptoms closely during this period, noticing any improvements or changes. Regularly evaluate the results of your dietary adjustments. Are your symptoms improving? Are you feeling better overall? If so, you're on the right track. If not, you may need to refine your approach or consider consulting a healthcare professional for further guidance.
Beyond Food: Other Factors to Consider
Underlying Medical Conditions
Often overlooked in the quest to identify food sensitivities, underlying medical conditions can mimic the symptoms of food allergies or intolerances. For instance, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) can present with abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea, similar to symptoms triggered by certain foods. A thorough medical evaluation is crucial to rule out any other potential health issues before embarking on an elimination diet. This initial step helps ensure that any observed symptoms are accurately attributed to dietary factors rather than an undiagnosed condition, preventing unnecessary dietary restrictions and promoting accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Certain autoimmune diseases can also manifest with gastrointestinal symptoms that overlap with food sensitivities. A physician can perform relevant tests and provide a comprehensive assessment to differentiate between the two. This careful evaluation is essential to ensure appropriate management of any underlying medical conditions and avoid potentially harmful dietary restrictions that could exacerbate the condition.
Lifestyle Factors
Stress, lack of sleep, and inadequate hydration can significantly impact digestive health, leading to symptoms that might be wrongly attributed to food sensitivities. Chronic stress, in particular, can disrupt the gut microbiome, making individuals more susceptible to digestive issues. Addressing these lifestyle factors is often a crucial part of improving overall well-being and could alleviate symptoms that appear to be food-related.
Regular exercise, stress management techniques, and prioritizing sufficient sleep can play a significant role in optimizing gut health. Incorporating these lifestyle adjustments alongside an elimination diet can provide a more holistic approach to identifying and managing potential food triggers, ensuring that dietary restrictions are not the sole focus of treatment.
Emotional Well-being
Emotional factors, including anxiety and depression, can indirectly influence digestive health, potentially leading to symptoms that mimic food sensitivities. Stress and emotional distress can disrupt the delicate balance of the gut microbiome, resulting in a cascade of issues that manifest as gastrointestinal problems. Addressing these emotional factors through therapy, mindfulness practices, or other suitable methods may improve overall well-being and reduce symptoms that could be incorrectly attributed to dietary triggers.
Recognizing the interplay between emotional well-being and digestive health is crucial in the context of elimination diets. An elimination diet alone may not address the root cause of symptoms if underlying emotional stressors are not addressed. A holistic approach that considers both dietary and emotional factors is important for effective symptom management and overall well-being.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to environmental toxins, such as certain chemicals or pollutants, can also contribute to digestive issues and symptoms that resemble food sensitivities. These environmental exposures can disrupt gut health, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Identifying and minimizing exposure to these toxins can significantly improve digestive function and reduce symptoms that are mistakenly linked to dietary triggers.
The quality of the water you drink and the environment you live in could be important factors that contribute to digestive issues. Conducting a thorough assessment of potential environmental exposures can help identify potential culprits and reduce their impact. Addressing environmental factors alongside dietary changes may lead to a more comprehensive approach to improving digestive health and reducing symptoms.
Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome, the complex community of microorganisms residing in the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in overall health. Imbalances in the gut microbiome, or dysbiosis, can contribute to a range of digestive issues, potentially mimicking symptoms of food sensitivities. Understanding and supporting a healthy gut microbiome is vital for optimizing digestive function and reducing the likelihood of misattributing symptoms to dietary triggers. A balanced diet, prebiotics, and probiotics can contribute to a healthier gut microbiome.
Maintaining a diverse and balanced gut microbiome is essential for optimal digestive health. This is significant when evaluating potential food sensitivities because imbalances in the microbiome can lead to symptoms that overlap with food intolerance. Considering the gut microbiome in the context of elimination diets provides a more comprehensive approach to addressing digestive issues and identifying true food triggers.