HTML
CSS
HTML element
CSS class
Migraine
MSG
MSG(글루탐산나트륨)이 잠재적인 편두통 유발 물질로서
MSG와 식품에서의 역할 소개 이미지 

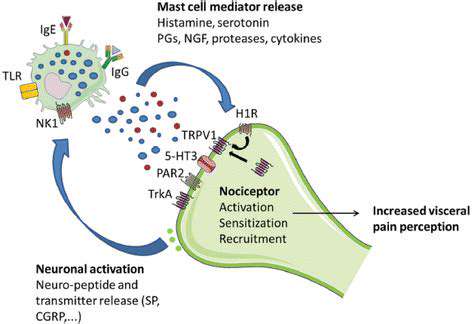
MSG 섭취로 인한 편두통 가능 메커니즘

가능한 세포 메커니즘
일반적으로 가공식품에 널리 사용되는 풍미 증진제인 글루탐산나트륨(MSG)은 편두통 유발 가능성에 대한 논쟁을 불러일으켰습니다.
MSG가 편두통 유발 물질로서의 연구 및 증거
초기 연구 및 구전 증거
MSG와 편두통의 연관성에 대한 초기 조사는 주로 자발적인 보고 사례에 크게 의존했습니다. 많은 피험자들이 유사한 증상 패턴을 기술했습니다.
Read more about MSG(글루탐산나트륨)이 잠재적인 편두통 유발 물질로서
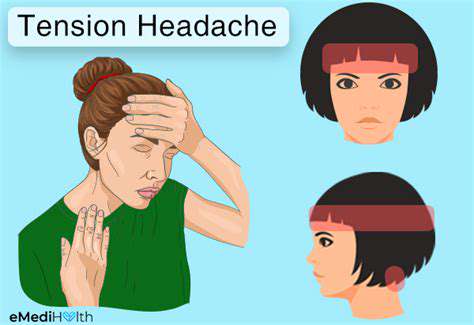
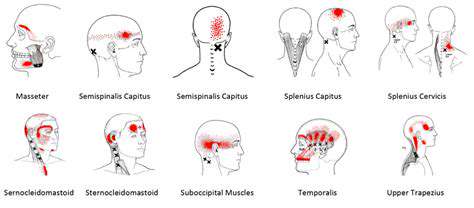
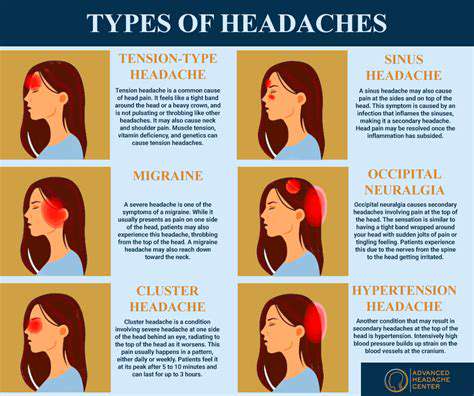
일반 두통 이해 및 관리. 긴장성 두통, 부비동염, 편두통 및 눈의 피로를 포함한 일반적인 두통 유형을 관리하기 위한 효과적인 전략을 발견하십시오. 가장 흔한 형태인 긴장성 두통은 종종 스트레스와 근육 긴장으로 인해 발생하며, 이마 주변에 둔하고 조여오는 느낌으로 나타납니다. 증상을 식별하고 원인을 인식하며 불편함을 완화하기 위한 다양한 치료 옵션을 탐색하는 방법을 배우십시오. 얼굴 통증과 압박감이 특징인 부비동염은 감염 및 알레르기 때문에 발생할 수 있습니다. 합병증을 예방하기 위해 시기적절한 진단과 맞춤형 치료 계획의 중요성을 이해하십시오. 또한, 강한 박동성이 있는 통증과 메스꺼움 같은 추가 증상으로 특징지어지는 편두통 발작에 대해 깊이 살펴보고, 그 빈도와 심각성을 관리하기 위한 급성 및 예방적 치료를 탐색하십시오. 눈의 피로는 특히 장시간 화면을 사용할 때 두통과 동반될 수 있습니다. 20-20-20 규칙, 화면 조정 및 적절한 조명 같은 실용적인 팁으로 긴 relief를 찾으십시오. 긴장성 두통이나 기타 두통 관련 질환을 겪고 있다면 이 포괄적인 가이드는 증상 인식, 생활 습관 조정 및 의학적 조언을 요청해야 할 시기를 상에귀에 대한 귀중한 인사이트를 제공합니다.---*두통을 효과적으로 관리하고 삶의 질을 회복하세요!*
Jan 07, 2025