HTML
CSS
HTML element
CSS class
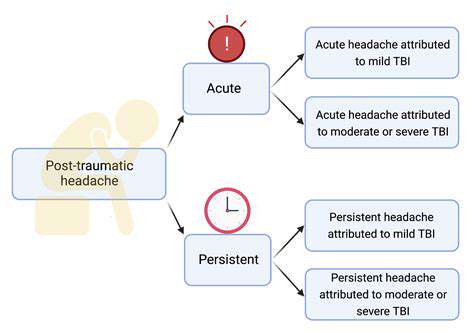
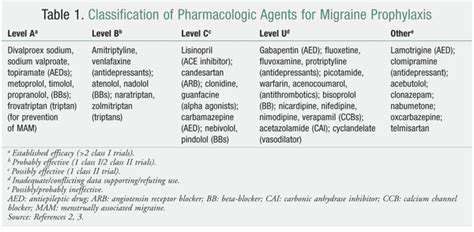
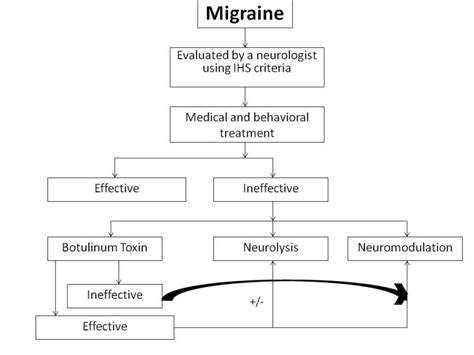
Migraine
MSG
味精(麩胺酸鈉)作為潛在的偏頭痛誘因

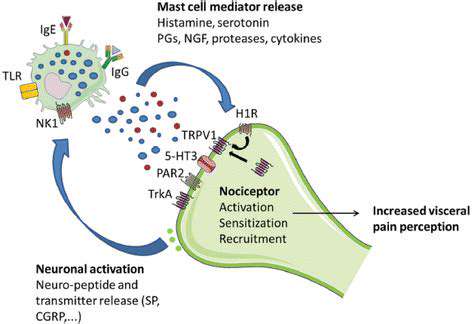
可能的味精誘發偏頭痛機制
Read more about 味精(麩胺酸鈉)作為潛在的偏頭痛誘因
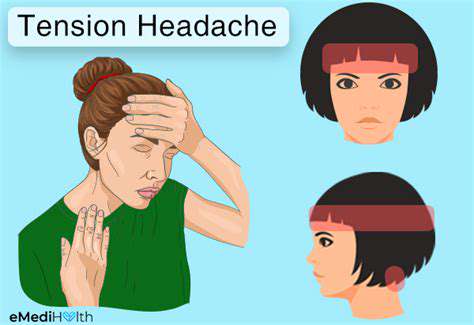
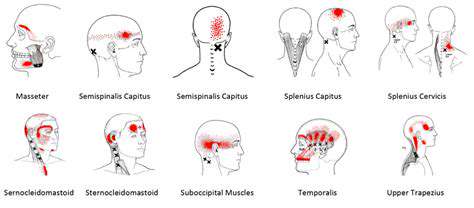
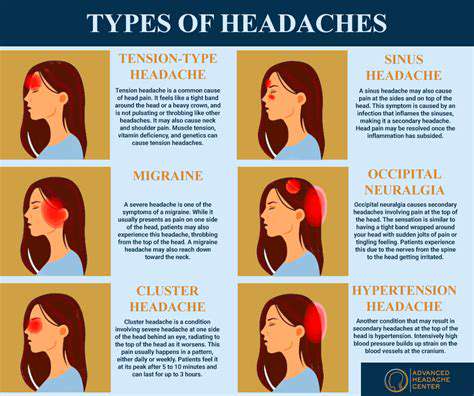
理解和管理常見的頭痛。發現有效的策略來管理常見的頭痛類型,包括緊張性頭痛、鼻竇炎、偏頭痛和眼睛疲勞。緊張性頭痛是最常見的類型,通常源於壓力和肌肉緊張,表現為額頭周圍的鈍痛和緊繃感。了解如何識別症狀,認識病因,並探索各種治療選項來緩解不適。鼻竇炎以面部疼痛和壓力為特徵,可能由感染和過敏引起。理解及時診斷和個性化治療計劃以防止併發症的重要性。此外,深入探討偏頭痛發作——以強烈的搏動性疼痛和噁心等附加症狀為特徵——並探討控制發作頻率和嚴重性的急性和預防性治療。眼睛疲勞可能伴隨頭痛,特別是在長時間使用螢幕之後。透過20-20-20法則、螢幕調整和適當的照明等實用技巧來尋找舒緩方案。無論你面對的是緊張性頭痛或其他與頭痛相關的病症,這本全面的指南提供了關於症狀識別、生活方式調整和何時尋求醫療建議的寶貴見解。---*有效管理你的頭痛,重拾生活品質!*
Jan 07, 2025