HTML
CSS
HTML element
CSS class
Migraine
MSG
MSG (glutamat mononatri) như một tác nhân gây ra đau đầu chóng mặt tiềm ẩn

Cơ chế của Viêm Đầu Migraine Có Thể Gây Bởi MSG
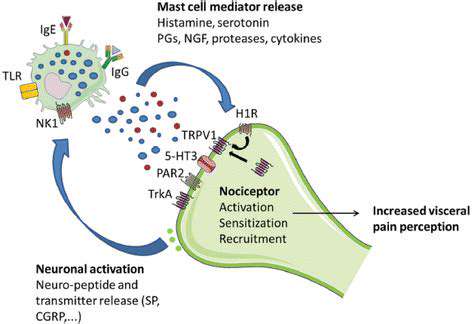
Các Cơ chế Tế bào Tiềm năng
Monosodium glutamate (MSG), một chất tăng vị phổ biến được sử dụng trong thực phẩm chế biến, đã gây ra nhiều tranh luận
Nghiên cứu và bằng chứng về MSG như một chất kích hoạt đau nửa đầu
Nghiên cứu ban đầu và bằng chứng kể lại
Các nghiên cứu ban đầu về mối liên hệ MSG-đau nửa đầu chủ yếu dựa vào các trường hợp tự báo cáo, với nhiều đối tượng mô tả các triệu chứng tương tự p
Read more about MSG (glutamat mononatri) như một tác nhân gây ra đau đầu chóng mặt tiềm ẩn
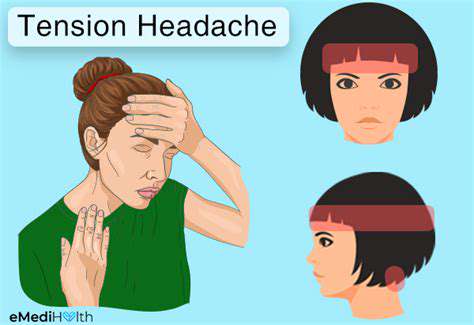
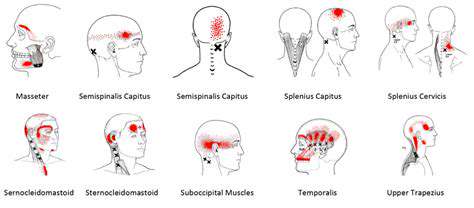
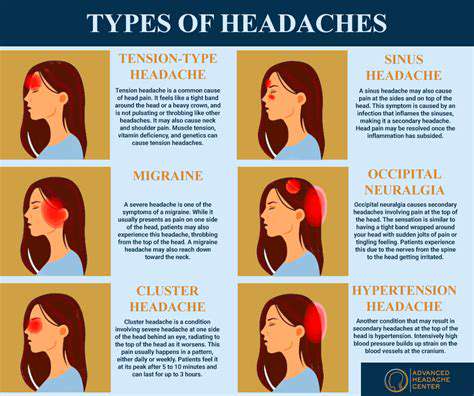
Hiểu và quản lý các cơn đau đầu phổ biến. Khám phá các chiến lược hiệu quả để quản lý các loại đau đầu phổ biến, bao gồm đau đầu căng thẳng, viêm xoang, đau nửa đầu và mệt mỏi mắt. Đau đầu căng thẳng, dạng phổ biến nhất, thường xuất phát từ stress và căng cơ, thể hiện dưới dạng cảm giác đau âm ỉ và căng quanh vùng trán. Tìm hiểu cách nhận diện triệu chứng, nhận ra nguyên nhân và khám phá nhiều lựa chọn điều trị khác nhau để giảm thiểu sự khó chịu. Viêm xoang, được đánh dấu bằng cơn đau và áp lực ở mặt, có thể do nhiễm trùng và dị ứng gây ra. Hiểu tầm quan trọng của việc chẩn đoán kịp thời và một kế hoạch điều trị cá nhân để ngăn ngừa các biến chứng. Hơn nữa, khám phá các cơn đau nửa đầu - đặc trưng bởi cơn đau nhói dữ dội và các triệu chứng bổ sung như buồn nôn - và khám phá các phương pháp điều trị cấp tính và phòng ngừa để quản lý tần suất và mức độ nghiêm trọng của chúng. Mệt mỏi mắt có thể đi kèm với đau đầu, đặc biệt là sau thời gian dài sử dụng màn hình. Tìm kiếm sự giảm nhẹ thông qua các mẹo thực tiễn như quy tắc 20-20-20, điều chỉnh màn hình và ánh sáng phù hợp. Dù bạn đang đối mặt với đau đầu căng thẳng hay các tình trạng liên quan đến đau đầu khác, hướng dẫn toàn diện này cung cấp những hiểu biết quý giá về cách nhận diện triệu chứng, điều chỉnh lối sống và thời điểm tìm kiếm lời khuyên y tế. ---*Quản lý hiệu quả cơn đau đầu của bạn và khôi phục chất lượng cuộc sống của bạn!*
Jan 07, 2025
Đau đầu khi quay đầu: Hiểu về các triệu chứng
Apr 30, 2025
Điều trị bằng phương pháp chỉnh nha cho chứng đau đầu: Nghiên cứu nói gì?
May 08, 2025
Huấn luyện phản hồi sinh học để kiểm soát đau nửa đầu
May 16, 2025
Phô mai lên men và thịt xông khói: Tyramine và đau đầu
May 19, 2025
Xây dựng sức đề kháng khi sống chung với chứng đau nửa đầu
May 21, 2025
Mối liên hệ giữa dị ứng, vấn đề xoang và đau nửa đầu
May 30, 2025
Đau đầu chóng mặt là gì? Mối liên hệ giữa chóng mặt và đau đầu
May 30, 2025
Tương lai của thuốc điều trị chứng đau đầu nhức mỏi: Những gì đang chờ đón?
Jun 03, 2025
Mối liên hệ giữa thay đổi thời tiết và đau đầu
Jun 05, 2025